un/scetdg/36/wpxx
... applied by the country in which the pressure receptacles are manufactured, provided the provisions of 6.2.3 are met; are authorized for the transport of UN 3XXX and UN 3YYY. For UN 3XXX and UN 3YYY packed in refillable gas receptacles, the maximum test period for periodic inspection shall be 10 year ...
... applied by the country in which the pressure receptacles are manufactured, provided the provisions of 6.2.3 are met; are authorized for the transport of UN 3XXX and UN 3YYY. For UN 3XXX and UN 3YYY packed in refillable gas receptacles, the maximum test period for periodic inspection shall be 10 year ...
0191 271 0222 Nitrogen (Oxygen Free)
... When required, wear suitable safety shoes and other personal protective equipment when handling gas cylinders ...
... When required, wear suitable safety shoes and other personal protective equipment when handling gas cylinders ...
Elemental Analysis of Semiconductor Gases Using a Gas Exchange
... smoke etc) and these will be explored in subsequent studies. ...
... smoke etc) and these will be explored in subsequent studies. ...
Targets of Opportunity
... Yesterday, July 9, an explosion occurred at a Texas oil refinery which resulted in the release of an unspecified, but potentially large amount of hydrogen fluoride. According to the article which appeared in today's Corpus Christi Caller Times, a seven block area adjacent to the plant was soon evacu ...
... Yesterday, July 9, an explosion occurred at a Texas oil refinery which resulted in the release of an unspecified, but potentially large amount of hydrogen fluoride. According to the article which appeared in today's Corpus Christi Caller Times, a seven block area adjacent to the plant was soon evacu ...
Life in the Trenches
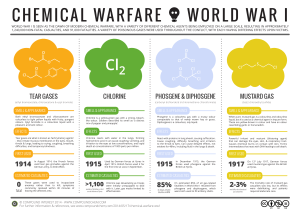
... adopted by both German and Allied armies. Phosgene often had a delayed effect; apparently healthy soldiers were taken down with phosgene gas poisoning up to 48 hours after inhalation. Mustard Gas Remaining consistently ahead in terms of gas warfare development, Germany unveiled an enhanced form of g ...
... adopted by both German and Allied armies. Phosgene often had a delayed effect; apparently healthy soldiers were taken down with phosgene gas poisoning up to 48 hours after inhalation. Mustard Gas Remaining consistently ahead in terms of gas warfare development, Germany unveiled an enhanced form of g ...
New Weapons.WWI
... Tanks1: The development of tanks in World War I began as a solution to the stalemate which trench warfare had brought to the western front. The first prototype of the Mark I tank was tested for the British Army in September 1915. The British Mark I was a tracked vehicle developed by the British Army ...
... Tanks1: The development of tanks in World War I began as a solution to the stalemate which trench warfare had brought to the western front. The first prototype of the Mark I tank was tested for the British Army in September 1915. The British Mark I was a tracked vehicle developed by the British Army ...
World War I Interactive Worksheet
... 2. By winter of 1916, the main food was pea-soup with a few lumps of ______________ ...
... 2. By winter of 1916, the main food was pea-soup with a few lumps of ______________ ...
Gas Stoichiometry
... Determine volume ratios for gaseous reactants and products by using coefficients from chemical equations. Apply gas laws to calculate amounts of gaseous reactants and products in a chemical reaction. ...
... Determine volume ratios for gaseous reactants and products by using coefficients from chemical equations. Apply gas laws to calculate amounts of gaseous reactants and products in a chemical reaction. ...
New Weapons of the Great War
... have caused a break through, cutting the Allied defenses in half. However, the Germans were not expecting such success from the new weapon and were unprepared to take advantage of the situation. When Germany launched its chlorine attack at Ypres on 22 April 1915, it caught the world by surprise. It ...
... have caused a break through, cutting the Allied defenses in half. However, the Germans were not expecting such success from the new weapon and were unprepared to take advantage of the situation. When Germany launched its chlorine attack at Ypres on 22 April 1915, it caught the world by surprise. It ...
Chemical weapons in World War I

Chemical weapons in World War I were primarily used to demoralize, injure, and kill entrenched defenders, against whom the indiscriminate and generally slow-moving or static nature of gas clouds would be most effective. The types of weapons employed ranged from disabling chemicals, such as tear gas and the severe mustard gas, to lethal agents like phosgene and chlorine. This chemical warfare was a major component of the first global war and first total war of the 20th century. The killing capacity of gas was limited, with four percent of combat deaths caused by gas. Gas was unlike most other weapons of the period because it was possible to develop effective countermeasures, such as gas masks. In the later stages of the war, as the use of gas increased, its overall effectiveness diminished. The widespread use of these agents of chemical warfare, and wartime advances in the composition of high explosives, gave rise to an occasionally expressed view of World War I as ""the chemists' war"".The use of poison gas performed by all major belligerents throughout World War I constituted war crimes as its use violated the 1899 Hague Declaration Concerning Asphyxiating Gases and the 1907 Hague Convention on Land Warfare, which prohibited the use of ""poison or poisoned weapons"" in warfare.