* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Genetic Code
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
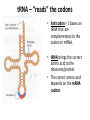
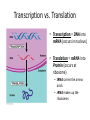
The Genetic Code Essential Questions 1. Use the Genetic Code to identify condons, anti-codons and amino acids from a DNA sequence. (Essential Skill 2-2) The Universal Genetic Code • Codon = every 3 bases on mRNA that codes for a specific amino acid. – Start Codon = AUG = Methionine – Stop Codons = (UAA, UAG, UGA) • This is what the tRNA reads The Genetic Code is the same for all organisms!!! tRNA – “reads” the codons • Anticodon = 3 bases on tRNA that are complementary to the codon on mRNA. • tRNA brings the correct amino acid to the ribosome/protein. • The correct amino acid depends on the mRNA codons How to Use the Genetic Code • Each codon has 3 letters (nucleotides: G, C, A & U) – 1st letter can be found along the left side of the chart – 2nd letter can be found along the top of the chart – 3rd letter can be found along the right side of the chart • it must be in the same row as the first letter • Where all three letters intersect is the name of the amino acid this codon codes for! – Each code always starts with AUG (start) and ends with a stop codon! • NOTE: The Genetic Code always uses the mRNA sequence!!! Basic Decoding Example tDNA TAC TCT GGG CTG ACT ATC mRNA AUG AGA CCC GAC UAG AA Met Arg Pro Asp AA Letter Letter (start) W H S ! How Mutations Affect the Amino Acid Sequence • A mutation (change in the nucleotide sequence) can affect protein structure in 3 ways: – No Change: It doesn’t change the amino acid sequence – Small Change: It changes only 1 amino acid – Large Change: It changes the whole protein Protein Synthesis Review DNA mRNA protein Transcription vs. Translation • Transcription = DNA into mRNA (occurs in nucleus) • Translation = mRNA into Protein (occurs at ribosome) – tRNA carries the amino acids – rRNA makes up the ribosomes Protein Synthesis Review