* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download chemistry 232 elementary organic chemistry ii
Kinetic resolution wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Cracking (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
Aldol reaction wikipedia , lookup
1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Vinylcyclopropane rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
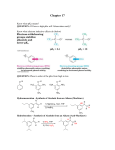
CHEMISTRY 232 ELEMENTARY ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II Exam #2 Study Guide Chapters 1 – 11, 15-17 Functional Groups to Identify/Name using the IUPAC system: NOTE: This list is not intended to be comprehensive but serves only as an overview of the major topics which will nd be assessed on the 2 in-class examination. Alkanes (Ch. 2) Alkenes (Ch. 6) Alkynes (Ch. 7) Alkyl Halides (Ch. 8) Alcohols (Ch. 10) Thiols (Ch. 10) Ethers (Ch. 11) Oxiranes (Ch. 11) Sulfides (Ch. 11) Organometallics (Ch. 15) Aldehydes (Ch. 16) Ketones (Ch. 16) Carboxylic Acid (Ch. 17) Reaction Classes for which a Mechanistic Understanding is Required: NOTE: This list is not intended to be comprehensive but serves only as an overview of the major topics which will nd be assessed on the 2 in-class examination. Electrophilic Addition to Alkenes/Alkynes (Ch. 6 & 7, 11) Hydrohalogenation (i.e. addition of HCl) Halogenation (i.e. addition of Br2) Oxymercuration [addition of Hg(OAc)2] Hydroboration/Oxidation [addition of BH3 followed by NaOH/H2O2] Epoxidation (i.e. addition of mCPBA) Free-Radical Halogenation of Alkanes (Ch. 8) Free-Radical Formation of organomagnesium (Grignard) reagents (Ch. 15) Substitution Reactions (Ch. 9 – 11) via SN2 Reaction Pathway (concerted) via SN1 Reaction Pathway (step-wise) Elimination Reactions (Ch. 9 – 11) via E2 Reaction Pathway (concerted) via E1 Reaction Pathway (step-wise) Acid-Base Protonation/Deprotonation Reactions (Ch. 7 & 10) Protonation/Deprotonation of Alcohols Deprotonation of Alkynes Acid-Catalyzed Rearrangements (Ch. 9 & 10) via SN1 Reaction Pathway (step-wise) The Pinacol Rearrangement Nucleophilic Addition to Carbonyl Compounds (Ch. 15, 16, & 17) Organometallic addition reactions Addition of alcohols to aldehydes/ketones (acetal/ketal formation) Addition of amines to aldehydes/ketones (imine formation) Functional Group Conversions of Which Knowledge is Required NOTE: This list is not intended to be comprehensive but serves only as an overview of the major topics which will nd be assessed on the 2 in-class examination. Alkene Alkyl Halide HX (Markovnikov) or HX/Peroxides (antiMarkovnikov) Alkene Alcohol Hg(OAc)2, then NaBH4 (Markovnikov) or BH3, then NaOH/H2O2 (anti-Markovnikov) Alcohol Alkyl Halide HX (3° ROH) where X = Cl, Br, or I ZnX2 / HX (2° or 1° ROH) where X = Cl or Br SOX2 (2° or 1° ROH) where X = Cl or Br PX3 (2° or 1° ROH) where X = Cl or Br TsCl or MsCl with R3N, followed by LiX (where X = Cl or Br) Alcohol Alkene Alkene Epoxide mCPBA, DMDO, or peracetic acid H2SO4 or H3PO4 (best for 3° ROH) TsCl or MsCl with R3N, followed by KOtBu or LDA (best for 2° or 1° ROH) Alkene 1,2-Dihalide 1,2-Diol Ketone or Aldehyde X2 (anti addition product) catalytic H2SO4 (Pinacol Rearrangement) Alkene 1,2-Diol OsO4 or cold KMnO4 (syn addition product) 1,2-Diol α,ω-Dicarbonyl HIO4 Alkene α,ω-Dicarbonyl 1,2-Diol Epoxide O3 followed by DMS or Ph3P OsO4, followed by HIO4 catalytic H2SO4 (3° ROH only) LiOH / ∆ (2° or 1° ROH only) Alkene α,ω-diol (via ozonolysis) Alcohol Ether O3 followed by NaBH4 Alkyne Alkenyl Halide HX (Markovnikov) or HX/Peroxides (antiMarkovnikov) catalytic H2SO4 (symmetrical ethers only) _ + R-X, + RO Na (Williamson synthesis) Alkyne/Alkene Alkane catalytic Pt/Pd, H2 Alkyne Ketone or Aldehyde Alkyne/Alkene Alkene (cis only) Hg(OAc)2, then NaBH4 (Markovnikov) or BH3, then NaOH/H2O2 (anti-Markovnikov) Alkyne 1,2-Dihaloalkene X2 (anti addition product) Alkane Alkyl Halide X2 / hν or NXS / hν Alkyl Halide Alkene KOtBu or LDA (or other large, hindered base) catalytic Pd/CaCO3, H2 (Lindlar’s Catalyst) Aldehyde/Ketone Alcohol + LiAlH4/Et2O, then H3O (reduction) + NaBH4/CH3OH, then H3O (reduction) + RLi, then H3O (C-C bond formation) + RMgBr, then H3O (C-C bond formation) + RZnX, then H3O (C-C bond formation; only for aldehydes) Functional Group Conversions of Which Knowledge is Required NOTE: This list is not intended to be comprehensive but serves only as an overview of the major topics which will nd be assessed on the 2 in-class examination. Alkyl Halide Alkane + LiAlH4/Et2O, then H3O (reduction) + R2CuLi, then H3O (C-C bond formation; best for iodides) Alkene Cyclopropane + IZnCH2I, then H3O (Simmons-Smith) Aldehyde/Ketone Acetal/Ketal ROH (xs), catalytic H2SO4 (+ heat for acid) Acetal/Ketal Aldehyde/Ketone H2O, catalytic H2SO4 Carboxylic Acid 3° ROH + R-Li (xs), then H3O (C-C bond formation) Carboxylic Acid 1° ROH + LiAlH4, then H3O (reduction) + Dibal-H (xs) in CH2Cl2, then H3O (reduction) Acid Chloride Ketone R2CuLi (xs), THF, then H3O + Epoxide Alcohol + R-MgBr/Et2O, then H3O (C-C bond formation) Alkyl Halide Organometal Halide Mg/Et2O (Grignard Reagent) Li (2 eq)/Pentane (Organolithium) Zn/Hexanes (Organozinc) Organometal Halide Organo Cuprate CuI/Ether (or THF)