* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review #3 - California Lutheran University
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
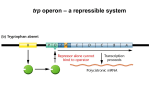
Molecular Biology Spring, 2011 This review for the third exam covers chapters 14 through 17. The exam will be essay and problems. No multiple choice, matching, or true/false questions. Translation In prokaryotic translation, where does the ribosome bind the mRNA? What are the important parts of that site? Why are prokaryotes able to translate more than one protein per mRNA? In eukaryotic translation, where does the ribosome bind the mRNA? What are the important parts of that site? Why are eukaryotes not able to translate more than one protein per mRNA? What is the structure of tRNA? What is its tertiary structure? What are aminoacyl tRNA synthetases? What are the two classes of synthetases and how do they differ? If there are 61 codons and 32 or more tRNAs, why are there only 20 synthetases? What parts of the tRNA do the synthetases recognize? Why is the error rate for synthetases low (10-3 to 10-4 per amino acid)? What is selenocysteine and why is it of interest? What are the major components of ribosomes? What is the general “ribosome cycle” for translation? How many ribosomes can there be per mRNA? How are peptide bonds formed in the peptidyl transferase reaction? What is the important part of the ribosome for this reaction? What are the sites on the ribosome for tRNA? What is the purpose of each site? What are the purposes of the channels on the ribosomes? What happens in the process of initiation of translation in prokaryotes? Which proteins are important in addition to the ribosome, and what is each doing? What happens in the process of initiation of translation in eukaryotes? Which proteins are important in addition to the ribosome, and what is each doing? How does the process in prokaryotes differ from that in eukaryotes? Why is the first AUG sometimes skipped in eukaryotes? What is the process of translation elongation? How is the error rate improved by the ribosome? Besides the ribosome, which proteins are involved? What are release factors? What are their functions? How do class I release factors recognize codons? What is the process of termination of translation? How do the following antibiotics inhibit translation: chloramphenicol, tetracycline, puromycin, ricin, and diphtheria toxin? What happens in prokaryotes if there are no stop codons in an mRNA? How do eukaryotes degrade mRNA without stop codons? What happens if there is a premature stop codon in eukaryotic mRNA? How does the absence of polyA reduce translation of a eukaryotic mRNA? Genetic code When the genetic code was analyzed, it was discovered that it minimizes the chances of detrimental mutations. How is it organized and how did it minimize problems? How does wobble work, and how is it involved in “loosening” the base pairing rules? Which experiments showed how the code works: how many bases per codon, whether there were gaps or punctuation, and whether the codons overlapped? What types of experiments were performed to figure out which codons coded for which amino acids? What are missense, nonsense, and frameshift muations? How can mutations be suppressed? What are suppressor tRNAs, and how do they work? Why are cells that use suppressor tRNAs a “little sick”? Why is the “universal” genetic code not universal? What are the most common changes? 1 Prokaryotic gene regulation What is a “basal” level of transcription? When does it occur? Where does a repressor bind? Where does an activator bind? What is recruitment? What are two ways that activators can stimulate transcription? What are two ways that repressors can prevent transcription? Why can activators work even when their binding sites are far away from promoters? What type of proteins help? What is cooperativity? What type of binding curve do they have? Why are cooperative processes important for regulating cellular processes? Lac operon: What does the operon look like? What is the function of each of the genes? What are the two regulators of the operon? What is each regulator sensing? Under what conditions is the operon expressed? Why? What does the lac operator look like? What does that tell us about the repressor protein? What are “positive control” mutants? How can you determine which parts of CAP bind to RNA polymerase? Why does the operon have three operators? What is the real inducer of the operon? If you need the permease to get lactose into the cell, how can the operon ever be turned on? What regulates CAP? What is DNA footprinting? How does the procedure work? What are mobility shift experiments? What do they tell you? What is chemical interference footprinting? What does it tell you? What are activator bypass experiments? What do they tell you? How did the Jacob and Monod cis/trans test determine if a mutation affected a protein or a regulatory part of the gene? What are some alternative σ factors? When are they used? How do the σ factors change after SPO1 infection of B. subtilis? How does NtrC affect the glnA gene? When does the system work? What σ factor is involved? Where does NtrC bind? How does it activate the glnA gene? How does MerR affect the MerT gene? When does the system work? Where does MerR bind? How does it activate the gene? How does the Gal repressor turn off the gal operon? How does the AraC protein affect the araBAD operon? Under what circumstances is the operon turned on or off? What are the two types of regulation of the trp operon? How does the repression work? How does the attenuation work? How does E. coli control how much of the ribosomal proteins are made? What are riboswitches, and how do they work? Eukaryotic gene regulation What are reporter genes? Why are these genes used for studies? What are the important parts of an activator? How does Gal4 activate the GAL1 gene? What experiments were used to dissect the activation, and what did each type of experiment prove? How do two-hybrid assays work? Why would you use them? What are the four types of motifs of the DNA-binding portion of activators? How do they bind DNA? What do activating regions look like in activators? How do activators stimulate transcription? What is chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), and what can it tell you? What are the two types of chromatin modifiers? How do they make chromatin more accessible? Why can some enhancers work even when 100 kb away from the gene they enhance? 2 What are insulators? What is silencing? What are locus control regions? How do they work? What is signal integration? How does the HO gene illustrate signal integration? How do activators turn on the human β–interferon gene? What is combinatorial control? How does that help explain how we can individually turn on genes? How does mating type switching occur in yeast? Which experiments could be performed to show how this system works? What are the major ways that transcriptional repressors turn off genes? How is the GAL1 gene repressed? What is signal transduction? What is the typical pathway for signal transduction? How does the STAT pathway work? What is the major difference for the Ras pathway compared to the STAT pathway? How are transcriptional regulators regulated? What are the two major methods of regulation of them? What is gene silencing? What causes it? How is the yeast telomere silenced? How does methylation of DNA affect transcription? What protein recognizes methylated DNA, and what happens after it binds? What is imprinting, and how does it work in the H19 and Igf2 genes in humans? Old exam 1) Explain how prokaryotes and eukaryotes differ in how they select the AUG that is used for initiating translation. 2) What happens in eukaryotes if: (Answer two out of three, and be sure to describe the proteins/steps involved in the problem) a) There is no poly-A in the mRNA? b) There is a premature stop codon? c) There is no stop codon? 3) The genetic code was figured out by the use of two major techniques. Describe how these techniques work and how they were used to figure out which codon codes for which amino acid. 4) How does E. coli control how much of the ribosomal proteins are made? 5) Many mutants have been made that affect the lac operon. a) One mutation causes the lac operon to always be turned on. What type of mutation could do this and how does it cause the operon to always be on? b) A second mutation causes the operon to always be off. What type of mutation could do this and how could it cause the operon to always be off? c) A third mutation can eliminate the effects of glucose on the lac operon. What mutation could do this and how does it work? 6) Pick two out of three of the following questions: a) What are two alternative σ factors, and under what circumstances are they used? b) How does MerR affect the MerT gene? Describe how it works. c) How does the AraC protein regulate the araBAD operon? Describe when and how it affects the operon. 3