* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hormones
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Graves' disease wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Kallmann syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
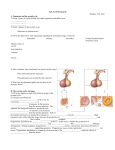
Hormones 1. Production and Role of Hormones a. Hormones act as chemical signals i. Each has a specific shape that is recognized by target cells ii. Binding to receptor on or in target cell causes chemical reactions within the cell b. Hormone control i. hypothalamus – area of the brain secretes hormones that cause the ii. pituitary gland to secrete other hormones that cause other parts of the endocrine system to secrete hormones. 1. TSH – secreted by the pituitary gland – controls Thyroid a. Thyroxine is a hormone produced by thyroid i. Controls: vertebrate development and maturation, blood pressure, heart rate, muscle tone, digestion and reproduction ii. Deficiency: weight gain, intolerance to cold, lethargy or if iodine is lacking: goiter iii. Too much: loss of weight, high body temp, profuse sweating, irritiability 2. ACTH – secreted by the pituitary gland – controls adrenal glands a. Adrenaline (epinephrine) is hormone produce by adrenal glands i. Secreted in response to positive or negative stress: responsible for quickening heart rate, goose bumps, etc. ii. Increases basal metabolic rate, and available energy sources (rate of glocygen breakdown, release of glucose from liver, release of fatty acid from fat cells) iii. Affects cardiovascular and respiratory system iv. Increases oxygen in the blood v. Causes blood to flow away from skin, digestive organs, and kidneys and to the heart, brain and skeletal muscles. 3. FSH/LH – secreted by the pituitary gland – controls gonads a. 3 kinds of steroid hormones released by gonads i. Androgens (testosterone) 1. made in testes 2. responsible for development of male reproductive system ii. Estrogens (estradiol) 1. Made in ovaries 2. responsible for development of female reproductive system iii. Progestins (progesterone) 1. Made in ovaries 2. responsible for preparation and maintenance of uterus b. Estrogen, Progesterone, FSH and LH are responsible for controlling the female menstrual cycle. i. The secretion of FSH and LH can be controlled by the amount of estrogen and progesterone present ii. Without FSH and LH, ovulation (release of egg from ovary) cannot occur. iii. This is how oral contraceptives work – pill is mixture of estrogen and progesterone that work to prevent release of FSH and LH from pituitary gland and thereby prevent ovulation. No ovulation = no egg in uterus = no baby. iii. Insulin 1. is a hormone that is not controlled by the pituitary gland but by the amount of glucose in the blood 2. Secreted by the Pancreas 3. Regulates the concentration of glucose in blood a. Ideal point is 90 mg/100 mL b. If too high: insulin is released causing i. Cells to take up glucose ii. Reduction in glycogen breakdown in liver iii. Inhibition of conversion of amino acids and fatty acids to sugar c. If too low: glucagon is released causing the opposite reactions 4. Deficiency of insulin causes Diabetes a. Type I: childhood onset, need shots b. Type II: adulthood onset, need to control through diet and exercise 2. Outline the use and abuse of steroids a. Use: i. Treatment of wasting illness ii. To regain muscle tissue iii. Treatment of eczema b. Abuse: i. Increase muscle mass to enhance performance ii. Increase strength