* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BioMI 2900
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Oligonucleotide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cyanobacteria wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
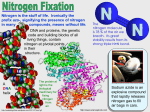
BioMI 2900 Dr. Hay Fall 2016 09/30/16 Week 6: Lecture 3 of 3 (Lecture 15) Title: Nitrogen Fixation and Assimilation Keywords: Modularity, Biosynthesis, Nitrogen Cycle, Nitrification (Nitrogen Fixation), Nitrogenase, NifH, Protection from Oxygen, Heme, Heterocysts, Bacteroids, Gas Chromatograph, Ammonia, Ammonium, Hydrozene, Tetrapyrroles, Amino Acid Biosynthesis, Activated Sugars, Peptidoglycan Generation, Lysozyme Review the second part of Lecture 11 (Panopto on Blackboard)!!! What is a Module? ● A molecule which can be used for a plethora of different pathways ● The basic, central machinery of many energy production processes is conserved ● Makes HGT simple and conserves genes ● Evolution is thus accelerated Overview of Biosynthesis: Overview of the Nitrogen Cycle: Nitrification (Nitrogen Fixation) ● It is both lithotrophy and respiration ● The challenge of this cycle is to reduce the inert N2 into organic forms ● Learn Horizontal Transfer of Nitrogenase Genes (NifH) Slide!! ● Takeaway: there is a lot of HGT of this gene, making it differ GREATLY from the 16s rRNA phylogeny ● Why is nitrogen fixation so common? 99.99% of Nitrogen in nature is inert! ● Here is a table of some common nitrogen-fixing organisms: ● The coupling of photosynthesis with N-fixation allows a wide environmental range (e.g. for cyanobacteria) ● N-fixation needs protection from O2: ○ some structures to protect it from oxygen are heterocysts in cyanobacteria, nodule formation in legumes/plants (Rhizobia), slime layers (Azotobacter) ○ Bacteroids in plant nodules are differentiated bacteria which fix nitrogen for the plant. They are red in color due to a heme molecule. There environments are largely anoxic, due to the heme molecule. Fixation with Nitrogenase: ● Requires unusual cofactors ● Learn net reaction ● Relies on reduction of NADH ● Having a HYDROGENASE can recuperate energy lost in N-fixation. ● Hydrozene is a toxic byproduct, so it is reduced again to form ammonia and ammonium ● There is a high energy investment to make ammonia Measuring N-Fixation: ● Where does reducing power come from? Glycolysis! Assimilation of NH4+ ● It is condensed Ammonia Assimilation: Amino Acid Biosynthesis ● Carbon comes from Glycolysis, Pentose Phosphate, and TCA ● Very modular process: ○ ● Very complicated processes have a common, relative origin in the simple backbones of respiration The molecule Chorismate is associated with Aromatic amino acids (Trypophan, Tyrosine, Phenylalanine) Tetrapyrroles are modular structures used to make heme, chloropyll, vitamin Band many other ringed structures: ● Lead Poisoning directly affects tetrapyrrole formation Nucleotide Biosynthesis ● Sugar from Pentose Phosphate Pathway is activated ● PRPP is gateway molecule, affecting the speed of the pathway ● 2 Phosphates are released, making the process irreversible (nucleotide biosynthesis is important and central) ● Again, this process is modular, in that it has many different diverse outcomes Peptidoglycan Biosynthesis ● Starts with activated sugar (UDP) ● UDP-NAM joins UDP-NAG to make chains and added to bactoprenol, which is then cleaved by Bacitracin ● Vancomycin and Penicillin directly inhibit this synthesis with lysozyme ● Neomycin has Bacitracin (in addition to protein synthesis inhibitors), which also cleaves the cell wall