* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 6 Learning
History of psychology wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Subfields of psychology wikipedia , lookup
Developmental psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cross-cultural psychology wikipedia , lookup
Conservation psychology wikipedia , lookup
Music psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
Educational psychology wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Social cognitive theory wikipedia , lookup
Albert Bandura wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
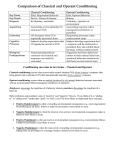
AP Psychology Reitz Name:___________________________________ Date:__________________ Hour:_______________ Unit 6 Learning Use SQ3R: Survey, Question, Read, Rehearse, and Review every section you read Introduction and How Do We Learn? (pp 214-217) 1: Define learning, and identify two forms of learning. Classical Conditioning (pp 218-228) 2: Define classical conditioning and behaviorism, and describe the basic components of classical conditioning. 3: Summarize the processes and adaptive value of acquisition, extinction, spontaneous recovery, generalization, and discrimination. 4: Discuss the importance of cognitive processes and biological predispositions in classical conditioning. 5: Summarize Pavlov’s contribution to our understanding of learning and to improvements in human health and well-being. AP Psychology Reitz Operant Conditioning (pp 228-242) 6: Identify the two major characteristics that distinguish classical conditioning from operant conditioning. 7: Describe the process of operant conditioning, including the shaping procedure. 8: Identify the different types of reinforcers, and describe the major schedules of partial reinforcement. 9: Discuss how punishment and negative reinforcement differ, and list some drawbacks of punishment as a behavior-control technique. 10: Explain the importance of cognitive processes and biological predispositions in operant conditioning. AP Psychology Reitz 11: Describe the controversy over Skinner’s views of human behavior, and identify some ways to apply operant conditioning principles at school, in sports, at work, and at home. 12: Identify the major similarities and differences between classical and operant conditioning. Learning by Observation (pp 242-253) 13: Describe the process of observational learning, and Bandura’s finding on what determines whether we will imitate a model. 14: Discuss the impact of prosocial modeling and the relationship between watching violent TV and antisocial behavior. Define in 5 words or less: Learning: Habituation: Associative learning: Classical conditioning: AP Psychology Behaviorism: Unconditional Response (UR): Unconditional Stimulus (US): Conditioned Response (CR): Conditioned Stimulus (CS): Acquisition: Higher-order conditioning Extinction: Spontaneous recovery: Generalization: Discrimination: Learned helplessness: Operant conditioning: Respondent behavior: Operant Behavior: Law of effect: Operant chamber: Shaping: Discriminative stimulus: Reinforcer: Positive reinforcement: Negative reinforcement: Primary reinforcement: Conditioned reinforcer (secondary reinforcer): Continuous reinforcement: Partial (intermittent) reinforcement: Reitz AP Psychology Fixed-ratio schedule: Variable-ratio schedule: Fixed-interval schedule: Variable-interval schedule: Punishment: Cognitive map: Insight: Latent learning: Intrinsic motivation: Extrinsic motivation: Observational learning: Biofeedback: Modeling: Mirror neurons: Prosocial behavior: Albert Bandura: B.F. Skinner: Edward Thorndike: John Watson: Ivan Pavlov: John Garcia: Robert Rescorla: Edward Tolman: Reitz