* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Practice problems for week 8 PDF
Kinetic resolution wikipedia , lookup
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Diels–Alder reaction wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Organosulfur compounds wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Aromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
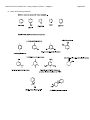
Chem 275 Practice Problem Set – Friday, October 15, 2010 – J. Magolan Page 1 of 6 This problem set includes questions covering material from chapters 7, 8 and 9 in your textbook. 1. Define and explain the word ‘meso’ as it applies to stereochemistry. Draw three examples of meso compounds. A meso compound is one that contains chiral centres but is achiral because of an intermal plane of symmetry. Thus, switching the R,S configuration does not produce a unique enantiomer but rather just another copy of the same compound. 2. Draw the product of this reaction. How many enantiomers and diastereomers could we draw for the starting compound. How many for the product? If the numbers are different, explain why they have changed. Chem 275 Practice Problem Set – Friday, October 15, 2010 – J. Magolan Page 2 of 6 3. Explain why, in the reaction below, a single enantiomer of starting material yields a racemic mixture of products? This is an SN1 reaction. What products would be formed in the SN2 version of this reaction (with NaOMe)? Explain your answer thoroughly. Chem 275 Practice Problem Set – Friday, October 15, 2010 – J. Magolan Page 3 of 6 4. A secondary alkyl halide treated with water, acid, and heat can undergo E1 and SN1 reactions. Draw ALL potential products of both of these reactions. (Consider multiple products!) 5. A secondary alkyl halide treated with a strong nucleophile/base such as NaOH will undergo E2 and SN2 chemistry. Draw ALL potential products of both of these reactions. Chem 275 Practice Problem Set – Friday, October 15, 2010 – J. Magolan 6. Draw the products of the following reactions: Page 4 of 6 Chem 275 Practice Problem Set – Friday, October 15, 2010 – J. Magolan Page 5 of 6 7. The first molecule below is a well-known aromatic compound called ‘furan’. The second is a common laboratory solvent called ‘tetrahydrofuran (or THF)’. Suggest why the second might have been given the name tetrahydrofuran? Discuss the hybridization of the oxygen atoms in the two compounds below. How and why are they different? Tetrahydrofuran has 4 more hydrogens than furan. Thus the name The oxygen of furan is sp2 hybridized. This is because one of its lone pairs exists in a p orbital and is involved in the aromatic ring – leaving just three regions of electron density (at 120o angles). The oxygen of tetrahydrofuran is a typical sp3 hybridized oxygen atom like we see in alcohols and ethers. It has two bonds and two equivalent lone pairs making a total of 4 regions of electron density. Chem 275 Practice Problem Set – Friday, October 15, 2010 – J. Magolan 8. Name the following molecules: Page 6 of 6