* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Concept Analysis Diagram
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Gluten immunochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Inflammation wikipedia , lookup
Vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmunity wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
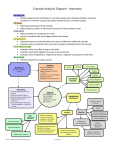
Concept Analysis Diagram - Immunity Nursing Care Directed toward what contributes to a normal concept and is thereby related to all factors involved in or with the concept. Not always needed to have a normal outcome. Attributes Defining characteristics of the concept What property, quality, or data must be present for the concept to exist Antecedents What precedes the concept for it to exist Events or incidents that must happen before the concept Consequences Untoward events or outcomes that occur due to malfunction within the concept Positive events or outcomes that occur due to proper functioning within the concept Interrelated Concept Concepts which can affect change in the other Concepts which work together to ensure a normal process Concepts which if depleted or impaired can cause a negative consequence in the other Sub-Concept Critical components of major concept Attributes Lab--normal WBC and Differential Counts Negative Bacterial and Viral Cultures Soft, Non-Tender Lymph Nodes Recognition of Self Recognition of Foreign Proteins Nursing Care Primary, Secondary, Tertiary Comfort Mobility Tissue Integrity Coping Nutrition Interrelated Concepts Cellular Regulation Functional Ability Antecedents Thermoregulation Intact Non-Specific Defenses or Barriers Functional Lymphatic System Optimal Innate Immune Response Functional Inflammatory Response Appropriate Adaptive (Acquired) Immune Response—Active and Passive IMMUNITY A physiologic process that provides an individual with protection or defense from disease. Consequences (Outcomes) Infection-Localized or Systemic Cancer Negative Positive Replaces Damaged Tissue and Cells with Repaired or Functional Tissue (i.e., healing) functional Sub Concepts Immune Response Infectious Response Immune Deficiency Exaggerated Immune Response Recognizes and Removes Cell Mutations that have Demonstrated Abnormal Cell Growth and Development Protects From Invasion of Microorganisms and Other Antigens Inflammatory Response 77 © 2015, Texas CBC Consortium. All Rights Reserved. Immune Suppression Revised 6.15 Chronic Inflammatory Response Allergic, Cytotoxic or Autoimmune Reaction Concept Analysis Diagram - Immunity Explanation of Immunity Diagram: The Immunity Concept Analysis Diagram begins with the definition of the concept, as based on the attributes and antecedents. The attributes - normal WBC and differential counts, negative bacterial and viral cultures, soft, non-tender lymph nodes, recognition of self and recognition of foreign proteins - are the defining characteristics of immunity or what constitutes immunity. The antecedents are events or incidents that must be in play in order for immunity to exist. The antecedents for immunity consist of intact non-specific defenses or barriers, a functional lymphatic system, an optimal innate immune response, a functional inflammatory response, and appropriate adaptive (acquired) immune response— active and passive. With these attributes and antecedents, immunity is a physiologic process that provides an individual with protection or defense from disease. There are interrelated concepts that impact immunity throughout the lifespan. These interrelated concepts include tissue integrity, cellular regulation, thermoregulation, comfort, coping, nutrition, mobility and functional ability. There are also sub-concepts that are major components of the immunity concept – inflammatory response, infectious response, and immune response. The sub-concepts are manifested when immunity is challenged. Consequences, positive or negative, are reliant upon the performance of the immune system. If any of the antecedents fail, for example, the result would be a negative outcome, such as infection-localized or systemic, cancer, immune suppression, immune deficiency, and chronic inflammatory response or exaggerated immune response that may lead to an allergic, cytotoxic or autoimmune reaction. If the immune system is healthy, positive outcomes will result; in that, damaged tissue and cells are replaced with repaired or functional tissue (i.e., healing), recognition and removal of cell mutations that have demonstrated abnormal cell growth and development is effected, and protection of the body from invasion of microorganisms and other antigens occurs. Last, but not least, nursing care may or may not be required, as indicated by the dotted directional lines on the diagram. Nursing care may/may not be needed to keep immunity intact, or assist with negative consequences. 78 © 2015, Texas CBC Consortium. All Rights Reserved. Revised 6.15