* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Anterior pituitary hormones
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of depression wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
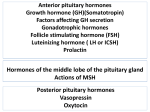
Anterior pituitary hormones • Five secretory cells producing 6 different hormones – Cortocotroph • ACTH – Gonadotroph • LH and FSH – Somatotroph • GH – Lactotroph • Prolactin – Thyrotroph • TSH ACTH • Part of larger protein – Pro-opiomelanocortin • One gene (8kb, three exons and two introns) – Codes for one large protein • Transcription of gene – Activated by CRH, arginine vasopressin, cytokines – Inhibted by glucocorticoids • Transcription of POMC gene – CRH type 1 receptor • Production of cAMP and activation of protein kinase A pathway – Activation of CREB transcription factor • Activation of MAP-Kinase pathway – Cytokine receptor (LIF) • Activation of JAK/Stat pathway – Interaction with CRH signaling pathway • Pro-opiomelanocortin – 266 amino acids – Proteolytically cleaved to produce corticotrophic, opioid, and melanotrophic peptides • Secretion of ACTH – Complex regulation through HPA (hypothalamus-pituitaryadrenal) axis – Circadian and ultradian rhythm • Hypothalamic control (CRH) – Activity of nuclei regulated by glucocorticoids • Pulse amplitude rather than frequency determines circadian rhythm Regulation of ACTH secretion • Exercise (short and exhausting) – Increased secretion of ACTH • Hypercortisolism in athletes • Stress – Increased production of cortisol • Integration of information received by the CNS • Constrain the inflammation Action of ACTH • Primary function – Proper maintenance of adrenal gland – Adrenal steroidogenesis • Cholesterol transport • Conversion to pregnenolone • Inhibited by glucocorticoids Gonadotropins • Two hormones from one type of cells – LH and FSH • Glycoprotein hormones – Two subunits • Alpha – Universal among all glycoprotein hormones • Beta – Hormone specific • Combination of alpha and beta subunits – Essential for biological activity Synthesis of gonadotropins • Alpha subunit – Generated from different gene • Chromosome 6 – Increased synthesis by GnRH and TRH • Beta subunits – Determinant of biological activity • LH beta on chromosome 19 • FSH beta on chromosome 11 • Transcription of LH beta subunit mRNA – GnRH – SF-1 – Estrogen • Transcription of FSH beta – Role of GnRH and steroids • Unclear • Different promoter structure from LH Regulation of gonadotropin secretion • Pulsatile secretion – Mirror image of GnRH pulses • Frequency and amplitude • LH more sensitive to changes in GnRH • Gonadal steroid hormones – Testosterone • Inhibits secretion • Enhances FSH beta subunit mRNA transcription – Estrogens • Dual function (stimulatory/inhibitory) • Cyclic changes in female during reproductive cycle • Gonadal peptides – Inhibins • Inhibits secretion of FSH – Activins • Stimulates FSH secretion and action – Follistatin • Inhibits FSH secretion and action Function of gonadotropins • Receptors for LH and FSH – Highly homologous • 50 % of extracellular domain • 80 % of transmembrane domain • Steroidogenesis in male and female – cAMP production • Increased cholesterol availability via increased production of steroidogenic acute regular protein (StAR) • Increased enzyme activity Function of gonadotropins • Receptors for LH and FSH • Steroidogenesis in male and female – cAMP production • Increased cholesterol availability via increased production of steroidogenic acute regular protein (StAR) • Increased enzyme activity • Development and function of gonadal cells and gametes – FSH Growth hormone • Human GH gene – Located in chromosome 17 • 66 kb in length • Cluster of genes that encode closely related genes – GH-V – Placental lactogen/chorionic somatotropins – Transcription of GH mRNA • POUF1 transcription factor – Pituitary specificity – Interacts with protein kinase A pathway • Large polypeptide hormone – 191 amino acids • Four alpha helices looped together • Interacts with binding protein (GHBP) – Extends half-life of GH – Found in rodents, rabbits, and humans • Extracellular domain of GH receptor in human and rabbit • Product of alternative transcription in rodents Regulation of GH secretion • Major GH pulses (70 % of total daily output) – Slow sleep (deep sleep) – Age-related loss of GH • Decrease quality of sleep • Obesity and diabetes – Decreased GH release – Nutritional status • One of the major regulatory factor of GH secretion • Hormones – Steroids • Acute elevation in glucocorticoids (+) • Chronic elevation in glucocorticoids (-) • Gonadal steroids (+) – Thyroid hormones • Inhibitory Action of GH • Growth and metabolism – Action mediated by IGF-I • Mediation of growth • Endocrine IGF-I – Liver • Local (autocrine/paracrine) IGF-I • Gender-specific pattern of GH secretion – Affects amount of steroidogenic enzymes • Gender-specific pattern of steroidogenesis – Gender-specific pattern of liver enzyme expression – Gender-specific action of GH • Mediated by STAT 5b activity TSH • Glycoprotein hormone – Alpha and beta subunits • Alpha is identical to that of gonadotropins • Thyrotroph-specific expression – Different region of gene promoter – Gene for TSH beta subunit • Located on chromosome 1 • Transcription regulated by Pit-1 • Post-translational modification – Glycosylation • Affects proper molecular folding • Combination of alpha and beta subunits • Regulated by TRH (+) and T3 (-) Secretion of TSH • Bioactivity of TSH – Glycosylation • Clearance rate • Pulsatile secretion – Not as pronoused as gonadotropins or GH • Low variation in concentrations – Circadian pattern • Increased secretion during night – Independent of sleep • Hormonal regulation – Major factor of TSH secretion • Thyroid hormone concentrations – Extremely important • • • • TRH Dopamine (-) Glucocorticoids (-) SS (-) Action of TSH • Thyroid hormone production – G-protein coupled receptor • Thyroid cell integrity maintenance Prolactin • Structurally similar to GH – Common ancestry • Chromosome 6 • Prolactin gene expression – – – – Estrogen Dopamine TRH Thyroid hormones • Exits as monomer or polymer in circulation – 23 kDa (monomer) • Most bioactive – 48-56 kDa (dimer) – > 100 kDa (polymer) – Glycosylated • Less active • Binds to prolactin binding protein Regulation of prolactin secretion • Inhibitory – Hypothalamic • Dopamine • Calcitonin – Paracrine factors • Endothelin-1 • TGF-beta 1 • Stimulatory – Growth factors • bFGF • EGF – Gut hormone • VIP – Estrogen Function of prolactin • Essential for survival – Lactation • Prolactin surge during labor – Essential for initiation of lactation • Not required for maintenance of lactation – Immune function • Stimulates lymphocyte development – Reproduction • Essential for rodents