* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 8 - Endocrine
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
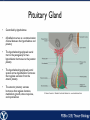
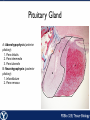
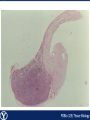
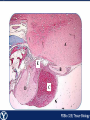
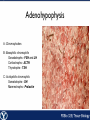
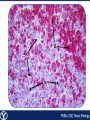
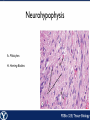
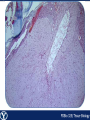
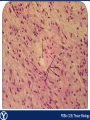
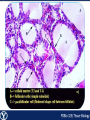
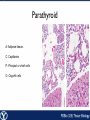
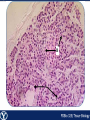
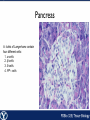
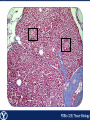
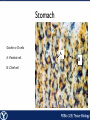
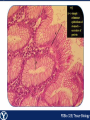
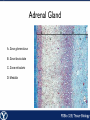
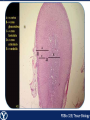
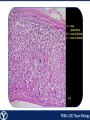
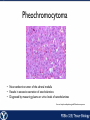
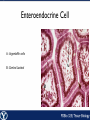
Endocrine Endocrine Function • Influences growth, metabolism, and homeostasis over prolonged periods • Secretes hormone products into interstitial spaces which are then absorbed into the blood and transported throughout the body • Hormonal control is much slower than nervous control, but the effects of the endocrine system are much longer lasting Key Features of Endocrine Glands • A rich capillary blood supply is necessary for secretion and reception of hormones • Endocrine glands are, by definition, ductless • Organelles required to synthesize specific hormones are in great supply Hormone Classifications Amino Acid Derivatives • Hormones derived from the amino acid tyrosine • Epinephrine, norepinephrine, and thyroxine Polypeptide Hormones • Hormones with a peptide structure • Insulin, prolactin, NGF, EGF, GH, PTH, TSH, enkephalin, TRH, ADH Steroids • Hormones derived from cholesterol • Testosterone, cortisol, aldosterone, progesterone, estradiol Pituitary Gland • Controlled by hypothalamus • Infundibulum serves as a communication channel between the hypothalamus and pituitary • The hypothalamohypophyseal neural tract is the passageway for two hypothalamic hormones to the posterior pituitary • The hypothalamohypophyseal portal system carries hypothalamic hormones that regulate secretion from the anterior pituitary • The anterior pituitary secretes hormones that regulate lactation, metabolism, growth, stress response, and reproduction Pituitary Gland A: Adenohypophysis (anterior pituitary): 1. Pars distalis. 2. Pars intermedia 3. Pars tuberalis B: Neurohypophysis (posterior pituitary): 1. Infundibulum 2. Pars nervosa A B A E B D C Practice Adenohypophysis A: Chromophobes B: Basophilic chromophils Gonadotrophs– FSH and LH Corticotrophs– ACTH Thyrotrophs– TSH C: Acidophilic chromophils Somatotrophs– GH Mammotrophs– Prolactin B C A Practice Neurohypophysis A: Pituicytes H: Herring Bodies A Review Fill in the missing hormones secreted from the pituitary or list their respective functions Hormone Function FSH Follicle maturation and spermatogenesis LH Causes follicle maturation and testosterone production in leydig cells ACTH Stimulates adrenal cortex TSH Stimulates T3 and T4 secretion from thyroid GH Controls growth Prolactin Stimulates mammary glands ADH Stimulates water resorption Oxytocin Smooth muscle contraction and milk letdown Thyroid 4 B A: Follicular cells B: Parafollicular cells A Parathyroid A: Adipose tissue. C: Capillaries P: Principal or chief cells O: Oxyphil cells B A Practice A B Pancreas A: Islets of Langerhans contain four different cells: 1. α-cells 2. β-cells 3. δ-cells. 4. PP– cells A Stomach Gastrin or G-cells A: Parietal cell. B: Chief cell. A B Adrenal Gland A A: Zona glomerulosa B: Zona fasciculata C: Zona reticularis D: Medulla B C D Practice Clinical Connections Pheochromocytoma • Neuroendocrine tumor of the adrenal medulla • Results in excessive secretion of catecholamines • Diagnosed by measuring plasma or urine levels of catecholamines Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pheochromocytoma Enteroendocrine Cell A: Argentaffin cells A B: Central Lacteal B Practice Review Know the following hormones, where they are secreted, their function, and target organ. Anterior Pituitary FSH LH ACTH TSH GH Prolactin Posterior Pituitary ADH Oxytocin Thyroid T3 and T4 Calcitonin Parathyroid PTH Pancreas Glucagon Insulin Somatostatin Pancreatic Peptide Stomach Gastrin Adrenal Aldosterone Cortisol DHEA Argentaffin Cell CCK Secretin Serotonin