Ch12 - ISpatula
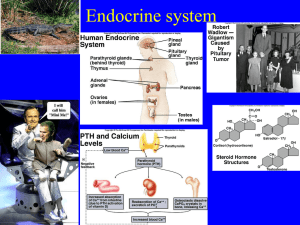
... In short, these hormones give the body what it needs for quick action. The adrenal glands also secrete several dozen steroids. These hormones, known as corticosteroids, are essential to life. One of them is called aldosterone, which helps the body retain the correct number of sodium ions. interestin ...
... In short, these hormones give the body what it needs for quick action. The adrenal glands also secrete several dozen steroids. These hormones, known as corticosteroids, are essential to life. One of them is called aldosterone, which helps the body retain the correct number of sodium ions. interestin ...
Chapter 18 - TeacherTube
... the pituitary gland _________________________________________________________________ 2. Cavity in the skull that contains the pituitary gland ______________________________________ 3. Tendency of an organism to maintain a constant internal environment ______________________ 4. Mimicking or copying ...
... the pituitary gland _________________________________________________________________ 2. Cavity in the skull that contains the pituitary gland ______________________________________ 3. Tendency of an organism to maintain a constant internal environment ______________________ 4. Mimicking or copying ...
hormones - Zanichelli
... Cushing syndrome is caused by a disfunction of the adrenal cortex and is characterized by a tendency toward diabetes mellitus, subcutaneous fat accumulation in the trunk and a moon-shape face. The thyroid regulates development and increases the ...
... Cushing syndrome is caused by a disfunction of the adrenal cortex and is characterized by a tendency toward diabetes mellitus, subcutaneous fat accumulation in the trunk and a moon-shape face. The thyroid regulates development and increases the ...
hormones - Zanichelli
... Cushing syndrome is caused by a disfunction of the adrenal cortex and is characterized by a tendency toward diabetes mellitus, subcutaneous fat accumulation in the trunk and a moon-shape face. The thyroid regulates development and increases the ...
... Cushing syndrome is caused by a disfunction of the adrenal cortex and is characterized by a tendency toward diabetes mellitus, subcutaneous fat accumulation in the trunk and a moon-shape face. The thyroid regulates development and increases the ...
Ch41_Endocrine Function - University of Perpetual Help System
... Hormones that are released into the bloodstream circulate as either free, unbound molecules or as hormones attached to transport carriers (Fig. 41-1). Peptide hormones and protein hormones usually circulate unbound in the blood. Steroid hormones and thyroid hormone are carried by specific carrier pro ...
... Hormones that are released into the bloodstream circulate as either free, unbound molecules or as hormones attached to transport carriers (Fig. 41-1). Peptide hormones and protein hormones usually circulate unbound in the blood. Steroid hormones and thyroid hormone are carried by specific carrier pro ...
PDF - the Houpt Lab
... Negative Feedback of Cortisol onto Hypothalamus and Pituitary • Cortisol levels are controlled by negative feedback loop of HPA. • High Cortisol levels in the blood act on GC receptors in the hypothalamus and pituitary to decrease CRH & ACTH synthesis and release • If cortisol synthesis is blocked ( ...
... Negative Feedback of Cortisol onto Hypothalamus and Pituitary • Cortisol levels are controlled by negative feedback loop of HPA. • High Cortisol levels in the blood act on GC receptors in the hypothalamus and pituitary to decrease CRH & ACTH synthesis and release • If cortisol synthesis is blocked ( ...
21 Endocrine 10a
... • The functional unit of the thyroid gland is the thyroid follicle. • The cells making up the perimeter of the follicle are called follicular cells. They make and secrete the light purple liquid within the follicle, called colloid. Colloid is water, filled with a lot of protein called thyroglobulin, ...
... • The functional unit of the thyroid gland is the thyroid follicle. • The cells making up the perimeter of the follicle are called follicular cells. They make and secrete the light purple liquid within the follicle, called colloid. Colloid is water, filled with a lot of protein called thyroglobulin, ...
Endocrine PPT
... • The functional unit of the thyroid gland is the thyroid follicle. • The cells making up the perimeter of the follicle are called follicular cells. They make and secrete the light purple liquid within the follicle, called colloid. Colloid is water, filled with a lot of protein called thyroglobulin, ...
... • The functional unit of the thyroid gland is the thyroid follicle. • The cells making up the perimeter of the follicle are called follicular cells. They make and secrete the light purple liquid within the follicle, called colloid. Colloid is water, filled with a lot of protein called thyroglobulin, ...
140 Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland
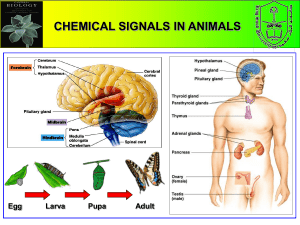
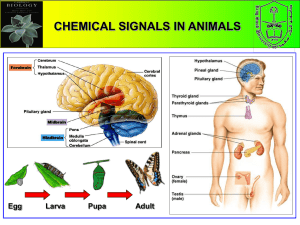
... An axis of signaling between the hypothalamus, pituitary, and an endocrine gland regulates the secretion of some hormones. An endocrine axis is a group of endocrine glands that signal to one another in sequential order. In an endocrine axis, the hypothalamus secretes releasing hormones that induce t ...
... An axis of signaling between the hypothalamus, pituitary, and an endocrine gland regulates the secretion of some hormones. An endocrine axis is a group of endocrine glands that signal to one another in sequential order. In an endocrine axis, the hypothalamus secretes releasing hormones that induce t ...
endocrine system
... trauma, and infection. It keeps the blood protein and glucose levels high enough to support the brain’s activities and affects the metabolic rate. When the brain perceives a stressful situation, the hypothalamus tells the pituitary to secrete ACTH, which travels to the adrenal gland and signals it t ...
... trauma, and infection. It keeps the blood protein and glucose levels high enough to support the brain’s activities and affects the metabolic rate. When the brain perceives a stressful situation, the hypothalamus tells the pituitary to secrete ACTH, which travels to the adrenal gland and signals it t ...
UNIT 16 Alterations in Endocrine Function
... hypothalamus and anterior pituitary are joined by a portal system. The hypothalamus releases hormones into this system, which then regulates the release of anterior pituitary hormones. Some stimulate release whereas others inhibit this release. The relationship between the hypothalamus and posterior ...
... hypothalamus and anterior pituitary are joined by a portal system. The hypothalamus releases hormones into this system, which then regulates the release of anterior pituitary hormones. Some stimulate release whereas others inhibit this release. The relationship between the hypothalamus and posterior ...
UNIT 16 Alterations in Endocrine Function
... hypothalamus and anterior pituitary are joined by a portal system. The hypothalamus releases hormones into this system, which then regulates the release of anterior pituitary hormones. Some stimulate release whereas others inhibit this release. The relationship between the hypothalamus and posterior ...
... hypothalamus and anterior pituitary are joined by a portal system. The hypothalamus releases hormones into this system, which then regulates the release of anterior pituitary hormones. Some stimulate release whereas others inhibit this release. The relationship between the hypothalamus and posterior ...
topic13 - Bukowian metodyczka - misiek-puchatek
... impulses transmitted to the central nervous system stimulate the hypothalamus to manufacture and release several releasing or inhibiting factors. These substances are transferred to the anterior pituitary gland, where they lead to the release of certain tropic hormones. Control of the endocrine syst ...
... impulses transmitted to the central nervous system stimulate the hypothalamus to manufacture and release several releasing or inhibiting factors. These substances are transferred to the anterior pituitary gland, where they lead to the release of certain tropic hormones. Control of the endocrine syst ...
Frank MacDonald RN, MN - University of Calgary
... hypothalamus and anterior pituitary are joined by a portal system. The hypothalamus releases hormones into this system, which then regulates the release of anterior pituitary hormones. Some stimulate release whereas others inhibit this release. The relationship between the hypothalamus and posterior ...
... hypothalamus and anterior pituitary are joined by a portal system. The hypothalamus releases hormones into this system, which then regulates the release of anterior pituitary hormones. Some stimulate release whereas others inhibit this release. The relationship between the hypothalamus and posterior ...
Endocrine System
... pituitary gland by producing chemicals that either stimulate or suppress hormone secretions from the pituitary. • Posterior Pituitary Gland - It is responsible for a function of the pituitary gland which releases the oxytocin hormone. This hormone is required after distension of the cervix and the v ...
... pituitary gland by producing chemicals that either stimulate or suppress hormone secretions from the pituitary. • Posterior Pituitary Gland - It is responsible for a function of the pituitary gland which releases the oxytocin hormone. This hormone is required after distension of the cervix and the v ...
139 Endocrine System
... development of secondary sex characteristics in both males and females (Figure 2). GnRH stimulates the anterior pituitary to release two gonadotropins, luteinizing hormone (LH) and folliclestimulating hormone (FSH). Gonadotropins are peptide hormones that target the gonads. In males, these hormones ...
... development of secondary sex characteristics in both males and females (Figure 2). GnRH stimulates the anterior pituitary to release two gonadotropins, luteinizing hormone (LH) and folliclestimulating hormone (FSH). Gonadotropins are peptide hormones that target the gonads. In males, these hormones ...
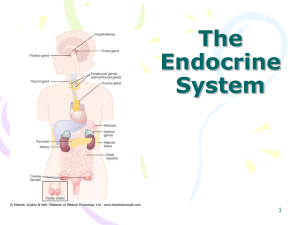
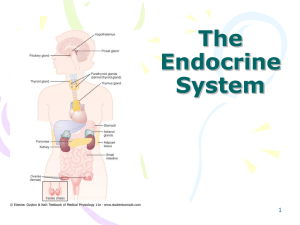
Lecture 4: Endocrine System
... immune system to shrink. In this experiment, the thymus gland will represent the organs of the immune system. ...
... immune system to shrink. In this experiment, the thymus gland will represent the organs of the immune system. ...
Document
... • 3 types of regulatory molecules: • 1) Hormones: regulatory chemicals secreted into blood by endocrine gland – Work only on ____________ cells (those that can be influenced by its “message”) ...
... • 3 types of regulatory molecules: • 1) Hormones: regulatory chemicals secreted into blood by endocrine gland – Work only on ____________ cells (those that can be influenced by its “message”) ...
13. Name the hormones and their functions that are secreted from
... dwarfs are all a result of too much or too little growth hormone. Which gland secretes this? ...
... dwarfs are all a result of too much or too little growth hormone. Which gland secretes this? ...
hormones
... Function and Secretion • Hormones are substances secreted by cells that act to regulate the activity of other cells in the body. – Hormones affect all cells in the body and are made and secreted by endocrine glands. • Endocrine glands are ductless organs that secret hormones either into the bloodst ...
... Function and Secretion • Hormones are substances secreted by cells that act to regulate the activity of other cells in the body. – Hormones affect all cells in the body and are made and secreted by endocrine glands. • Endocrine glands are ductless organs that secret hormones either into the bloodst ...
Slide 1
... Function and Secretion • Hormones are substances secreted by cells that act to regulate the activity of other cells in the body. – Hormones affect all cells in the body and are made and secreted by endocrine glands. • Endocrine glands are ductless organs that secret hormones either into the bloodst ...
... Function and Secretion • Hormones are substances secreted by cells that act to regulate the activity of other cells in the body. – Hormones affect all cells in the body and are made and secreted by endocrine glands. • Endocrine glands are ductless organs that secret hormones either into the bloodst ...
Document
... Effect on active mammary glands: Stimulation of teat/nipple by nursing or milking causes oxytocin release into bloodstream Causes contraction of musclelike myoepithelial cells around mammary gland alveoli and small ducts Forces milk into lower parts of gland, making it accessible for nursing/m ...
... Effect on active mammary glands: Stimulation of teat/nipple by nursing or milking causes oxytocin release into bloodstream Causes contraction of musclelike myoepithelial cells around mammary gland alveoli and small ducts Forces milk into lower parts of gland, making it accessible for nursing/m ...
pituitary gland - Biology Notes Help
... The pituitary ,a pea sized gland at the base produces a number of hormones, each of which specific part of the body (a target organ or the pituitary controls the functions of most glands. ...
... The pituitary ,a pea sized gland at the base produces a number of hormones, each of which specific part of the body (a target organ or the pituitary controls the functions of most glands. ...