* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Hormonal contraception wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Cryptorchidism wikipedia , lookup
Bovine somatotropin wikipedia , lookup
Polycystic ovary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
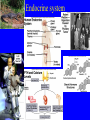
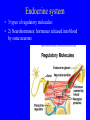
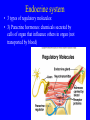
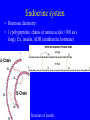
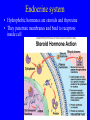
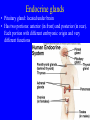
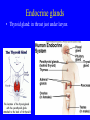
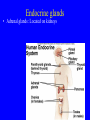
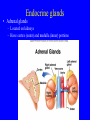
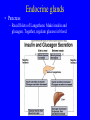
Endocrine system Endocrine system • 3 types of regulatory molecules: • 1) Hormones: regulatory chemicals secreted into blood by endocrine gland – Work only on ____________ cells (those that can be influenced by its “message”) Endocrine system • 3 types of regulatory molecules: • 2) Neurohormones: hormones released into blood by some neurons Endocrine system • 3 types of regulatory molecules: • 3) Paracrine hormones: chemicals secreted by cells of organ that influence others in organ (not transported by blood) Endocrine system 3) Paracrine hormones. Example: prostaglandins. Derived from cholesterol • Many functions: one is to promote inflammation (pain, fever) • Aspirin, ibuprofen, celebrex: inhibit prostaglandin production but vary in side effects (some can cause _____________ in small intestine, etc) Endocrine system • Hormone chemistry: • 1) polypeptides: chains of amino acids (<100 aa’s long). Ex, insulin, ADH (antidiuretic hormone) Structure of insulin Endocrine system • Hormone chemistry: • 2) glycoproteins: long polypeptide (>100 aa’s long) with carbohydrate attached. Ex, FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) and luteinizing hormone (LH) Endocrine system • Hormone chemistry: • 3) amines: variations of the amino acids tyrosine and tryptophan. Ex, adrenalin, thyroxine. tyrosine tyramine tryptophan adrenaline Endocrine system • Hormone chemistry: • 4) steroids: lipids derived from cholesterol. Ex, testosterone, estradiol, progesterone cholesterol Endocrine system • Most hormones are hydrophilic (water soluble) • Recall from BIOL 1020 that cell membranes are hydrophobic • This means that water-soluble molecules can’t cross them. • How signal transmitted into cells? By __________ protein in membrane Endocrine system • Hydrophilic hormone example • Hormone binding temporary, detaches and can travel to another cell and bind again (and again) • 1 hormone molecule can signal many ________! Endocrine system • Hydrophobic hormones are steroids and thyroxine • They penetrate membranes and bind to receptors inside cell Endocrine system • Example hydrophobic hormones are steroids (testosterone, estradiol) and thyroxine Endocrine glands • Pituitary gland: located under brain • Has two portions: anterior (in front) and posterior (in rear). Each portion with different embryonic origin and very different functions Endocrine glands • Posterior pituitary gland hormones – Antidiuretic hormone (ADH): influences water reabsorption in kidneys. – Note: alcohol consumption inhibits ADH secretion (so frequent need to _______________). Endocrine glands • Posterior pituitary gland hormones – Oxytocin: stimulates milk “let-down” in nursing mothers (milk secreted into ducts in breast). Also stimulates uterine contractions during childbirth. Endocrine glands • Anterior pituitary gland hormones – growth hormone (GH): stimulates growth of bone and muscle – Too much: gigantism 8 feet 11 inches, 485 pounds. Lived 22 years, never stopped growing! Endocrine glands • Anterior pituitary gland hormones – growth hormone (GH): stimulates growth of bone and muscle – Too little: pituitary dwarfism Endocrine glands Anterior pituitary gland hormones – follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH): involved in menstrual cycle in females and sperm production in males Endocrine glands Anterior pituitary gland hormones – follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH): involved in menstrual cycle in females and sperm production in males – prolactin (PRL): stimulates milk production in mammals Endocrine glands • Thyroid gland: in throat just under larynx Endocrine glands • Thyroid gland hormone (main): – Thyroxine: helps set body’s metabolic rate – Too little: ______________. Often severe retardation. Endocrine glands • Parathyroid glands: On thyroid – Make parathyroid hormone (PTH): vital to maintain Ca+2 level in body – Can influence Ca+2 reabsorption in kidney, Ca+2 release from bone, and absorption of Ca+2 in small intestine. Endocrine glands • Adrenal glands: Located on kidneys Endocrine glands • Adrenal glands – Located on kidneys – Have cortex (outer) and medulla (inner) portions Endocrine glands • Adrenal glands – Medulla: secretes ______________ when stimulated by nerve system. Part of “fight or flight” response. Increase heart rate, blood pressure, blood glucose. Reduced blood flow to skin and digestive system Endocrine glands • Adrenal glands – Cortex: secretes corticosteroids. Involved in _________ balance, glucose balance, etc. Endocrine glands • Pancreas – Located below liver in abdomen Endocrine glands • Pancreas – Recall Islets of Langerhans. Make insulin and glucagon. Together, regulate glucose in blood. Endocrine glands • Gonads (testes and ovaries) Endocrine glands • Gonads (testes and ovaries) • Make steroid sex hormones • Testosterone, estradiol, progesterone (discussed) Endocrine disruptors • Chemicals from environment that can interfere with endocrine system • Chemical structures similar to those of some hormones • Examples: pesticides, herbicides, etc. Endocrine disruptors • Ex, Lake Apopka, Florida • 1980: chemical spill of pesticide DDT • Affected development of male alligators (lower testosterone levels, smaller __________ size, anatomical defects) Endocrine disruptors • Human concerns: • Puberty of females coming earlier • Many possible causes, but endocrine disruptors may be involved Endocrine disruptors • • • • • Ex, Michigan 1973 Chemical called PBB accidentally mixed into cattle food Meat and dairy products reached 4,000 people Daughters of women exposed surveyed in late 1990s Menstruation started ______ years earlier in daughters of exposed women