Direct stimulation from the nervous system
... quickly be released after the hypothalamus is stimulated to send out ACTH- releasing factor to the anterior pituitary via the portal system Mosby items and derived items © 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. ...
... quickly be released after the hypothalamus is stimulated to send out ACTH- releasing factor to the anterior pituitary via the portal system Mosby items and derived items © 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. ...
Endocrine System - El Camino College
... Neural – nerve impulses stimulate adrenal medulla to secrete Epinephrine Hormonal – hormones of hypothalamus stimulate anterior pituitary body to secrete its hormones. Hypothalamus Hypothalamus regulates hormone secretion by other endocrine glands by 3 mechanisms. It secretes hormones to regulate an ...
... Neural – nerve impulses stimulate adrenal medulla to secrete Epinephrine Hormonal – hormones of hypothalamus stimulate anterior pituitary body to secrete its hormones. Hypothalamus Hypothalamus regulates hormone secretion by other endocrine glands by 3 mechanisms. It secretes hormones to regulate an ...
Glands - cloudfront.net
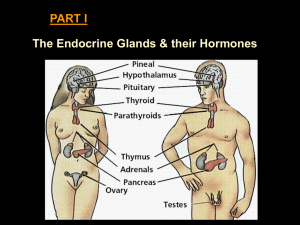
... Other glands of the endocrine system are described below. You can refer to Figure 1.1 to see where they are located. • The thyroid gland is a large gland in the neck. Thyroid hormones increase the rate of metabolism in cells throughout the body. They control how quickly cells use energy and make pro ...
... Other glands of the endocrine system are described below. You can refer to Figure 1.1 to see where they are located. • The thyroid gland is a large gland in the neck. Thyroid hormones increase the rate of metabolism in cells throughout the body. They control how quickly cells use energy and make pro ...
The Endocrine System
... Other glands of the endocrine system are described below. You can refer to Figure 1.1 to see where they are located. • The thyroid gland is a large gland in the neck. Thyroid hormones increase the rate of metabolism in cells throughout the body. They control how quickly cells use energy and make pro ...
... Other glands of the endocrine system are described below. You can refer to Figure 1.1 to see where they are located. • The thyroid gland is a large gland in the neck. Thyroid hormones increase the rate of metabolism in cells throughout the body. They control how quickly cells use energy and make pro ...
What is the Endocrine System
... potassium by the kidneys. It plays an important role in maintaining normal sodium and potassium concentrations in blood and in controlling blood volume and blood pressure. Aldosterone is produced by the adrenal cortex, the outer portion of the adrenal glands located at the top of each kidney. Its pr ...
... potassium by the kidneys. It plays an important role in maintaining normal sodium and potassium concentrations in blood and in controlling blood volume and blood pressure. Aldosterone is produced by the adrenal cortex, the outer portion of the adrenal glands located at the top of each kidney. Its pr ...
Endocrine Virtual Lab! AP Biology
... amount of hormone has been released, it communicates or ‘‘feeds back’’ to suppress the releasing organ. In other words, the gland has released enough hormone to fulfill its function; this is sensed by the body, and production of the hormone ceases. Negative feedback not only inhibits the releasing o ...
... amount of hormone has been released, it communicates or ‘‘feeds back’’ to suppress the releasing organ. In other words, the gland has released enough hormone to fulfill its function; this is sensed by the body, and production of the hormone ceases. Negative feedback not only inhibits the releasing o ...
Endokrin Sistem - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... Role : In both sexes, promotes the development of reproductive cells (gametes) and promotes secretion of gonadal hormones Males : stimulates sperm production Females : stimulates growth of primary follicle of ovary ...
... Role : In both sexes, promotes the development of reproductive cells (gametes) and promotes secretion of gonadal hormones Males : stimulates sperm production Females : stimulates growth of primary follicle of ovary ...
The Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland
... brain focus in on socially relevant sensory input. It also is becoming clear that oxytocin often does not work alone but requires other permissive or synergistic neurotransmitters, like serotonin or ADH, which may be why some oxytocin-only clinical trials have had limited results. ...
... brain focus in on socially relevant sensory input. It also is becoming clear that oxytocin often does not work alone but requires other permissive or synergistic neurotransmitters, like serotonin or ADH, which may be why some oxytocin-only clinical trials have had limited results. ...
growth hormone (GH)
... a glucocorticoid hormone secreted by the adrenal cortex that increases the use of fat and excess amino acids for energy; causes the “glucose sparing effect” during times of physiological stress. depressants a type of drug which decreases the likelihood of neuron excitation by impacting on the limbic ...
... a glucocorticoid hormone secreted by the adrenal cortex that increases the use of fat and excess amino acids for energy; causes the “glucose sparing effect” during times of physiological stress. depressants a type of drug which decreases the likelihood of neuron excitation by impacting on the limbic ...
Chapter 9 Endocrine System
... antidiuretic hormone (ADH) – inhibits diuresis (prevents excess water excretion by the kidneys) Ethanol inhibits release of ADH, which leads to urination and dry mouth. Diuretics interfere with the production of ADH. Prescribed to lower blood pressure by decreasing blood volume. oxytocin – contracts ...
... antidiuretic hormone (ADH) – inhibits diuresis (prevents excess water excretion by the kidneys) Ethanol inhibits release of ADH, which leads to urination and dry mouth. Diuretics interfere with the production of ADH. Prescribed to lower blood pressure by decreasing blood volume. oxytocin – contracts ...
Endocrine Anatomy and Physiology
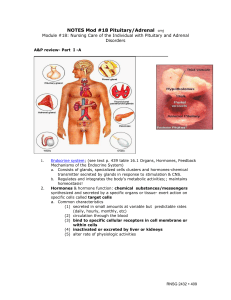
... There are five major endocrine organs in the body: the hypothalamus, the pituitary, the adrenal glands, the thyroid gland, and the pancreas. Other organs have endocrine functions as well, but will not be covered in this article. Endocrine organs secrete hormones that act on specific “target tissu ...
... There are five major endocrine organs in the body: the hypothalamus, the pituitary, the adrenal glands, the thyroid gland, and the pancreas. Other organs have endocrine functions as well, but will not be covered in this article. Endocrine organs secrete hormones that act on specific “target tissu ...
Pituitary Hormones and Their Control by the Hypothalamus
... the median eminence before being transported to the anterior pituitary gland . Electrical stimulation of this region excites these nerves endings , and therefore causes release of essentially all the hypothalamic hormones however the neuronal cell bodies that give rise to these median eminence nerve ...
... the median eminence before being transported to the anterior pituitary gland . Electrical stimulation of this region excites these nerves endings , and therefore causes release of essentially all the hypothalamic hormones however the neuronal cell bodies that give rise to these median eminence nerve ...
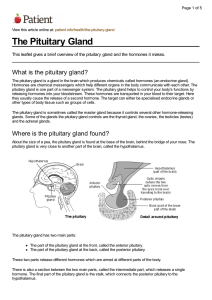
The Pituitary Gland
... Triggers ovulation - the release of an egg (ovum) ready for fertilisation. Stimulates cells in the testes to produce testosterone ...
... Triggers ovulation - the release of an egg (ovum) ready for fertilisation. Stimulates cells in the testes to produce testosterone ...
21 Endocrine
... the brain’s activities and affects the metabolic rate. When the brain perceives a stressful situation, the hypothalamus tells the pituitary to secrete ACTH, which travels to the adrenal gland and signals it to release cortisol to most of the cells of the body. ...
... the brain’s activities and affects the metabolic rate. When the brain perceives a stressful situation, the hypothalamus tells the pituitary to secrete ACTH, which travels to the adrenal gland and signals it to release cortisol to most of the cells of the body. ...
Introduction to the Hypothalamo- Pituitary
... There are several other characteristics of this system worth mentioning. The short portal veins could enable reverse flow from the anterior pituitary to the posterior pituitary. This would result in a direct communication between the anterior pituitary and the hypothalamus via reverse axonal transpor ...
... There are several other characteristics of this system worth mentioning. The short portal veins could enable reverse flow from the anterior pituitary to the posterior pituitary. This would result in a direct communication between the anterior pituitary and the hypothalamus via reverse axonal transpor ...
Hypothalamic and Pituitary Hormones
... stimulate the growth, nutrition and function of : • other endocrine glands • TSH : regulates Thyroid gland secretion • ACTH : controls secretion of Adrenal Cortex • FSH : maintains female sex hormones level and follicle growth • LH : regulates Testosterone and secondary sex characters ...
... stimulate the growth, nutrition and function of : • other endocrine glands • TSH : regulates Thyroid gland secretion • ACTH : controls secretion of Adrenal Cortex • FSH : maintains female sex hormones level and follicle growth • LH : regulates Testosterone and secondary sex characters ...
Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 10: Endocrine System
... (2) Hormones. The hormones of the endocrine system serve to control the tissues and organs in general. (Vitamins have a similar role.) Both hormones and vitamins are chemical substances required only in small quantities. (3) Nervous system. More precise and immediate control of the structures of the ...
... (2) Hormones. The hormones of the endocrine system serve to control the tissues and organs in general. (Vitamins have a similar role.) Both hormones and vitamins are chemical substances required only in small quantities. (3) Nervous system. More precise and immediate control of the structures of the ...
The Endocrine System - healingenergies-at
... cells communicate with each other is by chemical signals. The chemical signals are carried in the blood stream to the cells which they act upon by molecules called hormones. These hormones are produced by a number of glands and other body organs which collectively form the endocrine system. Hormones ...
... cells communicate with each other is by chemical signals. The chemical signals are carried in the blood stream to the cells which they act upon by molecules called hormones. These hormones are produced by a number of glands and other body organs which collectively form the endocrine system. Hormones ...
Antidiuretic Hormone
... • Chemical messengers produced by endocrine glands • Absorbed into blood vessels and will contact all cells of the body. ...
... • Chemical messengers produced by endocrine glands • Absorbed into blood vessels and will contact all cells of the body. ...
1. overview of the endocrine system
... potential to grown. The growth hormone stimulates the increase in size, proliferation and differentiation of cells. It also increases the cellular uptake of amino acids to form proteins, whereas it restricts the use of glucose for energy supply. It also increases the mobilization of fatty acids rele ...
... potential to grown. The growth hormone stimulates the increase in size, proliferation and differentiation of cells. It also increases the cellular uptake of amino acids to form proteins, whereas it restricts the use of glucose for energy supply. It also increases the mobilization of fatty acids rele ...
Notes - Austin Community College
... of hypothalamus: composed mostly of axons of hypothalamic neurons-extend downward as large bundle behind anterior pituitarylso forms so-called pituitary stalk-appears to suspend anterior gland from hypothalamus. 3) intermediate (pars intermedia) *secretes MSH (melanocytes for skin pigmentation ...
... of hypothalamus: composed mostly of axons of hypothalamic neurons-extend downward as large bundle behind anterior pituitarylso forms so-called pituitary stalk-appears to suspend anterior gland from hypothalamus. 3) intermediate (pars intermedia) *secretes MSH (melanocytes for skin pigmentation ...
Ch.V-2 GalactopoiesisHormone
... However, timing of inhibition of milk yield in cattle coincides approximately with the period of increasing placentally-derived plasma estrogen ...
... However, timing of inhibition of milk yield in cattle coincides approximately with the period of increasing placentally-derived plasma estrogen ...
Chapter 6 The endocrine system
... Growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH) AP growth hormone (GH) Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) 體介素 & regulates growth and energy metabolism ...
... Growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH) AP growth hormone (GH) Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) 體介素 & regulates growth and energy metabolism ...
Chapter 6
... Growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH) AP growth hormone (GH) Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) 體介素 & regulates growth and energy metabolism ...
... Growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH) AP growth hormone (GH) Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) 體介素 & regulates growth and energy metabolism ...
hormones
... The sex and the form of a developing fetus are affected by events that take place in the woman's womb. Even though a fetus's sex is determined genetically, the proper hormones must be available for the fetus to develop the appropriate sex organs. Its gonads are fairly inactive at birth, but gradual ...
... The sex and the form of a developing fetus are affected by events that take place in the woman's womb. Even though a fetus's sex is determined genetically, the proper hormones must be available for the fetus to develop the appropriate sex organs. Its gonads are fairly inactive at birth, but gradual ...