* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Antidiuretic Hormone
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Adrenal gland wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
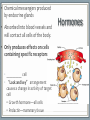
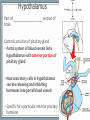
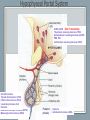
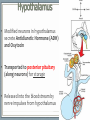
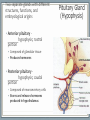
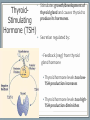
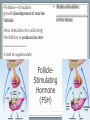
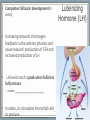
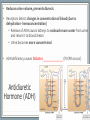
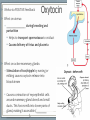
Endocrine System Mosby items and derived items © 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Endocrine System • Primary function: produce ____________ • Works together with ______________ system to maintain homeostasis. • Hormones act on specific target cells to produce specific effects • No _________, use circulatory system. Mosby items and derived items © 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Endocrine System vs. Nervous System Characteristic Endocrine System Nervous System General Function Maintain homeostasis Maintain homeostasis Reaction to stimuli slow rapid Duration of effect long short Target tissues throughout body muscles and glands Chemical messenger hormone neurotransmitter Messenger producing cell endocrine gland neurons Distance to target cells long (via bloodstream) short (across synaptic space) Mosby items and derived items © 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Exocrine/Endocrine Glands Gland Exocrine Pancreas Ovary Testes Kidney digestive enzymes egg sperm urine Endocrine insulin, glucagon estrogen, progesterone testosterone erythropoietin Mosby items and derived items © 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. • Chemical messengers produced by endocrine glands • Absorbed into blood vessels and will contact all cells of the body. Hormones • Only produces effects on cells containing specific receptors • __________ cell • ‘Lock and key’ arrangement causes a change in activity of target cell • Growth hormone—all cells • Prolactin—mammary tissue Mosby items and derived items © 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Control of Hormone Secretion ___________ feedback systems (like a thermostat) • If hormone level is low: •Appropriate endocrine gland is stimulated to produce more hormone • Once adequate hormone concentration is attained in the bloodstream: •Stimulation of endocrine gland is reduced and production of the hormone is stopped/reduced Mosby items and derived items © 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Hypothalamus • Part of ___________________ section of brain • Controls activities of pituitary gland Portal system of blood vessels links hypothalamus with anterior portion of pituitary gland •Neurosecretory cells in hypothalamus secrete releasing and inhibiting hormones into portal blood vessels •Specific for a particular anterior pituitary hormone Mosby items and derived items © 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Hypophyseal Portal System GHRH, GHIH (Don’t memorize) Thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) Gonadaotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) PRH, PIH Corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH) Growth hormone Thyroid stim hormone (TSH) Follicle stim hormone (FSH) Luteinizing hormone (LH) Prolactin Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) Melanocyte stim hormone (MSH) Posterior pituitary Oxytocin Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) Mosby items and derived items © 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Hypothalamus • Modified neurons in hypothalamus secrete Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) and Oxytocin • Transported to posterior pituitary (along neurons) for storage • Released into the bloodstream by nerve impulses from hypothalamus Mosby items and derived items © 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. • Two separate glands with different structures, functions, and embryological origins Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis) •Anterior pituitary _______hypophysis; rostral portion • Composed of glandular tissue • Produces hormones •Posterior pituitary _______hypophysis; caudal portion • Composed of neurosecretory cells • Stores and releases hormones produced in hypothalamus Rostral Caudal Mosby items and derived items © 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. HORMONES MADE BY THE ANTERIOR PITUITARY Mosby items and derived items © 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Growth Hormone (GH) • Promotes bone and muscle growth in young animals, but targets all cells of the body. • Helps regulate metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids in animals of all ages. • Proteins are synthesized via _______bolism • Lipids are released from storage and go through _______bolism for energy use by the body. • Since GH promotes the use of lipids for energy, glucose accumulates in the blood. This is known as the hyperglycemic effect. • It is important for the animal to have normal production of ____________ by the pancreas to counteract the hyperglycemia Mosby items and derived items © 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Prolactin • Helps trigger and maintain _____________ in females • Secretion of milk by mammary glands • Prolactin production continues as long as the animal is stimulated by nursing or milking 1. Baby sucks/stimulates 2. ↓PIH, ↑PRH 3-4. Stimulates milk glands • When prolactin stimulation stops: • Milk production stops • Mammary gland shrinks to nonlactatingMosby size items and derived items © 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. ThyroidStimulating Hormone (TSH) • Stimulates growth/development of thyroid gland and causes thyroid to produce its hormones. • Secretion regulated by: •Feedback (neg) from thyroid gland hormone •Thyroid hormone levels too lowTSH production increases •Thyroid hormone levels too highTSH production diminishes Mosby items and derived items © 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. • Stimulates growth/development of adrenal cortex and the release of its hormones • Regulated by levels of cortisol: Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) •When low or patient is stressed, the hypothalamus will produce CRF which causes anterior pituitary to release ACTH •When elevated, negative feedback will cause CRF and ACTH levels to be reduced. • NOTE: administering steriods that mimic the effects of cortisol (ex: prednisone, dexamethasome) can also cause negative feedback Mosby items and derived items © 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. •Females—stimulates growth/development of ovarian follicles • Males- stimulates ____________________ in the testes •Also stimulates the cells lining the follicles to produce/secrete _______________ •Used to superovulate FollicleStimulating Hormone (FSH) Mosby items and derived items © 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. • Completes follicular development in ovary Luteinizing Hormone (LH) • Increasing amounts of estrogen feedback to the anterior pituitary and cause reduced production of FSH and increased production of LH • LH levels reach a peak when follicle is fully mature • causes _______________________ • In males, LH stimulates interstitial cells to produce ___________________ Mosby items and derived items © 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. HORMONES STORED BY THE POSTERIOR PITUITARY Mosby items and derived items © 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. • Reduces urine volume, prevents diuresis • Receptors detect changes in concentration of blood (due to dehydration - hemoconcentration) • Release of ADH causes kidneys to reabsorb more water from urine and return it to bloodstream • Urine becomes more concentrated • ADH deficiency causes Diabetes ______________ (PU/PD occurs) Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) Mosby items and derived items © 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. ► Works via POSITIVE feedback Oxytocin ► Effect on uterus: • _______________ during breeding and parturition Helps to transport spermatozoa to oviduct Causes delivery of fetus and placenta ► Effect on active mammary glands: • Stimulation of teat/nipple by nursing or milking causes oxytocin release into bloodstream Causes contraction of myoepithelial cells around mammary gland alveoli and small ducts. This forces milk into lower parts of gland, making it accessible (________ Mosby items and derived items © 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. __________________).