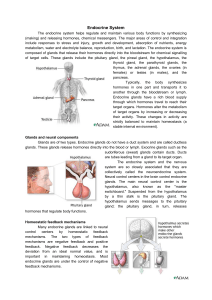
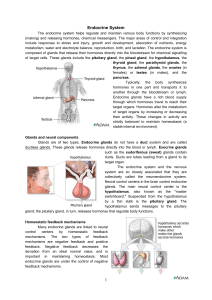
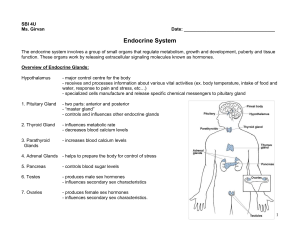
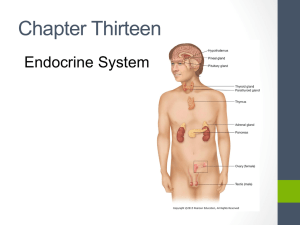
Endocrine System
... 1. Nervous system uses physical structures for communication 2. Endocrine system uses body fluids to transport messages (hormones) a. referred to as humeral versus neural control II. Hormones A. Classically, hormones are defined as chemical substances produced by ductless glands and secreted into th ...
... 1. Nervous system uses physical structures for communication 2. Endocrine system uses body fluids to transport messages (hormones) a. referred to as humeral versus neural control II. Hormones A. Classically, hormones are defined as chemical substances produced by ductless glands and secreted into th ...
Endocrine System
... do not require continuous adjustment. In positive feedback mechanisms, the original stimulus is promoted rather than negated. Positive feedback increases the deviation from an ideal normal value. Unlike negative feedback that maintains hormone levels within narrow ranges, positive feedback is rarely ...
... do not require continuous adjustment. In positive feedback mechanisms, the original stimulus is promoted rather than negated. Positive feedback increases the deviation from an ideal normal value. Unlike negative feedback that maintains hormone levels within narrow ranges, positive feedback is rarely ...
Endocrine System
... do not require continuous adjustment. In positive feedback mechanisms, the original stimulus is promoted rather than negated. Positive feedback increases the deviation from an ideal normal value. Unlike negative feedback that maintains hormone levels within narrow ranges, positive feedback is rarely ...
... do not require continuous adjustment. In positive feedback mechanisms, the original stimulus is promoted rather than negated. Positive feedback increases the deviation from an ideal normal value. Unlike negative feedback that maintains hormone levels within narrow ranges, positive feedback is rarely ...
Endocrine System booklet
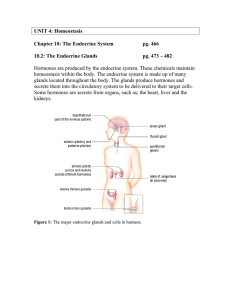
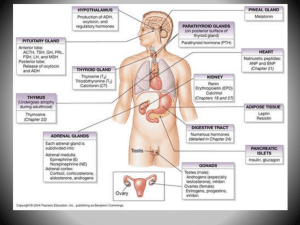
... Endocrine System The endocrine system involves a group of small organs that regulate metabolism, growth and development, puberty and tissue function. These organs work by releasing extracellular signaling molecules known as hormones. Overview of Endocrine Glands: Hypothalamus ...
... Endocrine System The endocrine system involves a group of small organs that regulate metabolism, growth and development, puberty and tissue function. These organs work by releasing extracellular signaling molecules known as hormones. Overview of Endocrine Glands: Hypothalamus ...
The Endocrine System
... C. Endothelin and bradykinin are paracrine molecules that are used in the circulatory system for control of vessel constriction and dilation. D. Paracrine molecules are released directly into the circulatory system. E. Nerve growth factor, platelet-growth factor, and insulin-like growth factor are s ...
... C. Endothelin and bradykinin are paracrine molecules that are used in the circulatory system for control of vessel constriction and dilation. D. Paracrine molecules are released directly into the circulatory system. E. Nerve growth factor, platelet-growth factor, and insulin-like growth factor are s ...
The Endocrine System
... Anterior Pituitary III Follicle-Stimulating Hormone • stimulates development of ova and estrogen production in ovaries; stimulates sperm production Lutenizing Hormone • stimulates ovulation and prepares uterus for possible implantation of fertilized ovum; stimulates the production of testosterone ...
... Anterior Pituitary III Follicle-Stimulating Hormone • stimulates development of ova and estrogen production in ovaries; stimulates sperm production Lutenizing Hormone • stimulates ovulation and prepares uterus for possible implantation of fertilized ovum; stimulates the production of testosterone ...
Principles of Endocrinology
... • neuroendocrine reflex - hormone release in response to nervous system signals • suckling infant stimulates nerve endings hypothalamus posterior lobe oxytocin milk ejection ...
... • neuroendocrine reflex - hormone release in response to nervous system signals • suckling infant stimulates nerve endings hypothalamus posterior lobe oxytocin milk ejection ...
chapter 16-the endocrine system
... a. Somatotrophic Hormone (STH)-regulates the growth of the skeleton. It is regulated by the hypothalamus via Growth Hormone Releasing. Factor and Growth Hormone Inhibiting Factor. This is also known as Human Growth Hormone. 1) What is gigantism? 2) What is acromegaly? 3) What is pituitary dwarfism? ...
... a. Somatotrophic Hormone (STH)-regulates the growth of the skeleton. It is regulated by the hypothalamus via Growth Hormone Releasing. Factor and Growth Hormone Inhibiting Factor. This is also known as Human Growth Hormone. 1) What is gigantism? 2) What is acromegaly? 3) What is pituitary dwarfism? ...
Dr. AASHISH H. PANCHAL (M.PHARM., Ph.D.) GSEB, CBSE, ICSE
... 3) The main function of thyroid gland is to control :(A) Growth (B) Reproduction (C) Secondary sexual characters (D) Basal metabolic rate 4) The two lobes of thyroid gland are joined by a horizontal connection called :(A) Inter thyroidal connective (B) Inter thyroidal commissure (C) Interme diary lo ...
... 3) The main function of thyroid gland is to control :(A) Growth (B) Reproduction (C) Secondary sexual characters (D) Basal metabolic rate 4) The two lobes of thyroid gland are joined by a horizontal connection called :(A) Inter thyroidal connective (B) Inter thyroidal commissure (C) Interme diary lo ...
Chemical messengers - Our eclass community
... 3. Are either proteins, amines (small molecules derived from amino acids) or steroids (derived ...
... 3. Are either proteins, amines (small molecules derived from amino acids) or steroids (derived ...
Endocrinology
... the blood stream or lymph, Their production called hormones which they have either stimulating or inhibitor effects upon the development or function of the body organs. There is no anatomical continuity between these glands, except on a physiological level. Note: Not all ductless organs are endocrin ...
... the blood stream or lymph, Their production called hormones which they have either stimulating or inhibitor effects upon the development or function of the body organs. There is no anatomical continuity between these glands, except on a physiological level. Note: Not all ductless organs are endocrin ...
Objectives Endocrine System
... influence metabolic activities, growth, and development. Maintenance of homeostasis through feedback loops.. ...
... influence metabolic activities, growth, and development. Maintenance of homeostasis through feedback loops.. ...
File - Anatomy & Physiology
... body’s activities (but still controlled by the hypothalamus) • Size of a grape • Connected to hypothalamus by a stalk called infundibulum • Consists of two distinct portions: • Anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis) – hormonally controlled • Posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis)- neurally controlled ...
... body’s activities (but still controlled by the hypothalamus) • Size of a grape • Connected to hypothalamus by a stalk called infundibulum • Consists of two distinct portions: • Anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis) – hormonally controlled • Posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis)- neurally controlled ...
Note 10.2 - Endocrine Gland
... nervous systems. The hypothalamus receives nerve impulses and produces special type of hormones, called a neurohormone. The hypothalamus coordinates actions between the brain and the endocrine system. Neurohormone leaves the hypothalamus and travels to the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus is also i ...
... nervous systems. The hypothalamus receives nerve impulses and produces special type of hormones, called a neurohormone. The hypothalamus coordinates actions between the brain and the endocrine system. Neurohormone leaves the hypothalamus and travels to the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus is also i ...
Chapter 15-B Endocrine Glands
... function of the gonads; ovaries and testes • Two gonadotrophins secrete from ant. Pituitary are: • LH (Luteinizing hormone) & FSH (Follicle stimulating hormone) : – Both hormones regulate production of gametes sperm cells in testes and oocytes in ovaries – And reproductive hormones • Testosterone in ...
... function of the gonads; ovaries and testes • Two gonadotrophins secrete from ant. Pituitary are: • LH (Luteinizing hormone) & FSH (Follicle stimulating hormone) : – Both hormones regulate production of gametes sperm cells in testes and oocytes in ovaries – And reproductive hormones • Testosterone in ...
CRYDERS-Endocrine System
... – GHRH. Growth hormone-releasing hormone : Causes the ant. pituitary to release growth hormone – TRH. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone : Causes ant. pituitary to release thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) – CRH. Corticotropin-releasing hormone : Causes ant. pituitary to produce adrenocorticotropic hormo ...
... – GHRH. Growth hormone-releasing hormone : Causes the ant. pituitary to release growth hormone – TRH. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone : Causes ant. pituitary to release thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) – CRH. Corticotropin-releasing hormone : Causes ant. pituitary to produce adrenocorticotropic hormo ...
内分泌学―――Lecture Note
... 1) Almost all secretion by the pituitary is controlled by either hormonal or nervous signals from hypothalamus. 2) Hypothalamus is the highest integrative center in the endocrine hierarchy. The secretion of hypothalamic hormones is pulsatile which is critical for maintaining normal secretion of pitu ...
... 1) Almost all secretion by the pituitary is controlled by either hormonal or nervous signals from hypothalamus. 2) Hypothalamus is the highest integrative center in the endocrine hierarchy. The secretion of hypothalamic hormones is pulsatile which is critical for maintaining normal secretion of pitu ...
Transcripts/3_9 2
... h. We have vasopressin and OT generated by cells in the hypothalamus, they are released into the bloodstream of the posterior pituitary and they affect collecting ducts increasing permeability to water for vasopressin and uterine and breast tissue for OT. X. Feedback loop and hierarchical control[S1 ...
... h. We have vasopressin and OT generated by cells in the hypothalamus, they are released into the bloodstream of the posterior pituitary and they affect collecting ducts increasing permeability to water for vasopressin and uterine and breast tissue for OT. X. Feedback loop and hierarchical control[S1 ...
Part B
... • Posterior pituitary (composed of nervous tissue) • Anterior pituitary (true gland tissue) ...
... • Posterior pituitary (composed of nervous tissue) • Anterior pituitary (true gland tissue) ...
The Endocrine System
... • Is located at the base of the brain just below the hypothalamus. • Is known as the master gland • Secretes hormones on the basis of the emotional and seasoal changes • Divided into two part: the anterior lobe and the posterior lobe ...
... • Is located at the base of the brain just below the hypothalamus. • Is known as the master gland • Secretes hormones on the basis of the emotional and seasoal changes • Divided into two part: the anterior lobe and the posterior lobe ...
Slides - gserianne.com
... – Has a corresponding effect on target organ – Remember, this can apply to hypothalamus, pituitary, or other endocrine organ (recall ‘axis’) ...
... – Has a corresponding effect on target organ – Remember, this can apply to hypothalamus, pituitary, or other endocrine organ (recall ‘axis’) ...
Endocrinology of reproduction I (Lecture 6 and 7 combined)
... disulfide bonds. It is similar in size and structure to insulin. 2. Secreted by CL during pregnancy. 3. In some species it may be secreted by the uterus and/or placenta. 4. Generally requires tissue first be exposed to estrogens for its effects. 5. Functions • cervical dilation • inhibits uterine co ...
... disulfide bonds. It is similar in size and structure to insulin. 2. Secreted by CL during pregnancy. 3. In some species it may be secreted by the uterus and/or placenta. 4. Generally requires tissue first be exposed to estrogens for its effects. 5. Functions • cervical dilation • inhibits uterine co ...