Effects of high-altitude hypoxia on the hormonal response to
... obtained from Roussel Laboratories (Paris, France) in the form of injection solutions. Blood samples were centrifuged and then stored in liquid nitrogen during the remaining days at altitude and during transport to Paris. Analyses were performed at Necker Hospital. Concentrations of TSH, T3, fT3, T4 ...
... obtained from Roussel Laboratories (Paris, France) in the form of injection solutions. Blood samples were centrifuged and then stored in liquid nitrogen during the remaining days at altitude and during transport to Paris. Analyses were performed at Necker Hospital. Concentrations of TSH, T3, fT3, T4 ...
PTA/OTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 2
... Function of the Pineal Gland • Pineal secretion peaks between the ages of 1 and 5 and declines by 75% by the end of puberty. • Produces two hormones, serotonin and melatonin. • Melatonin increase at night, due to a light rate-limiting enzyme that converts serotonin to melatonin- serotonin N-acetyl- ...
... Function of the Pineal Gland • Pineal secretion peaks between the ages of 1 and 5 and declines by 75% by the end of puberty. • Produces two hormones, serotonin and melatonin. • Melatonin increase at night, due to a light rate-limiting enzyme that converts serotonin to melatonin- serotonin N-acetyl- ...
Endocrinology-general physiolofy of hormone, hormonal feed
... Growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH) – causes release of growth hormone Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) – causes release of the 2 gonadotropic hormones (luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormone) ...
... Growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH) – causes release of growth hormone Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) – causes release of the 2 gonadotropic hormones (luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormone) ...
Hormones
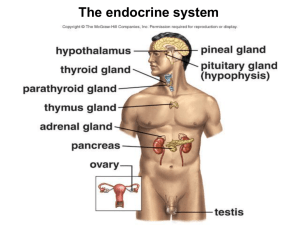
... • The endocrine system comprises a group of ductless glands that secrete chemical messenger substances, called hormones, into the bloodstream. • Hormones are responsible for the longterm regulation of many bodily functions. • The endocrine system includes the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, thymus ...
... • The endocrine system comprises a group of ductless glands that secrete chemical messenger substances, called hormones, into the bloodstream. • Hormones are responsible for the longterm regulation of many bodily functions. • The endocrine system includes the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, thymus ...
Chapter 25 The Endocrine Glands
... Pituitary Gland (5 of 6) • Pituitary tumors – Many pituitary endocrine disturbances caused by anterior lobe pituitary tumors – Clinical manifestations depend on size of tumor and the hormone produced • Functional tumors: produce hormones that cause clinical manifestations • Nonfunctional tumors: do ...
... Pituitary Gland (5 of 6) • Pituitary tumors – Many pituitary endocrine disturbances caused by anterior lobe pituitary tumors – Clinical manifestations depend on size of tumor and the hormone produced • Functional tumors: produce hormones that cause clinical manifestations • Nonfunctional tumors: do ...
Hormones and the Endocrine System
... corticotropin releasing hormone thyrotropin releasing hormone leuteinizing hormone releasing hormone follicle stimulating hormone releasing hormone growth hormone releasing hormone growth hormone inhibiting releasing hormone prolactin release-inhibiting hormone prolactin releasing hormone ...
... corticotropin releasing hormone thyrotropin releasing hormone leuteinizing hormone releasing hormone follicle stimulating hormone releasing hormone growth hormone releasing hormone growth hormone inhibiting releasing hormone prolactin release-inhibiting hormone prolactin releasing hormone ...
Pitutary disorders:
... Oestradiol (E2) production. This increasing E2 level initially suppresses FSH secretion (negative feedback) but then results in increased LH secretion (positive feedback); this is due to an increase in both the frequency &litude of GnRH. • LH in male stimulates interstitial (Leydig) cells to prod ...
... Oestradiol (E2) production. This increasing E2 level initially suppresses FSH secretion (negative feedback) but then results in increased LH secretion (positive feedback); this is due to an increase in both the frequency &litude of GnRH. • LH in male stimulates interstitial (Leydig) cells to prod ...
Biology 30 Notes October 3, 2014 Introduction Endocrine System
... Posterior Pituitary – part of the nervous system since it does not produce any of its own hormones. It instead stores and releases hormones produced by the hypothalamus. ADH (antidiuretic hormone) and oxytocin. Anterior Pituitary – is a true hormone gland. It produces and releases hGH (human growth ...
... Posterior Pituitary – part of the nervous system since it does not produce any of its own hormones. It instead stores and releases hormones produced by the hypothalamus. ADH (antidiuretic hormone) and oxytocin. Anterior Pituitary – is a true hormone gland. It produces and releases hGH (human growth ...
Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology
... Controlling centers of the CNS Neural pathways Hypothalamus Hypothalamic hormones Adenohypophysis Adenohypophysal hormones Peripheral glands Hormones of peripheral glands Tissue ...
... Controlling centers of the CNS Neural pathways Hypothalamus Hypothalamic hormones Adenohypophysis Adenohypophysal hormones Peripheral glands Hormones of peripheral glands Tissue ...
Introduction To Endocrinology: The Hypothalamic
... The peptide hormones of the anterior pituitary are essential for the regulation of growth and development, reproduction, response to stress, and intermediary metabolism. Their synthesis and secretion are controlled by hypothalamic hormones and by hormones from the peripheral endocrine organs. A larg ...
... The peptide hormones of the anterior pituitary are essential for the regulation of growth and development, reproduction, response to stress, and intermediary metabolism. Their synthesis and secretion are controlled by hypothalamic hormones and by hormones from the peripheral endocrine organs. A larg ...
HMC Pulse
... – The Hypothalamus produces hormones that: – Are released by the posterior pituitary – Raise or lower production of anterior pituitary hormones – The pituitary gland: – Produces hormones that regulate other endocrine glands in the body – Each of these hormones has a feedback loop that maintains ...
... – The Hypothalamus produces hormones that: – Are released by the posterior pituitary – Raise or lower production of anterior pituitary hormones – The pituitary gland: – Produces hormones that regulate other endocrine glands in the body – Each of these hormones has a feedback loop that maintains ...
hGH - ISpatula
... • Hypothalamus is a major link between nervous and endocrine system • Pituitary is attached to hypothalamus by infundibulum and divided in to: • Anterior pituitary or adenohypophysis • Posterior pituitary or neurohypophysis • The anterior pituitary receives signalling molecules from the hypothalamu ...
... • Hypothalamus is a major link between nervous and endocrine system • Pituitary is attached to hypothalamus by infundibulum and divided in to: • Anterior pituitary or adenohypophysis • Posterior pituitary or neurohypophysis • The anterior pituitary receives signalling molecules from the hypothalamu ...
Chapter41 Hormones Notes [Compatibility Mode]
... -Nervous system controls endocrine function; these ...
... -Nervous system controls endocrine function; these ...
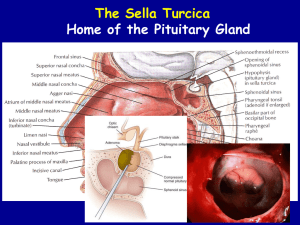
Normal pituitary Magnetic resonance scan
... Lactation Inhibits reproductive hormone secretion Release inhibited by dopamine Animals: osmoregulation, growth Stalk transection prolactin ...
... Lactation Inhibits reproductive hormone secretion Release inhibited by dopamine Animals: osmoregulation, growth Stalk transection prolactin ...
Hypopituitarism Presentation
... testosterone production. In women, it fosters production of estrogen. • Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). Working in tandem with LH, FSH helps stimulate sperm production in men, and egg development and ovulation in women. • Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). This hormone stimulates your adrenal g ...
... testosterone production. In women, it fosters production of estrogen. • Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). Working in tandem with LH, FSH helps stimulate sperm production in men, and egg development and ovulation in women. • Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). This hormone stimulates your adrenal g ...
AP Biology Animal Form and Function
... The posterior lobe of the pituitary gland is derived from neural tissue and its connection to the hypothalamus is neural. Posterior Pituitary produces 2 hormones: ADH and oxytocin. These are produced by the nerve cell bodies that are located in the hypothalamus, where they are packaged into secretor ...
... The posterior lobe of the pituitary gland is derived from neural tissue and its connection to the hypothalamus is neural. Posterior Pituitary produces 2 hormones: ADH and oxytocin. These are produced by the nerve cell bodies that are located in the hypothalamus, where they are packaged into secretor ...
Ch 18 Notes: Endocrine System 2014
... 2. Sebaceous >>> oil 3. Digestive >>> enzymes Endocrine glands = secrete hormones in extracellular space, which diffuse into capillaries and are carried throughout the circulatory system. Endocrine system = all the endocrine glands and organs that contain endocrine tissue. HORMONE FUNCTION IS TO REG ...
... 2. Sebaceous >>> oil 3. Digestive >>> enzymes Endocrine glands = secrete hormones in extracellular space, which diffuse into capillaries and are carried throughout the circulatory system. Endocrine system = all the endocrine glands and organs that contain endocrine tissue. HORMONE FUNCTION IS TO REG ...
The Endocrine System The Endocrine System The endocrine
... grow and mature; it is also responsible for estrogen secretion. In men, the FSH hormone controls the growth of the seminiferous tubules and sperm growth. Luteinizing hormone (LH) has separate functions for females and males. In females, it functions to mature the ovarian follicle and ovum, helps wit ...
... grow and mature; it is also responsible for estrogen secretion. In men, the FSH hormone controls the growth of the seminiferous tubules and sperm growth. Luteinizing hormone (LH) has separate functions for females and males. In females, it functions to mature the ovarian follicle and ovum, helps wit ...
What is the median eminence? The median eminence is the nucleus
... 18. Can a woman have excessively high or excessively low prolactin levels and still be fertile? a. Probably not 19. What are the two hormones needed in breastfeeding and what are their functions? a. Oxytocin (produced by the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus and released by the posterior p ...
... 18. Can a woman have excessively high or excessively low prolactin levels and still be fertile? a. Probably not 19. What are the two hormones needed in breastfeeding and what are their functions? a. Oxytocin (produced by the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus and released by the posterior p ...
Regulation and Control
... Aquaporins Contraction during activated; H2O labor; ejection of reabsorbed milk during nursing ...
... Aquaporins Contraction during activated; H2O labor; ejection of reabsorbed milk during nursing ...
Student Academic Learning Services The
... posterior pituitary for storage. B) Antidiuretic hormone, released by the posterior pituitary, causes urine volume to increase and blood volume to decrease. C) Luteinizing hormone, an anterior pituitary hormone, triggers ovulation of an egg from the ovary and causes the ruptured follicle to produce ...
... posterior pituitary for storage. B) Antidiuretic hormone, released by the posterior pituitary, causes urine volume to increase and blood volume to decrease. C) Luteinizing hormone, an anterior pituitary hormone, triggers ovulation of an egg from the ovary and causes the ruptured follicle to produce ...
Function Nervous System Endocrine System
... During Pregnancy, high prolactin promote development of breast for milk secretion ...
... During Pregnancy, high prolactin promote development of breast for milk secretion ...









![Chapter41 Hormones Notes [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016605577_1-a7aad459db07937df65df4f3a411aef9-300x300.png)