1 lecture ES Hyp APG File - Progetto e
... with essentially all cells. However, a given hormone usually affects only a limited number of cells, which are called target cells. A target cell responds to a hormone because it bears receptors for the hormone. ...
... with essentially all cells. However, a given hormone usually affects only a limited number of cells, which are called target cells. A target cell responds to a hormone because it bears receptors for the hormone. ...
17. Pituitary and Adrenal Glands
... FSH – a) in females: stimulates growth and development of ovarian follicles, and promotes estrogen secretion. b) in males: it is required for sperm production. LH – a) in females: responsible for ovulation and for luteinization. Regulates estrogen and progesterone. b) in males: stimulates inter ...
... FSH – a) in females: stimulates growth and development of ovarian follicles, and promotes estrogen secretion. b) in males: it is required for sperm production. LH – a) in females: responsible for ovulation and for luteinization. Regulates estrogen and progesterone. b) in males: stimulates inter ...
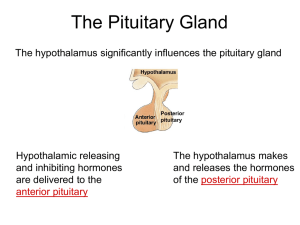
Hypothalamus - pituitary
... differentiation, promoting overall tissue and organ growth. GH inhibits ageing via many ways (eg. it inhibits formation of free radicals). GH stimulates skeletal and tissue growth via the polypeptide growth factors – somatomedins (IGF-I, IGF-II), which are produced in the liver. GH also exhibits mul ...
... differentiation, promoting overall tissue and organ growth. GH inhibits ageing via many ways (eg. it inhibits formation of free radicals). GH stimulates skeletal and tissue growth via the polypeptide growth factors – somatomedins (IGF-I, IGF-II), which are produced in the liver. GH also exhibits mul ...
Function of hypothalamo - pituitary
... differentiation, promoting overall tissue and organ growth. GH inhibits ageing via many ways (eg. it inhibits formation of free radicals). GH stimulates skeletal and tissue growth via the polypeptide growth factors – somatomedins (IGF-I, IGF-II), which are produced in the liver. GH also exhibits mul ...
... differentiation, promoting overall tissue and organ growth. GH inhibits ageing via many ways (eg. it inhibits formation of free radicals). GH stimulates skeletal and tissue growth via the polypeptide growth factors – somatomedins (IGF-I, IGF-II), which are produced in the liver. GH also exhibits mul ...
IB BIO endocrine system
... They secrete certain chemical substances which guide and control the various metabolic activities, the growth and differentiation of various systems and thereby bringing about a correct physiological balance between them. Such substances are also referred to as chemical co-ordinators. Differences be ...
... They secrete certain chemical substances which guide and control the various metabolic activities, the growth and differentiation of various systems and thereby bringing about a correct physiological balance between them. Such substances are also referred to as chemical co-ordinators. Differences be ...
CASE 33
... secretion increases rather than decreases as is the case for the other pituitary hormones. Most evidence points to dopamine rather than a peptide as being the prolactin inhibitory hormone. In addition to this inhibitory pathway, PRL secretion can be stimulated by TRH. The main target of PRL is the m ...
... secretion increases rather than decreases as is the case for the other pituitary hormones. Most evidence points to dopamine rather than a peptide as being the prolactin inhibitory hormone. In addition to this inhibitory pathway, PRL secretion can be stimulated by TRH. The main target of PRL is the m ...
The Endocrine System
... in the ovary, and regulation of ovarian secretion of female sex hormones. Males: stimulates cell in the testes to secrete testosterone ...
... in the ovary, and regulation of ovarian secretion of female sex hormones. Males: stimulates cell in the testes to secrete testosterone ...
Hormone Review Guide
... wall and in milk-letdown by forcing milk into ducts from the milk glands Regulate energy metabolism Regulate energy metabolism Lowers blood levels of calcium and phosphate ions when they are too high Increases blood calcium ion concentration and decreases phosphate ion concentration “Fight or flight ...
... wall and in milk-letdown by forcing milk into ducts from the milk glands Regulate energy metabolism Regulate energy metabolism Lowers blood levels of calcium and phosphate ions when they are too high Increases blood calcium ion concentration and decreases phosphate ion concentration “Fight or flight ...
Anterior Pituitary
... initiates the formation of follicles within the ovary stimulates follicle cells to secrete estrogen stimulates sperm production in testes ...
... initiates the formation of follicles within the ovary stimulates follicle cells to secrete estrogen stimulates sperm production in testes ...
Document
... initiates the formation of follicles within the ovary stimulates follicle cells to secrete estrogen stimulates sperm production in testes ...
... initiates the formation of follicles within the ovary stimulates follicle cells to secrete estrogen stimulates sperm production in testes ...
Introduction to Endocrinology
... • Directly antagonizes effect of insulin on glucose metabolism • Provides hepatic gluconeogenesis • Stimulates lipolysis • Enhances protein synthesis in skeletal muscle & other tissues • Stimulates production of insulin-like growth factors ...
... • Directly antagonizes effect of insulin on glucose metabolism • Provides hepatic gluconeogenesis • Stimulates lipolysis • Enhances protein synthesis in skeletal muscle & other tissues • Stimulates production of insulin-like growth factors ...
Dissection of the Brain, Hypothalamus and Pituitary
... Synthesizes and secretes hormones that act on the pituitary (See Hormone Table): Releasing & Inhibiting hormones: small peptides secreted from hypothalamus that control the secretion of protein hormones from the pituitary gland Hormones directly associated with reproduction: GnRH, CRH, PIF, PRF Two ...
... Synthesizes and secretes hormones that act on the pituitary (See Hormone Table): Releasing & Inhibiting hormones: small peptides secreted from hypothalamus that control the secretion of protein hormones from the pituitary gland Hormones directly associated with reproduction: GnRH, CRH, PIF, PRF Two ...
AGING OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... There is considerable evidence that normal aging is accompained by primary testicular failure that is modest in degree in most individuals. This age-related testicular failure result in diminished availability of testosterone and inhibin as well as a decrease in sperm production. While there is a g ...
... There is considerable evidence that normal aging is accompained by primary testicular failure that is modest in degree in most individuals. This age-related testicular failure result in diminished availability of testosterone and inhibin as well as a decrease in sperm production. While there is a g ...
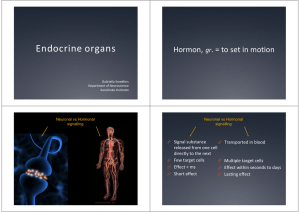
Endocrine organs - Ping Pong
... Estrogen and Progesterone Regulates reproduction cycle and secondary sex characteristics for women. ...
... Estrogen and Progesterone Regulates reproduction cycle and secondary sex characteristics for women. ...
The Endocrine System
... • Some organs are entirely endocrine in function. They are referred to as endocrine glands like pituitary glands, pineal body, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, and adrenal glands. • Groups of endocrine cells may be present in organs that have other functions like islets of pancreas, the interstiti ...
... • Some organs are entirely endocrine in function. They are referred to as endocrine glands like pituitary glands, pineal body, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, and adrenal glands. • Groups of endocrine cells may be present in organs that have other functions like islets of pancreas, the interstiti ...
1) What is the median eminence? a) The median eminence is the
... 16) When is FSH most abundant in the menstrual cycle? a) At the beginning of the month b) Major surge at ovulation 17) When is LH most abundant in the menstrual cycle? a) At ovulation, but generally pretty present all throughout cycle 18) What does LH do in men? a) Stimulates the production of testo ...
... 16) When is FSH most abundant in the menstrual cycle? a) At the beginning of the month b) Major surge at ovulation 17) When is LH most abundant in the menstrual cycle? a) At ovulation, but generally pretty present all throughout cycle 18) What does LH do in men? a) Stimulates the production of testo ...
Endocrine: Hormone - Phillips Scientific Methods
... contraction that delivers a baby and milk ejection from breast feeding; sight and sound of baby can causes nursing mother to release milk ...
... contraction that delivers a baby and milk ejection from breast feeding; sight and sound of baby can causes nursing mother to release milk ...
Hormone - WordPress.com
... corticosteroids: aldosterone and cortisol FSH stimulates follicle growth and ovarian estrogen production; stimulates sperm production and androgen-binding protein LH has a role in ovulation and the growth of the corpus luteum; stimulates androgen secretion by interstitial cells in testes ...
... corticosteroids: aldosterone and cortisol FSH stimulates follicle growth and ovarian estrogen production; stimulates sperm production and androgen-binding protein LH has a role in ovulation and the growth of the corpus luteum; stimulates androgen secretion by interstitial cells in testes ...
Hypothalamus - pituitary
... growth by: • increased deposition of protein by the chondrocytic and osteogenic cells that cause bone growth • increased rate of reproduction of these cells • the specific effect of converting chondrocytes into osteogenic cells, cells thus causing specific deposition of new bone. ...
... growth by: • increased deposition of protein by the chondrocytic and osteogenic cells that cause bone growth • increased rate of reproduction of these cells • the specific effect of converting chondrocytes into osteogenic cells, cells thus causing specific deposition of new bone. ...
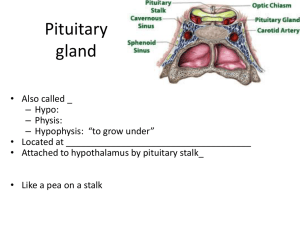
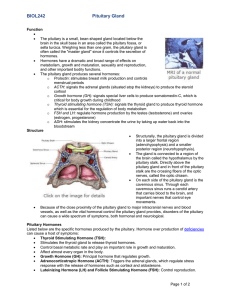
BIOL242pituitaryOCT2012
... brain in the skull base in an area called the pituitary fossa, or sella turcica. Weighing less than one gram, the pituitary gland is often called the "master gland" since it controls the secretion of hormones. Hormones have a dramatic and broad range of effects on metabolism, growth and maturation ...
... brain in the skull base in an area called the pituitary fossa, or sella turcica. Weighing less than one gram, the pituitary gland is often called the "master gland" since it controls the secretion of hormones. Hormones have a dramatic and broad range of effects on metabolism, growth and maturation ...