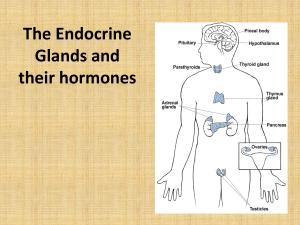
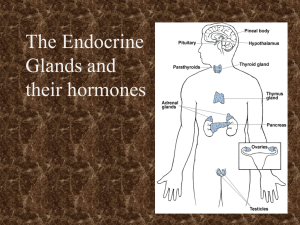
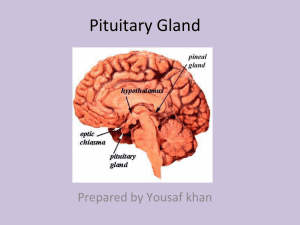
chapter 18 the endocrine system
... d. acetylcholine 24. When an excess of a hormone is present the number of target cell receptors may decrease. This change is called a. up-regulation b. down-regulation c. adaptation d. accommodation 25. Autocrines are a. neurohormones of the autonomic nervous system b. hormones that are circulating ...
... d. acetylcholine 24. When an excess of a hormone is present the number of target cell receptors may decrease. This change is called a. up-regulation b. down-regulation c. adaptation d. accommodation 25. Autocrines are a. neurohormones of the autonomic nervous system b. hormones that are circulating ...
Endocrine System
... Body cells that react to a particular hormone are called: Target organ cells When released from endocrine cells in the pancreas, insulin acts to: Lower blood sugar levels ...
... Body cells that react to a particular hormone are called: Target organ cells When released from endocrine cells in the pancreas, insulin acts to: Lower blood sugar levels ...
Endocrine System
... Body cells that react to a particular hormone are called: Target organ cells When released from endocrine cells in the pancreas, insulin acts to: Lower blood sugar levels ...
... Body cells that react to a particular hormone are called: Target organ cells When released from endocrine cells in the pancreas, insulin acts to: Lower blood sugar levels ...
Option D.5 Hormones and metabolism
... • ADH enhances fluid retention by making the kidneys permeable to water • Neurosecretory cells in the supra-optic nucleus of the hypothalamus synthesize ADH, transport it down axons, and store it in nerve endings in the posterior pituitary gland • The release of ADH is triggered by osmoreceptor cell ...
... • ADH enhances fluid retention by making the kidneys permeable to water • Neurosecretory cells in the supra-optic nucleus of the hypothalamus synthesize ADH, transport it down axons, and store it in nerve endings in the posterior pituitary gland • The release of ADH is triggered by osmoreceptor cell ...
ANATOMIA FUNCTIONALA/ FIZIOPATOLOGIA HIPOTALAMUSULUI
... and do not give information on the distribution of the fat. Techniques such as bioelectrical impedance rely on the fact that fat is not as good an electrical conductor as lean body mass. It is cheap but also does not allow an assessment of the distribution of the fat mass. Imaging techniques such as ...
... and do not give information on the distribution of the fat. Techniques such as bioelectrical impedance rely on the fact that fat is not as good an electrical conductor as lean body mass. It is cheap but also does not allow an assessment of the distribution of the fat mass. Imaging techniques such as ...
Your Hormones are your Helpers B
... Michel Odent cautions that even hunger, which also causes the body to release fight-or-flight hormones, can stop labour from progressing. He advises women to eat- if they are hungry- in the earliest stages of labour; many hospitals, though, have a policy that prevents labouring women from eating on ...
... Michel Odent cautions that even hunger, which also causes the body to release fight-or-flight hormones, can stop labour from progressing. He advises women to eat- if they are hungry- in the earliest stages of labour; many hospitals, though, have a policy that prevents labouring women from eating on ...
The Endocrine System - Mediapolis Community School
... • Growth hormone(GH)- stimulates cell growth in size and frequency. • Prolactin(PRL)- stimulates a woman’s milk production after the birth of an infant. • Thyroid-stimulating hormone(TSH)- controls thyroid gland secretion. • Adrenocorticotropic hormone(ACTH)- controls the manufacture and secretion o ...
... • Growth hormone(GH)- stimulates cell growth in size and frequency. • Prolactin(PRL)- stimulates a woman’s milk production after the birth of an infant. • Thyroid-stimulating hormone(TSH)- controls thyroid gland secretion. • Adrenocorticotropic hormone(ACTH)- controls the manufacture and secretion o ...
Classification of Hormones Lecture 1
... 2. Hormones which are water soluble and easily transported in plasma in a free state: • Their half-life is very short and their action is also for a very short time. • They bind to receptors on the cell membrane and their further action is mediated through a second messenger, the hormone itself bein ...
... 2. Hormones which are water soluble and easily transported in plasma in a free state: • Their half-life is very short and their action is also for a very short time. • They bind to receptors on the cell membrane and their further action is mediated through a second messenger, the hormone itself bein ...
Endocrine System
... 2. Discuss the hormonal effects in regulation of blood calcium level and regulation of blood glucose level. 3. List the hormones secreted and its functions (effects) of the following endocrine organs: thyroid, posterior pituitary, anterior pituitary, adrenal gland, pineal gland, pancreas, testes, an ...
... 2. Discuss the hormonal effects in regulation of blood calcium level and regulation of blood glucose level. 3. List the hormones secreted and its functions (effects) of the following endocrine organs: thyroid, posterior pituitary, anterior pituitary, adrenal gland, pineal gland, pancreas, testes, an ...
Endocrine Glands
... Prolactin: (non-steroid) • In females, prolactin promotes mammary gland development and lactation (milk production) – Inhibited by the hypothalamus through dopamine – Stimulation of the nipples during breast feeding trigger the release of secreting hormones from the hypothalamus – Increasing estroge ...
... Prolactin: (non-steroid) • In females, prolactin promotes mammary gland development and lactation (milk production) – Inhibited by the hypothalamus through dopamine – Stimulation of the nipples during breast feeding trigger the release of secreting hormones from the hypothalamus – Increasing estroge ...
Organs of the Endocrine System and Their Products
... Growth Hormone Excess in childhood leads to GIGANTISM ...
... Growth Hormone Excess in childhood leads to GIGANTISM ...
Thalamus, Hypothalamus, Prethalamus, and Epithalamus
... ACTCH, which target the adrenal cortex and stimulates cortisol secretion. Cortisol ol results in increases in fat, protein degradation, and blood glucose. It also has anti-inflammatory matory effects. es secreted by the hypothalamus include gonadotropin-releasing gonadotropin 6. Other hormones hormo ...
... ACTCH, which target the adrenal cortex and stimulates cortisol secretion. Cortisol ol results in increases in fat, protein degradation, and blood glucose. It also has anti-inflammatory matory effects. es secreted by the hypothalamus include gonadotropin-releasing gonadotropin 6. Other hormones hormo ...
Hormones of the Body
... Biggest (mind the pun) cause of gigantism and acromegaly is a tumour in the pituitary ...
... Biggest (mind the pun) cause of gigantism and acromegaly is a tumour in the pituitary ...
FEMALE HORMONES and their activity
... It is also devoured by fungus overgrowth. Testosterone is responsible for much more than defining sexual characteristics in men or influencing sex drive. Testosterone is essential for life since it helps to regulate basic metabolism. Testosterone also facilitates protein synthesis and the building ...
... It is also devoured by fungus overgrowth. Testosterone is responsible for much more than defining sexual characteristics in men or influencing sex drive. Testosterone is essential for life since it helps to regulate basic metabolism. Testosterone also facilitates protein synthesis and the building ...
Growth hormone
... It induces progesterone production by the corpus luteum and, in the male – gonadal testosterone production. It is used in hypopituitary anovular and other infertility in both sexes. It is also used for cryptorchidism in prepubertal boys (6 years of age; if it fails to induce testicular descent, ther ...
... It induces progesterone production by the corpus luteum and, in the male – gonadal testosterone production. It is used in hypopituitary anovular and other infertility in both sexes. It is also used for cryptorchidism in prepubertal boys (6 years of age; if it fails to induce testicular descent, ther ...
Biology 251 Fall 2015 1 TOPIC 9: THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM I
... Releases glucagon which promotes increase in blood glucose levels VI. Tropic Endocrine Systems ...
... Releases glucagon which promotes increase in blood glucose levels VI. Tropic Endocrine Systems ...
Hormone Function
... promotes secretion of estrogen by ovaries. Males: required for sperm production Luteinizing Hormone (LH): Females: responsible for ovulation, formation of corpus luteum in the ovary, and regulation of ovarian secretion of female sex hormones. Males: stimulates cell in the testes to secrete testoster ...
... promotes secretion of estrogen by ovaries. Males: required for sperm production Luteinizing Hormone (LH): Females: responsible for ovulation, formation of corpus luteum in the ovary, and regulation of ovarian secretion of female sex hormones. Males: stimulates cell in the testes to secrete testoster ...
Endocrinology
... Endocrinology - Answers 14. Which hormone would increase in the blood during dehydration? a. atrial natriuretic hormone b. antidiuretic hormone c. parathyroid hornome d. melatonin 15. Which hormone is most commonly associated with the “fight or flight” response to stress? a. insulin b. adrenalin c. ...
... Endocrinology - Answers 14. Which hormone would increase in the blood during dehydration? a. atrial natriuretic hormone b. antidiuretic hormone c. parathyroid hornome d. melatonin 15. Which hormone is most commonly associated with the “fight or flight” response to stress? a. insulin b. adrenalin c. ...
No Slide Title
... – Dominant negative activity – Disadvantages: • GH levels not suppressed • Difficult to monitor • Effect on tumor unknown – May actually stimulate tumor growth ...
... – Dominant negative activity – Disadvantages: • GH levels not suppressed • Difficult to monitor • Effect on tumor unknown – May actually stimulate tumor growth ...
What is the target tissue of ACTH and what does it do? 1.1. Target
... Estrogen overrides the system 24 hours before ovulation when the Graafian follicle that is pushing against the ovary sends a signal that the ovum is ready for ovulation by dumping all of its remaining estrogen into the bloodstream. This very high level of estrogen stimulates GnRH release which then ...
... Estrogen overrides the system 24 hours before ovulation when the Graafian follicle that is pushing against the ovary sends a signal that the ovum is ready for ovulation by dumping all of its remaining estrogen into the bloodstream. This very high level of estrogen stimulates GnRH release which then ...