Student Academic Learning Services The Endocrine System Quiz
... B) Antidiuretic hormone, released by the posterior pituitary, causes urine volume to increase and blood volume to decrease. C) Luteinizing hormone, an anterior pituitary hormone, triggers ovulation of an egg from the ovary and causes the ruptured follicle to produce progesterone and some estrogens. ...
... B) Antidiuretic hormone, released by the posterior pituitary, causes urine volume to increase and blood volume to decrease. C) Luteinizing hormone, an anterior pituitary hormone, triggers ovulation of an egg from the ovary and causes the ruptured follicle to produce progesterone and some estrogens. ...
Hormones and Reprodu..
... progesterone then totally suppresses the anterior pituitary for FSH and LH activity and stimulates it for the production of L.T.H. (Luteotrophic hormone) also called prolactin, which in turn maintains the C.L. for progesterone production. Progesterone plays an important role, which are as follows: ...
... progesterone then totally suppresses the anterior pituitary for FSH and LH activity and stimulates it for the production of L.T.H. (Luteotrophic hormone) also called prolactin, which in turn maintains the C.L. for progesterone production. Progesterone plays an important role, which are as follows: ...
hypothalamus,pituitary
... hormone "to set in motion," Classic definition- hormones are secretory product of the ductless glands, which are released in catalytic amount into blood stream and transported to specific target cells(or organs),where they elicit physiological, morphological and biochemical responses. ...
... hormone "to set in motion," Classic definition- hormones are secretory product of the ductless glands, which are released in catalytic amount into blood stream and transported to specific target cells(or organs),where they elicit physiological, morphological and biochemical responses. ...
You have completed this lesson regarding the Endocrine System of
... • Located just above either kidney, which are in the middle of your lower back. • Secretes hormones: Anti-Diuretic Hormone ...
... • Located just above either kidney, which are in the middle of your lower back. • Secretes hormones: Anti-Diuretic Hormone ...
File - Endocrine System
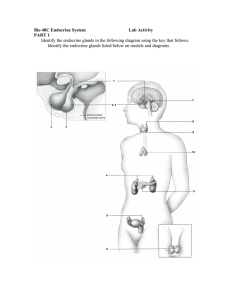
... to the stomach. The endocrine portion consists of scattered clusters of cells called pancreatic islets or islets of Langerhans.) _____ intestines (The intestine releases hormones that coordinate digestive activities.) _____ kidneys (KID-nē) Endocrine cells in the kidneys produce hormones important f ...
... to the stomach. The endocrine portion consists of scattered clusters of cells called pancreatic islets or islets of Langerhans.) _____ intestines (The intestine releases hormones that coordinate digestive activities.) _____ kidneys (KID-nē) Endocrine cells in the kidneys produce hormones important f ...
electrolyte regulation
... Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH, thyrotropin) Luteinizing hormone (LH) (gonadotropin) ...
... Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH, thyrotropin) Luteinizing hormone (LH) (gonadotropin) ...
endocrine system
... Posterior Pituitary Gland: • Secretes Two Hormones: (made by hypothalamus) • Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) – acts on the kidneys, increasing water retention and thus decreasing urine volume. ...
... Posterior Pituitary Gland: • Secretes Two Hormones: (made by hypothalamus) • Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) – acts on the kidneys, increasing water retention and thus decreasing urine volume. ...
Chapter 11 Review
... estrogen and progesterone) and testes (stimulate the production of testosterone). ...
... estrogen and progesterone) and testes (stimulate the production of testosterone). ...
2,3,4-Anterior Pituitary 12017-02-05 00:361.9 MB
... PRH (prolactin releasing hormone), also called prolactin releasing factor (PRF) ? PIH (prolactin inhibiting hormone), also called prolactin inhibiting factor. This hormone or factor is dopamine ...
... PRH (prolactin releasing hormone), also called prolactin releasing factor (PRF) ? PIH (prolactin inhibiting hormone), also called prolactin inhibiting factor. This hormone or factor is dopamine ...
Endocrine - Austin Community College
... Regulate the electrolyte concentrations of extracellular fluids Aldosterone – most important mineralocorticoid Maintains Na+ balance by reducing excretion of sodium from the body Stimulates reabsorption of Na+ by the kidneys Aldosterone secretion is stimulated by: Rising blood levels of K+ Low blood ...
... Regulate the electrolyte concentrations of extracellular fluids Aldosterone – most important mineralocorticoid Maintains Na+ balance by reducing excretion of sodium from the body Stimulates reabsorption of Na+ by the kidneys Aldosterone secretion is stimulated by: Rising blood levels of K+ Low blood ...
The Endocrine System Notes
... Endocrine system: produces and releases chemical messages; slower speed Both systems are integrated and help maintain homeostasis Both systems are regulated by positive and negative feedback mechanisms Negative feedback A change in an internal condition is sensed by the brain The brain cau ...
... Endocrine system: produces and releases chemical messages; slower speed Both systems are integrated and help maintain homeostasis Both systems are regulated by positive and negative feedback mechanisms Negative feedback A change in an internal condition is sensed by the brain The brain cau ...
The Endocrine System
... blood calcium levels by reducing bone calcium levels (calcium is regulated in the body by the antagonistic actions of PTH and calcitonin. ...
... blood calcium levels by reducing bone calcium levels (calcium is regulated in the body by the antagonistic actions of PTH and calcitonin. ...
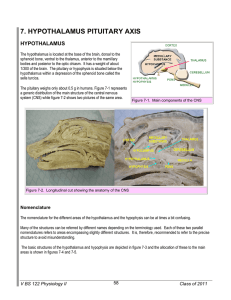
7. HYPOTHALAMUS PITUITARY AXIS
... hemorrhagicum (CH) and eventually the corpus luteum (CL). The CL is responsible for the production of progesterone, which in turn inhibits significant production of GnRH from the tonic centre of the hypothalamus. Lactotropes Lactotropes are stimulated by prolactin releasing hormone (PRH), same as PR ...
... hemorrhagicum (CH) and eventually the corpus luteum (CL). The CL is responsible for the production of progesterone, which in turn inhibits significant production of GnRH from the tonic centre of the hypothalamus. Lactotropes Lactotropes are stimulated by prolactin releasing hormone (PRH), same as PR ...
Anterior Pituitary: Growth Hormone (GH)
... Under conditions of fear or stress, a surge of the hormone adrenaline mobilizes the body for peak physical response. Flooding the bloodstream at up to 300 times the normal concentration, the adrenaline interacts with receptors on cells in various organs, increasing the heart rate and blood pressure ...
... Under conditions of fear or stress, a surge of the hormone adrenaline mobilizes the body for peak physical response. Flooding the bloodstream at up to 300 times the normal concentration, the adrenaline interacts with receptors on cells in various organs, increasing the heart rate and blood pressure ...
growth hormone releasing hormone
... Main pathways in regulation of growth and etabolism Effects of growth hormone on the tissues is anabolic. Increased height during childhood is the most widely known effect of GH. Height is stimulated by at least two mechanisms: 1.Through receptor mechanism GH directly stimulates division and multipl ...
... Main pathways in regulation of growth and etabolism Effects of growth hormone on the tissues is anabolic. Increased height during childhood is the most widely known effect of GH. Height is stimulated by at least two mechanisms: 1.Through receptor mechanism GH directly stimulates division and multipl ...
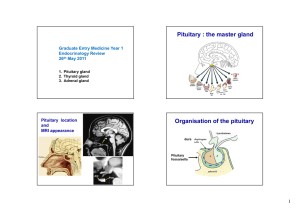
Pituitary : the master gland Organisation of the pituitary
... iodothyronines are unusual in that the main thyroid product (T4) is not the active hormone (T3) metabolism T4 to T3 occurs in the liver and kidney T4 is converted to T3 by Type I deiodinase ...
... iodothyronines are unusual in that the main thyroid product (T4) is not the active hormone (T3) metabolism T4 to T3 occurs in the liver and kidney T4 is converted to T3 by Type I deiodinase ...
Chapter 1: Animal Agriculture
... • Some names for placental gonadotropins • Pregnant mare serum • Equine chorionic gonadotropin • Human chorionic gonadotropins ...
... • Some names for placental gonadotropins • Pregnant mare serum • Equine chorionic gonadotropin • Human chorionic gonadotropins ...
Základní vyšetření v endokrinologii
... Secreted by the anterior pituitary under the control of prolactin inhibitory factor secreted by the hypothalamus levels rise during pregnancy and cause stimulation of milk production after childbirth elevated serum prolactin levels are the most common disorder of the hypothalamic-pituitary axis inhi ...
... Secreted by the anterior pituitary under the control of prolactin inhibitory factor secreted by the hypothalamus levels rise during pregnancy and cause stimulation of milk production after childbirth elevated serum prolactin levels are the most common disorder of the hypothalamic-pituitary axis inhi ...
... are very different. Anterior pituitary. Smallbodied hypothalamic neurons in several nuclei that surround the third ventricle (the arcuate, the paraventricular and ventromedial nuclei, and the medial preoptic and periventricular regions) secrete releasing and inhibitory factors into a rich funnel-sha ...