* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download You have completed this lesson regarding the Endocrine System of
Bovine somatotropin wikipedia , lookup
Cryptorchidism wikipedia , lookup
Hormonal contraception wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Adrenal gland wikipedia , lookup
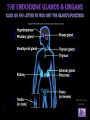
Click here to go to next slide By: Gabby Lutz Understanding the collection of glands in the Endocrine System that secrete different hormones in order to regulate the body’s many functions in an organism. A C B E D E F G I H Multiple Choice Question Return to Homepage • • • • Pituitary Gland Most important gland of the Endocrine System Pea-sized structure located at the base of the brain, below the hypothalamus Two lobes: Anterior & Posterior Posterior Pituitary Gland Hormones: -Oxytocin: signals contractions of the womb during labor in women & moves sperm in men -Anti-Diuretic Hormone (ADH): increase water reabsorption • Anterior Pituitary Gland Hormones: -Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH): triggers the thyroid into secreting hormones -Human Growth Hormone (HGH): stimulates growth of all tissues of the body, including bone -Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone (MSH): triggers the production & release of melanin -Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH): stimulates the maturation of ovarian follicles & sperm production -Luteinizing Hormone (LH): promotes the secretion of progesterone in females & testosterone in males -Prolactin: promotes milk production -Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH): stimulates production & release of cortisol from the cortex of the adrenal gland Return to Homepage • • • Hypothalamus Control and relay center of the Endocrine System Located in the brain, below the thalamus & above the brainstem Hormones secreted: -Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone (TRH): stimulates release of prolactin & TSH -Gonadatropin-Releasing Horome (GnRH): increases estrogen, pregesterone & testerone levels -Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone (CRH): triggers release of ACTH -Somatostatin: inhibit release of GH & TSH -Dopamine: inhibits the release of prolactin Return to Homepage Pineal Gland • Shaped like a pine cone, located on the midline of the brain • Actual function is unkown • Hormones secreted: -Melatonin: helps synchronize circadian rhythms in different parts of the body “sleeping hormone” Return to Homepage Thyroid Gland • Butterfly-shaped gland that sits low on the front of the neck • Hormones secreted: -Thyroxine: plays vital roles in digestion, heart and muscle function, brain development and maintenance of bones Return to Homepage Parathyroid Gland • Four tiny glands located on the posterior side of the Thyroid Gland • Hormone secreted: -Parathyroid Hormone (PTH): raises blood calcium level by breaking down the bone & causing calcium release -increases body’s ability to absorb calcium from food Return to Homepage Thymus • Located anatomically in the anterior superior mediastinum (behind sternum, in front of heart) • After puberty, the thymus slowly shrinks & is replaced by fat • Hormone secreted: -Thymosin: stimulates development of disease-fighting T-cells Return to Homepage • Located just above either kidney, which are in the middle of your lower back. • Secretes hormones: Anti-Diuretic Hormone (ADH) & Aldosterone -ADH: promotes the reabsorption of water -Aldosterone: promotes sodium reabsorption Return to Homepage Pancreas • Located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach • Hormones secreted: -Isulin: regulates how the body uses & stores fat and glucose -Glucagon: controls blood sugar (glucose) levels. Return to Homepage Testes • Located behind the male genitalia in a pouch of skin called the scrotum • Hormone secreted: -Testosterone: key role in the development of male reproductive tissues -increases muscle, bone mass and growth of body hair Return to Homepage Ovaries • Located on opposite ends of the pelvic wall, on either side of the uterus • Hormones secreted: -Estrogen: aids in the development of female secondary sexual characteristics -Progesterone: thickens the lining of the uterus each month, preparing the lining to receive and nourish a fertilized egg Multiple Choice Question Which gland/organ plays the most important role in the Endocrine System? A. Pancreas B. Pituitary Gland C. Thymus Return to Multiple Choice Question A. Pancreas Almost! • Although the Pancreas is a very important organ involved in the endocrine system, it only secretes two hormones. • Insulin & Glucagon are secreted by the Pancreas and aid in regulating the body’s blood sugar. Next B. Pituitary Gland Correct! • The Pituitary Gland is often considered the most important part of the endocrine system because it secretes hormones that control many functions of the other endocrine glands. Return to Multiple Choice Question C. Thymus Not quite! • The Thymus secretes the hormone that produces T cells which aid the immune system. However, the thymus becomes much smaller after puberty and is eventually replaced with fat. Return to Title Slide Congratulations! You have completed this lesson regarding the Endocrine System of the human body! Excellent work! Please click the “Return to Title Slide” button in order to return to the main menu.