HardasNails-Marianco
... breads, etc. - have a much lower energy level than kids who eat a higher proportion of protein and fat for breakfast - e.g. ham and eggs - thus did not perform as well in school. The shot of sugar gives them initial energy. But then when the sugar is absorbed and stored, they are left with lower adr ...
... breads, etc. - have a much lower energy level than kids who eat a higher proportion of protein and fat for breakfast - e.g. ham and eggs - thus did not perform as well in school. The shot of sugar gives them initial energy. But then when the sugar is absorbed and stored, they are left with lower adr ...
1. overview of the endocrine system
... Luteinizing hormone (LH): In females, it stimulates the ovulation and promotes the secretion of estrogens and progesterone by the ovaries and placenta in order to prepare the body for possible pregnancy. In males, the luteinizing hormone stimulates the secretion of adrogens, such as testosterone, by ...
... Luteinizing hormone (LH): In females, it stimulates the ovulation and promotes the secretion of estrogens and progesterone by the ovaries and placenta in order to prepare the body for possible pregnancy. In males, the luteinizing hormone stimulates the secretion of adrogens, such as testosterone, by ...
140 Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland
... anterior pituitary to release gonadotropins, hormones that stimulate the gonads — the ovaries in females and the testes in males. Two gonadotropins are produced in humans, FSH and LH. In males, FSH promotes growth of Sertoli cells, which nourish sperm cells, and LH stimulates testosterone production ...
... anterior pituitary to release gonadotropins, hormones that stimulate the gonads — the ovaries in females and the testes in males. Two gonadotropins are produced in humans, FSH and LH. In males, FSH promotes growth of Sertoli cells, which nourish sperm cells, and LH stimulates testosterone production ...
CASE 33
... secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) from cells in the arcuate nucleus. Unlike the other hypothalamic hormones, to be effective, GnRH must be secreted in a pulsatile manner at a frequency of around 1 pulse per hour. Frequencies much higher or lower than that are not effective at stimul ...
... secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) from cells in the arcuate nucleus. Unlike the other hypothalamic hormones, to be effective, GnRH must be secreted in a pulsatile manner at a frequency of around 1 pulse per hour. Frequencies much higher or lower than that are not effective at stimul ...
Adolescence: Physical Development
... serious consequences and reinfection are higher for teens than adults. Berger: The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence, 7th Edition, Chapter 14 ...
... serious consequences and reinfection are higher for teens than adults. Berger: The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence, 7th Edition, Chapter 14 ...
hypothalamic-pituitary axis
... • Range from mild (GH) to lethal (ACTH) • Causes: tumour, trauma, infection, developmental etc • May be combined: panhypopituitarism ...
... • Range from mild (GH) to lethal (ACTH) • Causes: tumour, trauma, infection, developmental etc • May be combined: panhypopituitarism ...
Hormones and Young Living Essential Oils
... ovaries are oestrogen and progesterone. Oestrogen and progesterone are responsible for breast development, ovulation, and menstrual periods, as well as maintaining a pregnancy. The ovaries also produce inhibin, a protein that inhibits the release of FSH from the pituitary gland and help control egg ...
... ovaries are oestrogen and progesterone. Oestrogen and progesterone are responsible for breast development, ovulation, and menstrual periods, as well as maintaining a pregnancy. The ovaries also produce inhibin, a protein that inhibits the release of FSH from the pituitary gland and help control egg ...
What is the Endocrine System
... gonadotropins (luteinizing hormone or LH and follicle-stimulating hormone or FSH), they also control the menstrual cycle. The ovaries also produce inhibin, a protein that curbs the release of follicle-stimulating hormone from the anterior pituitary and helps control egg ...
... gonadotropins (luteinizing hormone or LH and follicle-stimulating hormone or FSH), they also control the menstrual cycle. The ovaries also produce inhibin, a protein that curbs the release of follicle-stimulating hormone from the anterior pituitary and helps control egg ...
Growth hormone
... biological functions. Prolactin secretion is controlled by an inhibitory dopaminergic path. Hyperprolactinaemia may be caused by drugs (with antidopaminergic actions e.g. metoclopramide), hypothyroidism, or prolactin secreting adenomas. Medical treatment is with bromocriptine, cabergoline, or ...
... biological functions. Prolactin secretion is controlled by an inhibitory dopaminergic path. Hyperprolactinaemia may be caused by drugs (with antidopaminergic actions e.g. metoclopramide), hypothyroidism, or prolactin secreting adenomas. Medical treatment is with bromocriptine, cabergoline, or ...
topic13 - Bukowian metodyczka - misiek-puchatek
... produced by direct action on growing cartilage, interference with production of growth hormone, or interference with the response to or production of somatomedin. Because of the growth-suppressing effect of cortisone in excess of minimal requirements, therapy is limited to short-term administration ...
... produced by direct action on growing cartilage, interference with production of growth hormone, or interference with the response to or production of somatomedin. Because of the growth-suppressing effect of cortisone in excess of minimal requirements, therapy is limited to short-term administration ...
Endocrine System - El Camino College
... more K+ and help to maintain ionic balance of extracellular fluids 2 Glucocorticoids – influence the energy metabolism of most cells, stimulated by ACTH of anterior pituitary. 3 Sex Corticoids – influence secondary sex characters. Adrenal Medulla secretes 2 hormones – Norepinephrine under normal con ...
... more K+ and help to maintain ionic balance of extracellular fluids 2 Glucocorticoids – influence the energy metabolism of most cells, stimulated by ACTH of anterior pituitary. 3 Sex Corticoids – influence secondary sex characters. Adrenal Medulla secretes 2 hormones – Norepinephrine under normal con ...
Dissection of the Brain, Hypothalamus and Pituitary
... 2) To introduce the anatomical, neural, and vascular relationships between the hypothalamus and the pituitary (anterior and posterior), which allow them to communicate with each other. ...
... 2) To introduce the anatomical, neural, and vascular relationships between the hypothalamus and the pituitary (anterior and posterior), which allow them to communicate with each other. ...
13 Physiologicoanatomical peculiarities of endocrine system in
... generally be described as anabolic (building up). Like most other protein hormones GH acts by interacting with a specific receptor on the surface of cells. Height growth in childhood is the best known effect of GH action, and appears to be stimulated by at least two mechanisms. 1. GH directly stimul ...
... generally be described as anabolic (building up). Like most other protein hormones GH acts by interacting with a specific receptor on the surface of cells. Height growth in childhood is the best known effect of GH action, and appears to be stimulated by at least two mechanisms. 1. GH directly stimul ...
Hormone Function
... hormone responsible for regulating body growth, and is important in metabolism Thyroid-stimulating Hormone (TSH): stimulates secretion of thyroid hormone & growth of thyroid gland Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH): stimulates cortisol secretion by the adrenal cortex & promotes growth of adrenal cor ...
... hormone responsible for regulating body growth, and is important in metabolism Thyroid-stimulating Hormone (TSH): stimulates secretion of thyroid hormone & growth of thyroid gland Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH): stimulates cortisol secretion by the adrenal cortex & promotes growth of adrenal cor ...
Pituitary lecture slides
... glucocorticoid deficient- Addison's disease ….see adrenal lecture week 5 ...
... glucocorticoid deficient- Addison's disease ….see adrenal lecture week 5 ...
The Endocrine System
... Thyroid and antithyroid Drugs Adrenal Drugs Pancreatic Drugs Gonadal hormones and inhibitors ...
... Thyroid and antithyroid Drugs Adrenal Drugs Pancreatic Drugs Gonadal hormones and inhibitors ...
Do you have low testosterone? Why does it
... Do you have low testosterone? Why does it matter? Testosterone is a hormone that plays an important role in both men and women. Testosterone is a steroid hormone, or androgen, that is produced mainly in the testicles of men and a small amount in the adrenal glands. In females, testosterone is produc ...
... Do you have low testosterone? Why does it matter? Testosterone is a hormone that plays an important role in both men and women. Testosterone is a steroid hormone, or androgen, that is produced mainly in the testicles of men and a small amount in the adrenal glands. In females, testosterone is produc ...
The Endocrine System
... Hormones A chemical substance produced by an endocrine gland is known as a hormone. You can think of a hormone as a chemical messenger. Each hormone has a specific function and specific “targets” in the body. Once released into the bloodstream, a hormone travels to its target cells, where it turns o ...
... Hormones A chemical substance produced by an endocrine gland is known as a hormone. You can think of a hormone as a chemical messenger. Each hormone has a specific function and specific “targets” in the body. Once released into the bloodstream, a hormone travels to its target cells, where it turns o ...
1. Endocrine Glands of the Body
... Sex Steroid Disorders: A. Kallmann Syndrome (Hypogonadism) = insufficient hypothalamic GnRH production. Results in less pituitary LH & FSH. Causes ↓testes growth and ↓ testosterone and estrogen production. In male child – can interfere with development of penis, testes, sperm production, and other m ...
... Sex Steroid Disorders: A. Kallmann Syndrome (Hypogonadism) = insufficient hypothalamic GnRH production. Results in less pituitary LH & FSH. Causes ↓testes growth and ↓ testosterone and estrogen production. In male child – can interfere with development of penis, testes, sperm production, and other m ...
Endocrine Gland Matching
... Endocrine Gland Matching - KEY Match the hormones to the gland which secretes them. ...
... Endocrine Gland Matching - KEY Match the hormones to the gland which secretes them. ...
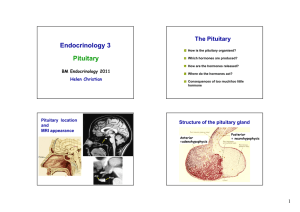
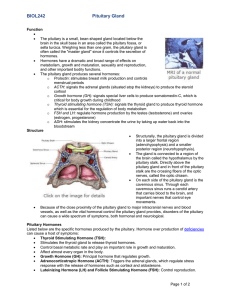
BIOL242pituitaryOCT2012
... The pituitary is a small, bean-shaped gland located below the brain in the skull base in an area called the pituitary fossa, or sella turcica. Weighing less than one gram, the pituitary gland is often called the "master gland" since it controls the secretion of hormones. Hormones have a dramatic ...
... The pituitary is a small, bean-shaped gland located below the brain in the skull base in an area called the pituitary fossa, or sella turcica. Weighing less than one gram, the pituitary gland is often called the "master gland" since it controls the secretion of hormones. Hormones have a dramatic ...
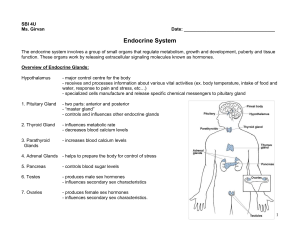
Endocrine System booklet
... Endocrine System The endocrine system involves a group of small organs that regulate metabolism, growth and development, puberty and tissue function. These organs work by releasing extracellular signaling molecules known as hormones. Overview of Endocrine Glands: Hypothalamus ...
... Endocrine System The endocrine system involves a group of small organs that regulate metabolism, growth and development, puberty and tissue function. These organs work by releasing extracellular signaling molecules known as hormones. Overview of Endocrine Glands: Hypothalamus ...
Puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction to enable fertilization. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a girl, the testes in a boy. In response to the signals, the gonads produce hormones that stimulate libido and the growth, function, and transformation of the brain, bones, muscle, blood, skin, hair, breasts, and sex organs. Physical growth—height and weight—accelerates in the first half of puberty and is completed when the child has developed an adult body. Until the maturation of their reproductive capabilities, the pre-pubertal physical differences between boys and girls are the external sex organs.On average, girls begin puberty at ages 10–11; boys at ages 11–12. Girls usually complete puberty by ages 15–17, while boys usually complete puberty by ages 16–17. The major landmark of puberty for females is menarche, the onset of menstruation, which occurs on average between ages 12–13; for males, it is the first ejaculation, which occurs on average at age 13. In the 21st century, the average age at which children, especially girls, reach puberty is lower compared to the 19th century, when it was 15 for girls and 16 for boys. This can be due to any number of factors, including improved nutrition resulting in rapid body growth, increased weight and fat deposition, or exposure to endocrine disruptors such as xenoestrogens, which can at times be due to food consumption or other environmental factors. Puberty which starts earlier than usual is known as precocious puberty. Puberty which starts later than usual is known as delayed puberty.Notable among the morphologic changes in size, shape, composition, and functioning of the pubertal body, is the development of secondary sex characteristics, the ""filling in"" of the child's body; from girl to woman, from boy to man. Derived from the Latin puberatum (age of maturity), the word puberty describes the physical changes to sexual maturation, not the psychosocial and cultural maturation denoted by the term adolescent development in Western culture, wherein adolescence is the period of mental transition from childhood to adulthood, which overlaps much of the body's period of puberty.