* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pituitary lecture slides
Human chorionic gonadotropin wikipedia , lookup
Bovine somatotropin wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Hormonal contraception wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency wikipedia , lookup
Vasopressin wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
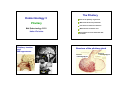
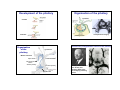
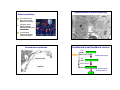
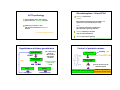
The Pituitary Endocrinology 3 How is the pituitary organised? Pituitary Which hormones are produced? How are the hormones released? BM Endocrinology 2011 Helen Christian Where do the hormones act? Consequences of too much/too little hormone Pituitary location and MRI appearance Structure of the pituitary gland Anterior A t i =adenohypophysis Ant Posterior = neurohypophysis Post 1 Development of the pituitary Organisation of the pituitary 5 weeks 20 weeks pituitary fossa Organisation of the pituitary ‘transphenoidal surgery’ The discovery of hypothalmic control of the pituitary hypothalamus Median eminence Optic chiasm ‘neurosecretion’ internal carotid branch Anterior pituitary Posterior pituitary jugular vein Geoffrey Harris 1913 – 1971 1977 Schally and Guillemin Nobel prize for identifying releasing factors 2 Ultrastructure of anterior pituitary Anterior pituitary PRL ACTH five endocrine cell types each secrete different hormone(s) cell types can be differentiated by antibody labelling and cell structure capillary non-secretory supporting cell type ‘folliculo-stellates’ Fenestrated capillaries Feedforward and feedback control - ve inhibitory feedback fenestrations Hypothalamus R l Releasing i hormone h - ve feedforward control Anterior pituitary Trophic hormone capillary Endocrine gland Target e.g. cortisol release from the adrenal 3 The hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis cold hypothalamus TRH Inhibitory feedback Ch i l type: Chemical t polypeptide l tid hormone h from f POMC precursor, secreted by corticotroph cells Thyrotrophin Releasing Hormone thyrotrophs anterior pituitary TSH Receptor: G protein coupled receptor to cAMP Thyroid Stimulating Hormone thyroid T3 and T4 GPCRGPCR cAMP Pathology of TSH secretion is v rare The hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis hypothalamus Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) Stress hypoglycaemia Actions: stimulates secretion of cortisol (glucocorticoid hormone) from adrenal cortex in stress stimulates growth of adrenal cortex Diurnal rhythm of plasma ACTH and cortisol Inhibitory feedback anterior pituitary corticotrophs ACTH adrenal cortex Corticotrophin Releasing Hormone co ortisol CRH glucocorticoids, cortisol 4 Gonadotrophins: LH and FSH ACTH pathology Actions: reproduction excess ACTH ACTH, and in turn excess glucocorticoid, - Cushing's disease deficiency of ACTH, in turn glucocorticoid deficient- Addison's disease ….see adrenal lecture week 5 Female: FSH follicle development and ovulation, LH synthesis of sex steroids by the ovary Male: LH controls testosterone production p production p FSH stimulates sperm Deficit: infertility in adult life lack of sexual maturation Excess: precocious puberty See Trinity term Reproduction lectures Hypothalamo-pituitary-gonadal axis hypothalamus GnRH anterior pituitary gonadotrophs -ve LH + FSH ovary estrogen LH = luteinising hormone FSH = follicle stimulating hormone Cyclical release in menstrual c cle cycle Control of prolactin release hypothalamus dopamine INHIBITORY anterior pituitary lactotrophs PRL tyrosine kinase enzyme -linked receptors testes testosterone suckling +ve Breast growth and milk production Inhibits reproduction lactational amenorrhaea 5 Control of prolactin release Growth hormone axis Hypothalamus Only yp pituitary y hormone whose principal control is inhibitory GHRH Anterior pituitary somatotrophs PRL production is stimulated by estrogen during pregnancy Dopamine agonists e.g. bromocryptine, suppress lactation Pathology: prolactinomas hypersecrete PRL – cause infertility and milk production Growth hormone release is pulsatile Li Liver IGFs GH -ve GH GH Enzymelinked receptors Long bone and muscle growth GH pathology Gigantism due to excess GH secretion Short stature if lack GH nb if prior to epiphyseal plate fusion at puberty March 2010 Sultan Kosen 8ft 1 is the tallest man in the world and China’s He Pingping the smallest at 2ft 5in. 6 Acromegaly Mutations in Aryl hydrocarbon-interacting protein predisposes to pituitary adenoma in childhood Due to excess GH secretion after epiphyseal plates have fused Enlargement of hands and feet Coarsening of facial features – largening of nose DNA extracted from the skeleton of a 7ft 7in patient b1761 kept in Hunterian museum, London. The same mutation was identified in 4 living N Ireland families who presented with gigantism. Weight gain Pituitary tumours hormonal effects: hormone-secreting tumours effects depend on cell type mechanical effects: affects vision as presses on optic chiasm Posterior pituitary Formed by axons and terminals of hypothalamic neurosecretory neurons Ant Post Secretes peptide hormones anti-diuretic hormone ((ADH,, also known as vasopressin) and oxytocin Adenoma 7 Stimulation of posterior pituitary hormone release hypothalamus: oxytocin and ADH produced in cell bodies Antidiuretic hormone - ADH ( = vasopressin) Chemical type: Peptide 9 amino acids Receptors G protein coupled to cAMP Stimulus depolarises neuron axon Ca2+ posterior pituitary Actions increases c eases water ate reabsorption eabso pt o in collecting ducts of kidney action potential exocytosis See Trinity term Kidney lectures Stimuli of ADH release Plasma osmolality Blood volume Diabetes insipidus Too little ADH function Two types: hypothalamic: lack of ADH production renal: lack of ADH action ‘Brattleboro rat’ lacks ADH, drinks 70% of body weight per day, urinates constantly 8 Oxytocin Chemical nature: peptide Receptors: PLC-coupled Control of oxytocin release stretch of cervix/vagina at parturition suckling – nipple stimulation causes milk-ejection reflex Actions: Pathology contraction of uterine muscle l in i childbirth hildbi th deficit may cause prolonged labour milk ejection by contraction of breast myoepithelium knockout mice labour normal but no milk-ejection See Trinity term Reproduction lectures Pituitary : the master gland Endocrinology Week 1 General principles Week 1 Hormone action Week 2 Endocrine pancreas Week 3 Pituitary Week 4 Thyroid Week 5 Adrenal Week 6 Endocrinology Cells and Tissues Any questions email: [email protected] 9