* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Dissection of the Brain, Hypothalamus and Pituitary
Progesterone wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Sexually dimorphic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Hormonal contraception wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Vasopressin wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Adrenal gland wikipedia , lookup
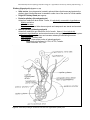
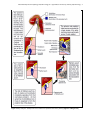
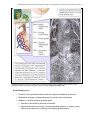
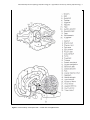
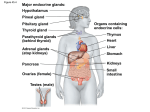
ANS 3319C Reproductive Physiology and Endocrinology Lab Hypothalamic and Pituitary Anatomy & Endocrinology Objectives 1) To provide an introduction to the gross anatomy of the brain with emphasis on dissection of the hypothalamus and pituitary. 2) To introduce the anatomical, neural, and vascular relationships between the hypothalamus and the pituitary (anterior and posterior), which allow them to communicate with each other. 3) To provide an introduction to hormones synthesized/secreted by the hypothalamus and the anterior and posterior pituitary with emphasis on reproductive hormones. Gross Anatomy of the Brain (Figure 5) Cerebrum: center of higher mental functions, voluntary muscle control. Cerebellum: controls the property of movements, speed, acceleration, and trajectory. Brainstem: midbrain: auditory and visual reflex centers. pons, medulla: postural reflexes and other reflex centers. Olfactory bulb: involved in distinguishing smell. Optic chiasma: where the optic nerves cross to contralateral sides. Pituitary: composed of neurohypophysis and adenohypophysis; master gland controlling body’s internal environment. Corpus collosum: the commissure between the hemispheres of the brain. Pineal body: synthesis and secretion of melatonin. Hypothalamus: controls body’s internal environment. Stalk median eminence: area between the hypothlalmus and the pituitary. Mammillary body Third ventricle of the brain Anatomy of the Hypothalamus, Pituitary & Pineal Gland Hypothalamus (Figures 1 & 5) • Neuroendocrine gland comprised of numerous paired nuclei that integrate physiological signals of the body. • Occupies a small portion of the third ventricle, extending from the optic chiasma to the mammillary bodies. • Synthesizes and secretes hormones that act on the pituitary (See Hormone Table): Releasing & Inhibiting hormones: small peptides secreted from hypothalamus that control the secretion of protein hormones from the pituitary gland Hormones directly associated with reproduction: GnRH, CRH, PIF, PRF Two important nuclei related to reproduction, which secrete GnRH: Arcuate nucleus - controls basal secretion of LH and FSH. Preoptic nucleus - controls preovulatory surge of LH and FSH. Hormones indirectly associated with reproduction: TRH, GHRH, GHIH Hormones Oxytocin - released from paraventricular nucleus (PVN). Vasopressin - released from supra-optic nucleus (SON). ANS 3319C Reproductive Physiology and Endocrinology Lab – Hypothalamic and Pituitary Anatomy & Endocrinology 2 AH – adenohypophysis AHA – anterior hypothalamic area ARC – arcuate nucleus DHA – dorsal hypothalamic area DMN – dorsal medial nucleus MB – mammillary body ME – median eminence NH – neurohypophysis OC – optic chiasm PHA – posterior hypothalamic area PM – premammillary nucleus PON – preoptic nuclei PT – pars tuberalis PVN – paraventricular nuclei SCN – suprachiasmatic nucleus SON – supraoptic nuclei VMN – ventromedial nucleus Figure 1. Schematic drawing of hypothalamic nuclei and pituitary from the side (top) and frontal view (bottom). Median Eminence (Figures 1, 2) • Area where hypothalamic hormones are released from nerve endings into the capillary plexus called the hypophyseal portal blood system that serves the anterior pituitary. Hypophyseal Portal Blood System (Figures 2, 4) • Capillary system that transports hypothalamic releasing/inhibiting hormones via a vasculature system to the anterior pituitary; allowing for “communication between the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary.” Prevents hormones from entering the general circulation where they would be degraded quickly. ANS 3319C Reproductive Physiology and Endocrinology Lab – Hypothalamic and Pituitary Anatomy & Endocrinology 3 Pituitary (Hypophysis) (Figures 1,2,3,5) • Sella turcica - bony depression located in sphenoid bone that houses and protects the pituitary gland. Named because it resembles a side view of the seat of a Turkish saddle. • Origin of Pituitary Gland (See Figure 3) • Posterior pituitary (Neurohypophysis) Arises from embryonic brain tissue. Hence, it is physically connected to hypothalamus. Median eminence Infundibular stem Pars nervosa - neural lobe where oxytocin and vasopressin are stored and secreted. • Anterior pituitary (Adenohypophysis) Arises from embryonic gut tissue from roof of mouth. Hence, it is not physically connected to hypothalamus and receives hormones via hypophyseal portal blood system. Pars intermedia - synthesizes and secretes melanocyte stimulating hormone. Pars tuberalis - pituitary stalk. Pars distallis - forms major portion of adenohypophysis. Reproductive hormones: LH, FSH, ACTH, Prolactin Other hormones: GH, TSH Figure 2. Schematic providing an anatomical overview of the hypothalamic-pituitary axis. ANS 3319C Reproductive Physiology and Endocrinology Lab – Hypothalamic and Pituitary Anatomy & Endocrinology 4 Figure 3 Early embryonic development of the anterior and posterior lobes of the pituitary (Figure 4.3 Senger text). ANS 3319C Reproductive Physiology and Endocrinology Lab – Hypothalamic and Pituitary Anatomy & Endocrinology 5 Figure 4. Diagramatic view of the hypophyseal portal system between the hypothalamus and the pituitary and a photograph showing the intense vascularity of the portal system (Figure 5.5; Senger text) Pineal Gland (Figure 5) • Posterior to the hypothlamus and between the cerebral hemispheres of the brain. • Responds to changes in photoperiod sensed by visual system of mammals. • Melatonin - hormone produced by pineal gland. • Secretion is enhanced by the onset of darkness. • Regulates reproductive function in seasonal breeding animals (i.e., sheep, horses, numerous wild animals) by inhibiting or stimulating gonadal function. ANS 3319C Reproductive Physiology and Endocrinology Lab – Hypothalamic and Pituitary Anatomy & Endocrinology 6 Figure 5. Gross anatomy of the equine brain – ventral view and sagittal section. ANS 3319C Reproductive Physiology and Endocrinology Lab – Hypothalamic and Pituitary Anatomy & Endocrinology 7 Summary of endocrine glands and hormones they secrete Gland Hormone Class Function Hypothalamus Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone (GnRH) Prolactin Inhibiting Factor (PIF) Prolactin Releasing Factor (PRF) Thyrotropin Releasing Hormone (TRH) Corticotropin Releasing Hormone (CRH) Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone (GHRH) Growth Hormone Inhibiting Hormone (GHIH) (Also known as Somatostatin) Peptide Peptide Peptide Peptide Peptide Peptide Peptide Stimulates release of FSH and LH Inhibits prolactin release Stimulates prolactin release Stimulates release of TSH, prolactin, GH (cattle & rats) Stimulates release of ACTH Stimulates release of GH Inhibits release of GH Oxytocin and Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) Peptide Produced in HYPOTH but stored in the posterior pituitary Growth Hormone (GH) Protein Promotes tissue growth and general metabolism Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) Peptide Stimulates the adrenal cortex Thyrotropic Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Glycoprotein Stimulates release of thyroid hormones Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) Glycoprotein Stimulates follicular growth, spermatogenesis, estrogen release Luteinizing Hormone (LH) Glycoprotein Ovulation - CL formation, function and progesterone secretion Secretion of estrogen and androgens Prolactin (PRL) Protein Promotes lactation and maternal behavior Stimulates CL formation and progesterone secretion some species Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) Peptide Water conservation, smooth muscle contraction Oxytocin Peptide Smooth muscle contraction, parturition, milk letdown Luteolytic action, sperm and egg transport Thyroid Thyroxin (T4) Triiodothyronine (T3) Modified AA Enhances protein synthesis, increases general metabolism Pineal Gland Melatonin Modified AA Regulates gonadal function in seasonal breeding animals Anterior Pituitary Posterior Pituitary ANS 3319C Reproductive Physiology and Endocrinology Lab – Hypothalamic and Pituitary Anatomy & Endocrinology 8 Gland Hormone Class Function Parathyroid Parathyroid Hormone Peptide Regulates calcium and phosphorous metabolism Pancreas Insulin Glucagon Protein Peptide Regulates carbohydrate metabolism Regulates carbohydrate metabolism Adrenal Medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine Modified AA Modified AA Augments sympathetic nervous system, prepares for emergencies Energy mobilization, activates adenylate cyclase Adrenal Cortex Glucorticoids (cortisol, cortisone, corticosterone) Steroid Initiation of parturition, milk synthesis, energy metabolism Decreases inflammatory and immunologic responses Mineralocorticoids (aldosterone) Steroid Regulate sodium and potassium metabolism Estrogen (from follicles) Steroid Promotes female sex behavior; maintenance of female duct system Stimulates secondary sex characteristics; anabolic actions Stimulates calcium uptake in bones Mammary growth and development Uterine contractions and secretions Progesterone (from corpus luteum - CL) Steroid Preparation and maintenance of uterus for pregnancy Stimulates endometrial secretions Prepares mammary gland for lactation Control of gonadotroptin secretion; anabolic effects Inhibins Protein Prevents release of FSH Testis Testosterone Steroid Male mating behavior and stimulates secondary sex characteristics Development and maintenance of male duct system Spermatocytogenesis Anabolic effects Placenta Equine Chorionic Gonadotropin (eCG) Estrogens/Progesterone Placental Lactogen Glycoprotein Steroid Glycoprotein Formation of accessory CL - progesterone synthesis See ovary Stimulates mammary growth and secretions; nutrient flow to fetus Uterus Prostaglandin F2α Relaxin Lipid Protein Regression of CL and initiation of parturition Dilates cervix Ovary