glands of the human body
... Suprarenal gland- ACTH stimulates the cortex of the suprarenal glands to secrete steroid hormones that help the body resist stress, they also affect the metabolism. Thyroid gland- TSH stimulates the thyroid to secrete hormones that affect metabolism and body heat production, and promote normal devel ...
... Suprarenal gland- ACTH stimulates the cortex of the suprarenal glands to secrete steroid hormones that help the body resist stress, they also affect the metabolism. Thyroid gland- TSH stimulates the thyroid to secrete hormones that affect metabolism and body heat production, and promote normal devel ...
Chapter 9 Concept Map Review
... What is the hormone that is present in the urine during pregnancy that is detectable by home pregnancy tests? ...
... What is the hormone that is present in the urine during pregnancy that is detectable by home pregnancy tests? ...
Endocrine Introduction
... Maintenance of homeostasis, fluid and electrolyte balance (Na+, K+, Ca++, glucose, water ) ...
... Maintenance of homeostasis, fluid and electrolyte balance (Na+, K+, Ca++, glucose, water ) ...
PDF - True-2-me
... of glucocorticoid by adrenals, contributing to normal blood pressure and electrolyte balance. • The second cell type (thyrotrophs) produces thyroid-stimulated hormone (TSH) that stimulates thyroid hormone release by the thyroid gland, contributing to metabolism. ...
... of glucocorticoid by adrenals, contributing to normal blood pressure and electrolyte balance. • The second cell type (thyrotrophs) produces thyroid-stimulated hormone (TSH) that stimulates thyroid hormone release by the thyroid gland, contributing to metabolism. ...
Indezine Template
... • Hormones: are natural chemicals that exert their effects on specific tissues known as target tissues. • Endocrine Glands are ductless and must use the blood system to transport secreted hormones to target tissues ...
... • Hormones: are natural chemicals that exert their effects on specific tissues known as target tissues. • Endocrine Glands are ductless and must use the blood system to transport secreted hormones to target tissues ...
Objectives for Chapter 9
... 1. Define negative feedback and understand how the endocrine system uses negative feedback mechanisms to maintain homeostasis. 2. Know the 3 different kinds of hormones and their mechanisms of action (i.e. how they bring about their effect in the body) 3. Locate on a diagram and describe the functio ...
... 1. Define negative feedback and understand how the endocrine system uses negative feedback mechanisms to maintain homeostasis. 2. Know the 3 different kinds of hormones and their mechanisms of action (i.e. how they bring about their effect in the body) 3. Locate on a diagram and describe the functio ...
Anterior pituitary hormones
... (neurohypophysis). The anterior pituitary hormones and their corresponding regulatory hormones/factors are described in detail below. Secretion of most of the hormones of the anterior pituitary is under the control of the hypothalamus. Secretion also controlled by the rate of secretion of ...
... (neurohypophysis). The anterior pituitary hormones and their corresponding regulatory hormones/factors are described in detail below. Secretion of most of the hormones of the anterior pituitary is under the control of the hypothalamus. Secretion also controlled by the rate of secretion of ...
BioBases Exam 2
... ACTH – adreno-co-tropic hormone: stimulates pn of cortisol from adrenal glands. 3) Posterior Pituitary: (a) releases 2 hormones pd in HYPOTHALAMUS (i) ADH – anti-diuretic hormone: blood volume control (retains water in blood) (ii) Oxytocin – stimulates uterine contractions and lactation Thyroid: g ...
... ACTH – adreno-co-tropic hormone: stimulates pn of cortisol from adrenal glands. 3) Posterior Pituitary: (a) releases 2 hormones pd in HYPOTHALAMUS (i) ADH – anti-diuretic hormone: blood volume control (retains water in blood) (ii) Oxytocin – stimulates uterine contractions and lactation Thyroid: g ...
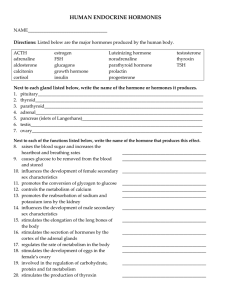
human endocrine hormones
... Directions: Listed below are the major hormones produced by the human body. ACTH adrenaline aldosterone calcitonin cortisol ...
... Directions: Listed below are the major hormones produced by the human body. ACTH adrenaline aldosterone calcitonin cortisol ...
The Pituitary Gland
... kidney cells, stimulating the nephrons to absorb or release water. This regulates the water balance inside the body. 2. oxytocin – produced only by females, this hormone is responsible for initiating uterine contractions, mild during monthly menstrual flow and strong during labor contractions. ...
... kidney cells, stimulating the nephrons to absorb or release water. This regulates the water balance inside the body. 2. oxytocin – produced only by females, this hormone is responsible for initiating uterine contractions, mild during monthly menstrual flow and strong during labor contractions. ...
ADENOHYPOPHYSIAL HORMONES
... Corticotrophin releasing factor (CRF) ===> corticotrophin or adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) ===> cortisol, aldosterone - cortisol in inhibits protein synthesis, stimulates gluconeogenesis (synthesis of glucose from proteins), inhibits conversion of carbohydrates to fats - aldosterone regulates ...
... Corticotrophin releasing factor (CRF) ===> corticotrophin or adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) ===> cortisol, aldosterone - cortisol in inhibits protein synthesis, stimulates gluconeogenesis (synthesis of glucose from proteins), inhibits conversion of carbohydrates to fats - aldosterone regulates ...
Lecture 8 - Endocrine
... • Influences growth, metabolism, and homeostasis over prolonged periods • Secretes hormone products into interstitial spaces which are then absorbed into the blood and transported throughout the body • Hormonal control is much slower than nervous control, but the effects of the endocrine system are ...
... • Influences growth, metabolism, and homeostasis over prolonged periods • Secretes hormone products into interstitial spaces which are then absorbed into the blood and transported throughout the body • Hormonal control is much slower than nervous control, but the effects of the endocrine system are ...
Endocrine Diseases
... Glucose challenge post fast- Elevated GH levels help confirm the diagnosis (should normally be < 1ng/mL). MRI- Usually identifies a pituitary adenoma. ...
... Glucose challenge post fast- Elevated GH levels help confirm the diagnosis (should normally be < 1ng/mL). MRI- Usually identifies a pituitary adenoma. ...
Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
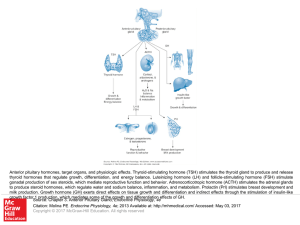
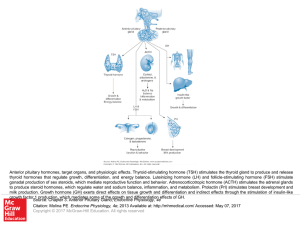
... Anterior pituitary hormones, target organs, and physiologic effects. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormones that regulate growth, differentiation, and energy balance. Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimu ...
... Anterior pituitary hormones, target organs, and physiologic effects. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormones that regulate growth, differentiation, and energy balance. Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimu ...
Slide ()
... Anterior pituitary hormones, target organs, and physiologic effects. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormones that regulate growth, differentiation, and energy balance. Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimu ...
... Anterior pituitary hormones, target organs, and physiologic effects. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormones that regulate growth, differentiation, and energy balance. Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimu ...
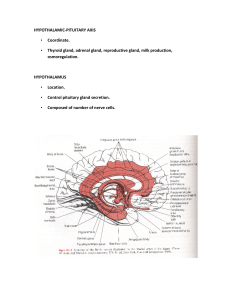
HYPOTHALAMIC-PITUITARY AXIS • Coordinate. • Thyroid gland
... HYPOTHALAMIC-HYPOPHYSIAL PORTAL SYSTEM ...
... HYPOTHALAMIC-HYPOPHYSIAL PORTAL SYSTEM ...
16kDa Prolactin Fragment Inhibits VEGF
... inhibitors and activators counter balance each other out until one overcomes the other. A build-up of activators leads to agiogenesis while a build-up of inhibitors prevents angiogenesis. In recent years, a great deal of research has been devoted to find ways to inhibit this event which would starve ...
... inhibitors and activators counter balance each other out until one overcomes the other. A build-up of activators leads to agiogenesis while a build-up of inhibitors prevents angiogenesis. In recent years, a great deal of research has been devoted to find ways to inhibit this event which would starve ...
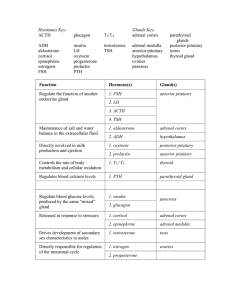
Hormones Key: Glands Key: ACTH glucagon T3/T4 adrenal cortex
... Maintenance of salt and water balance in the extracellular fluid ...
... Maintenance of salt and water balance in the extracellular fluid ...