* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Polycystic ovary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cryptorchidism wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
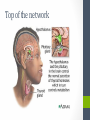
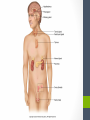
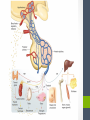
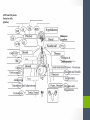
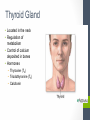
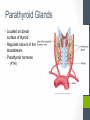
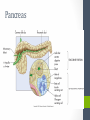
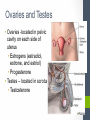
Chapter Thirteen Endocrine System Functions • Growth and development • Homeostasis (the internal balance of body systems) • Metabolism (body energy levels) • Reproduction • Response to stimuli (stress and/or injury) Hormones – “Messengers” • What is a hormone? • chemical transmitter that is transported via the bloodstream to a target organ or other cells • In Greek it means…. • to excite or to urge on. Hormones - Communicators Communicators – secretion Hypersecretion – too much Or Hyposecretion – too little of specific hormones can cause or be associated with conditions Top of the network Hypothalamus – “Governor” • Primary link between endocrine system and nervous system • The hypothalamus is highly involved in pituitary gland function. • When it receives a signal from the nervous system, the hypothalamus secretes substances known as neurohormones that start and stop the secretion of pituitary hormones. Name Primary Endocrine Glands • Pituitary Gland (hypophysis)- called the Master Gland • Anterior lobe • Posterior lobe • • • • • Pineal Gland Thyroid Gland Parathyroid Gland Pancreas (islets of Langerhans) Adrenals Gland (supraenals) • Adrenal Cortex • Adrenal Medulla • Ovaries • Testes Pituitary Gland/Hypophysis “Master Gland” • Anterior lobe/ adenohypophysis (aden/o, hypophys/o) GH- Growth ACTH - Andrenocortiocotropin TSH-Thyroid FSH- Follicle LH - Luteinizing PRL - Prolactin MSH- Melanocyte • Posterior lobe/ ADH- Antidiuretic (vasopressin neurohypophysis [VP]) (neur/o, hypophys/o) Oxytocin Pineal Gland Located near the hypothalamus Secretion of melatonin and serotonin Thyroid Gland • Located in the neck • Regulation of metabolism • Control of calcium deposited in bones • Hormones • Thyroxine (T4) • Triodothyronine (T3) • Calcitonin Parathyroid Glands • Located on dorsal surface of thyroid • Regulate calcium in the bloodstream • Parathyroid hormone • (PTH) Pancreas • Exocrine function (into a duct system or cavity) • Release digestive enzymes • Endocrine function (into the blood system) • Regulate glucose in blood • Islets of Langerhans • Glucagon- breakdown of glycogen to glucose • Insulin – maintains normal blood sugar • Somatostatin- suppresses the release of glucagon and insulin Pancreas Adrenal Glands/Suprarenals • Located on top of each kidney • Adrenal cortex • Cortisol • Corticosterone • Aldosterone • Testosterone • Androsterone • Adrenal medulla • Dopamine, • Epinephrine (adrenaline) • Norepinephrine (nonadrenaline) Ovaries and Testes • Ovaries -located in pelvic cavity on each side of uterus • Estrogens (estradiol, estrone, and estriol) • Progesterone • Testes – located in scrotum • Testosterone Thymus Gland • The thymus gland, located behind your sternum and between your lungs, is only active until puberty. • After puberty, the thymus starts to slowly shrink and become replaced by fat. • Thymosin promotes maturation of T Lymphocytes • Thymopoietin – influences the production Prefixes Challenge 1. Dia2. Eu3. Endo4. Ex5. Exo6. Hypo7. Pro8. Hydro9. Endo10. Hyper11. Para- 1. Through, between, complete 2. Good, normal 3. Within, inner, 4. Out, away from 5. Out, away from 6. Below, under, deficient 7. Before, in front of 8. Water 9. Within, inner 10. Above, under deficient 11. Beside, along side, abnormal Combining Forms- page 447 aden/o adren/o crin/o estr/o gluc/o, glyc/o galact/o ger/o gonad/o hirsut/o kal/I myx/o pancreat/o somat/o thyr/o, thyroid/o parathyroid/o calc/o thym/o trop/o Goiter – Thyroid • The term “goiter” simply refers to the abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland. • One cause is iodine deficiency • The gland cannot make enough thyroid hormone if it does not have enough iodine, which can lead to hypothyroid. Adrenal Gland Disorders • Addison disease • Hyposecretion of cortisol • Cushing disease • Hypersecretion of cortisol Cushing disease Diabetes Mellitus • With diabetes mellitus, either your body doesn't make enough insulin, it can't use the insulin it does produce, or a combination of both. • Dia – through • -betes – to go • Experience polyuria • They will become increasingly thirsty, polydipsia • Polyphagia • Lethargy Name one disease • Name one disease due to • Hypersecretion • Hypersecretion Signs and Symptoms of Endocrine Disorders • Hypo • Hyper • Para -Kalemia -Thyroidism -Gonadism -Physis -Thyroidism -Insulinism -Cortisone Excisions • Adrenalectomy • Hypophysectomy • Parathyroidectomy • Thyroidectomy Hypophysectomy