* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Endocrine System
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Polycystic ovary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Graves' disease wikipedia , lookup
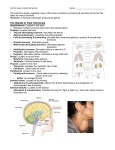
The Endocrine System -the 2nd in control- The Endocrine System Composed of several ductless glands – Pituitary (anterior & posterior) – Thyroid – Adrenal/ Supraranal – Pineal – Thymus – ALONG w/ the Pancreas, Placenta & Gonads Endocrine endo= within & crine=to secrete Made of glands • Secrete hormone directly into bloodstream (ductless glands) • Specialized epithelial tissue >12.5g Hormones (hormon = excite) – Chemical messengers released into the blood & lymph for transport around the body – Long lasting effect – Effect target cells or organs Hormone Function • reproduction • growth & development • mobilization of body defenses • cellular metabolism & homeostasis Mechanisms of hormone release (a) Humoral: in response to changing levels of ions or nutrients in the blood (b) Neural: stimulation by nerves (c) Hormonal: stimulation received from other hormones 6 Hormone Control Negative Feedback 1. Blood level of hormone falls 2. Brain gets message & sends out hormone to stimulate gland 3. Gland secretes hormone 4. When blood level of hormone increases, then brain hormone stops Hypothalamus Releasing hormones Nervous Anterior pituitary Posterior pituitary Thyrotropin Somatotropin LH ACTH Adrenal Thyroid Cortex Pancreas T3 Cortisol aldosterone Muscles liver Tissues FSH Ovary Vasopressin Prolactin Adrenal Medulla Testis Insulin, Estradiol Testosterone glucagon, somatostatin Liver, muscles Reproductive organs Oxytocin Epinephrine Mammary glands Pituitary Gland Anterior Pituitary I Growth Hormone • stimulates body to grow & burn carbohydrates (sugars) & fat Dwarfism hyposecretion Gigantism hypersecretion Anterior Pituitary II Melanocyte-stimulating Hormone • increases amount of pigmentation in skin Prolactin • stimulates milk production and maintains it Adrenocorticotropic Hormone • controls the secretion of hormones from the adrenal cortex Thyroid Stimulating Hormone • controls the release of hormones from the thyroid gland Anterior Pituitary III Follicle-Stimulating Hormone • stimulates development of ova and estrogen production in ovaries; stimulates sperm production Lutenizing Hormone • stimulates ovulation and prepares uterus for possible implantation of fertilized ovum; stimulates the production of testosterone Posterior Pituitary Oxytocin • stimulates contraction of uterus & of the cells surrounding the mammary glands Antidiuretic hormone • regulates fluid balance by reabsorbing water in the kidneys; also helps to regulate blood pressure Thyroid Gland Thyroxine & Triiodothyronine • stimulates metabolism; promotes protein synthesis, glucose uptake and lipid metabolism; is regulated by TSH Calcitonin • reduces Ca and P levels in blood; Thyroid Disorders Cretinism Hyposecretion (children) Graves’ Disease hypersecretion Myxedema Hyposecretion (adults) Goiter Adrenal or Suprarenal Glands (adrenal cortex)- glands on top of kidneys Aldosterone • maintains fluid balance by conserving Na and excretion of K; cause water retention and increased blood pressure Cortisol • promotes glucogenesis in liver; inhibits allergic response and reduces inflammation Androgens and Estrogens • sex hormones Adrenal or Suprarenal Glands (adrenal cortex) disorders Cushion’s Disease Androgenital syndrome Adrenal or Suprarenal Glands (Adrenal Medulla) epinephrine & norepinephrine • copy effects of the sympathetic nervous system Pancreas Glucagon • stimulates conversion of glycogen to glucose Insulin • stimulates conversion of glucose to glycogen; stimulates uptake of glucose by muscle and nerve cells • Diabetes Mellitus – Hypo/hyper secretion of insulin Pineal Gland Melatonin • regulates diurnal biorhythms; highest at night Thymus Gland Thymosin • stimulates the production of T-cells Gonads Ovaries - Estrogens • stimulates development of sex organs and secondary sex characteristics Testes -Testosterone • stimulates development of sex organs and secondary sex characteristics Placenta Human Chorionic Gonadotropin • stimulates production of estrogen and progesterone during pregnancy Human Placental Lactogen • prepare breasts for milk production Relaxin • loosens mother's pelvic ligaments and pubic symphysis ENDOCRINE DISORDERS GIGANTISM: • Hyperactive pituitary in preadolescence • Overgrowth of long bones Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal 20 ENDOCRINE DISORDERS ACROMEGALY: • Hyperactive pituitary in adulthood • Over development of bones in face, hands, feet Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal 20 ENDOCRINE DISORDERS Dwarfism: • Hypoactive pituitary in childhood Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal 20 ENDOCRINE DISORDERS GOITER • Thyroid hyper secretion • Enlarged thyroid gland due to iodine insufficiency Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal 22 ENDOCRINE DISORDERS CRETINISM • Results from thyroid hormone insufficiency in infancy Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal 21 ENDOCRINE DISORDERS Grave’s Disease/Exophthalmos • Hyperactive thyroid • Bulging eyes Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal 22 ENDOCRINE DISORDERS Hypothyroidism • Hypoactive thyroid Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal 22 ENDOCRINE DISORDERS CUSHING’S SYNDROME • hypersecretion of adrenal cortex • Adipose tissue accumulates in cheeks & base of neck Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal 23 ENDOCRINE DISORDERS Diabetes • hyposecretion of insulin • Untreated = hyperglycemia (too much sugar in blood) • Overtreated = hypoglycemia (too little sugar in blood) Endocrine System…. Professor KS Satyapal 23