* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Republican Government
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Roman Senate wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Sumptuary law wikipedia , lookup
Centuriate Assembly wikipedia , lookup
Leges regiae wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Senatus consultum ultimum wikipedia , lookup
Roman consul wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Conflict of the Orders wikipedia , lookup
Legislative assemblies of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Augustus wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Executive magistrates of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
History of the Roman Constitution wikipedia , lookup
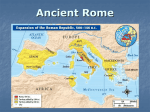
Name: KEY Period: Date: World History – Mrs. Schenck 1-3 Notes 5-7 brain Republican Government FQ: How did Roman republican government influence American government? 1. The evolution of government in ancient Greece: monarchy oligarchy dictatorship democracy (direct) 2. The evolution of government in ancient Rome: monarchy republic (representative democracy) dictatorship 3. Who are the Founders? The creators of the U.S. Constitution (tells how the govt. works) – the foundation of our government. What is Republican Government? Read “What did the Founders learn about government from the Romans?” (pgs 1-3) 4. Define republic: A country that has a government in which power is held by the people who elect representatives 5. Define direct democracy AND give an example: A government where the people vote directly on rules and laws Ex: classroom voting on a poster winner, ancient Athens 6. Define representative democracy AND give an example: A government where people elect representatives to make government decisions for them Ex: student council, US 7. Circle one: Is a republic a representative OR direct 8. The Roman Republic lasted nearly _______500_______ years, from ______509______BC to ______27_____BC. democracy? 9. What three features of the Roman Republican government influenced the Founders of the United States? A. citizens have the power to govern B. citizens delegate or entrust their power to leaders they elect to represent them and to serve their interests C. citizens and their representatives work cooperatively to promote the common good rather than their own interests 10. In a republican government what are the: Advantages Disadvantages 1. representatives are elected to serve the common good 1. republican govt. works best in small communities 2. having representatives make the laws is more efficient 2. the people in a republic have to be very much alike 3. the people have a say in their government 3. people in a large and diverse republic naturally divide into factions or interest groups and not work for the common good. 4. the representatives are responsible to the people How did the ROMAN Republic work? Read “From Monarchy to Republic” (pgs 4-5). 11. How many consuls were elected each year? TWO 12. What were the plebeians’ special officials called? tribunes 13. How did the tribunes exercise power? Veto (refuse to agree to or deny a law to pass) 14. What special action could Romans take in an emergency? appoint a dictator for six months 15. Complete the following chart: ROMAN REPUBLICAN GOVERNMENT CONSULS two elected every year by the Roman representatives, lead the armies, served as judges, could veto each other SENATE membership limited to Rome’s upper class, advised consuls, passed laws elect assemblies TRIBUNES elected by plebeians, could veto Senate laws, protected plebeian rights People from this class elected representatives from their class elect PLEBEIANS farmers, merchants, soldiers, and craftworkers of Rome – lower class PATRICIANS descendants of Rome’s earliest settlers – upper class Roman Citizens What does the US government look like? Read “How does separation of powers work?” (pg 6) 16. Define separation of powers: The power of government is not given to any one branch. Instead, some of the power is given to each branch. 17. Define checks and balances: The powers of the different branches of government are balanced. Examples: president can veto laws from Congress, Congress can override the president’s veto with a 2/3 majority vote Consuls (2) President (1) Ring master Enforces the laws – leader of military praetors Supreme Court Balancing act / lion tamer Make sure laws are fair Tribunes and Senate Senate and House of Representatives jugglers Make the laws 18. Complete the following chart: