* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Classical Conditioning
Biological motion perception wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Negative priming wikipedia , lookup
Mental chronometry wikipedia , lookup
Habituation wikipedia , lookup
Spontaneous recovery wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Conditioned place preference wikipedia , lookup
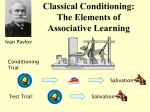
Classical Conditioning Ivan Pavlov • “Stumbled” across classical conditioning around 1900 • Studying “psychic reflexes” • Saliva experiments on dogs • Dogs started responding prior to the meat powder • Sounds of preparation • Realized a neutral stimulus was creating a response Important terms Unconditioned stimulus (US) – a stimulus that evokes an unconditioned response without previous conditioning Unconditioned response (UR) – an unlearned reaction to an unconditioned stimulus that occurs without previous conditioning Conditioned stimulus (CS) – a previously neutral stimulus that has, through conditioning, acquired the capacity to evoke a conditioned response Conditioned response (CR) – a learned reaction to a conditioned stimulus that occurs because of previous conditioning Neutral stimulus (NS) – a stimulus that does not evoke a response by itself Before Conditioning NS Tone No response US Meat powder During Conditioning NS Tone US Meat powder UR Salivation After Conditioning CS Tone CR Salivation A boy is fond of cookies, which make his mouth water whenever he eats them. He passes a bakery baking cookies making the area smell of cookies and he begins to salivate. NS Smell of cookies US Cookies UR Salivation CS Smell of cookies CR Salivation CS Smell of cookies US Cookies CR Salivation A young child who reaches out to pet a barking dog is bitten by the dog and cries. Every time she hears a dog bark, she whimpers. NS Dogs barking US Dog bite UR Cry (pain) CS Dogs barking CR Fear of dogs (whimper) CS Dogs barking US Dog bite CR Fear of dogs A boy who is trained in karate often practices by throwing mock punches at his sister. One day, he accidently hits her in the eye and hurts her. From that day on, every time he raises his hands, his sister flinches. NS Mock punches US Accidental hit UR Pain CS Raises hands (mock punches) CR Flinch CS Raises hands US Accidental hit CR Flinch When they were going together, a guy and his former girlfriend had a favorite CD which they frequently listened to together. Although she broke up with him over a year ago, whenever he hears a song from that CD he becomes depressed. NS Songs on CD US Break up UR Hurt feelings; mental pain; sadness CS Songs from CD CR Depression CS Songs from CD US Break up CR Depression Classical conditioning in everyday life • Conditioned fear and anxiety • Events and interactions can create phobias and other fears • Emotional responses as of a result of a certain smell, song, etc. • Physiological responses (i.e., immune system) • Evaluative conditioning - changes in the liking of a stimulus that result from pairing that stimulus with other positive or negative stimuli. (CR ) (UR) (CS) (US) Products Sexual imagery (e.g., jeans) Pleasant emotional response Processes of condition - acquisition Acquisition (CS-US pairings) 15 10 5 0 The initial stage of learning something. Processes of condition - extinction Extinction (CS alone) 15 10 5 0 The gradual weakening and disappearance of a conditioned response tendency. Processes of condition – spontaneous recovery Spontaneous Extinction Recovery (CS alone) (CS alone) 15 10 5 24-hour rest 0 The reappearance of an extinguished response after a period of nonexposure to the conditioned stimulus Basic processes of classical conditioning (CS) (US) White Rat Loud Gong (CR) (UR) Fear • Stimulus generalization • Stimulus discrimination Little Albert Higher order conditioning A conditioned stimulus functions as if it were an unconditioned stimulus.