* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Learning - Classical Conditioning
Psychometrics wikipedia , lookup
Educational psychology wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
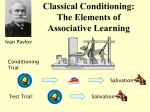
Learning: Classical Conditioning Psychology November 11, 2010 Learning Definition: a relatively permanent change in behavior that occurs because of experience What can affect learning? Biology/Genetics/Heredity Physical States Maturation Sleep/Fatigue/Emotion/etc Experience Observation/Practice/Rehearsal Classical Conditioning Pavlovian Conditioning Learning through associations CC Terminology Terms to be familiar with Unconditioned Stimulus (US) Unconditioned Response (UR) An unlearned, inborn reaction to a US Salivation Conditioned Stimulus (CS) A stimulus that can elicit a response without any learning Meat A stimulus that comes to elicit a response as a result of being paired with the US Bell Conditioned Response (CR) A response that is similar or identical to the UR that comes to be elicited by a CS Salivation Classical Conditioning Definition A form of learning in which a previously neutral stimulus (CS) is paired with a US to elicit a CR that is identical to, or very similar to, the UR. CC Phenomena Acquisition: rate of conditioning The more often the CS is paired with the US, the quicker it will be learned The CS must come before the US Extinction Process of unlearning a learned response because the US has been removed for a period of time. Spontaneous Recovery: sudden reappearance of CR after apparent extinction Generalization Tendency for similar stimuli to elicit the same response “Little Albert” Discrimination Tendency for an organism to distinguish between varieties in the CS Dogs won’t salivate to different tones of a bell CC Applications Rescorla & Wagner (1972) Predictability: learned association when two events occur close together Expectancy: awareness of the likelihood of a US Alcohol & Nausea Meds Garcia & Koelling (1966) Taste Aversions Fear associations Adaptation Supports Darwin’s Theory of Natural Selection










![Classical Conditioning (1) [Autosaved]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001671088_1-6c0ba8a520e4ded2782df309ad9ed8fa-150x150.png)