* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch 8 AP Practice
Host–guest chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Supramolecular catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
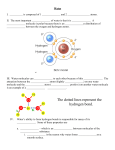
Hydrogen bond wikipedia , lookup
Jahn–Teller effect wikipedia , lookup
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Halogen bond wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Hamiltonian wikipedia , lookup
Pseudo Jahn–Teller effect wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Biological aspects of fluorine wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
Fluorochemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular biology wikipedia , lookup
Electronegativity wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Metastable inner-shell molecular state wikipedia , lookup
Molecular graphics wikipedia , lookup
Franck–Condon principle wikipedia , lookup
Bond valence method wikipedia , lookup
Implicit solvation wikipedia , lookup
Self-assembled monolayer wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
Aromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Bent's rule wikipedia , lookup
Molecular dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Rotational–vibrational spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Rotational spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Computational chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital diagram wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Resonance (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular scale electronics wikipedia , lookup
Chapter 8 Practice: Bonding and Molecular Structure 1984 Multiple Choice Questions 40. The geometry of the SO3 molecule is best described as (A) trigonal planar (B) trigonal pyramidal (C) square pyramidal (D) bent (E) tetrahedral 41. Which of the following molecules has the shortest bond length? (A) N2 (B) O2 (C) Cl2 (D) Br2 (E) I2 60. Which of the following has a zero dipole moment? (A) HCN (B) NH3 (C) SO2 (D) NO2 (E) PF5 80. For which of the following molecules are resonance structures necessary to describe the bonding satisfactorily? (A) H2S (B) SO2 (C) CO2 (D) OF2 (E) PF3 1989 17. The Lewis dot structure of which of the following molecules shows only one unshared pair of valence electron? (A) Cl2 (B) N2 (C) NH3 (D) CCl4 (E) H2O2 47. CCl4, CO2, PCl3, PCl5, SF6. Which of the following does not describe any of the molecules above? (A) Linear (D) Tetrahedral (B) Octahedral (E) Trigonal pyramidal (C) Square planar 1994 Questions 8-10 refer to the following diatomic species. (A) Li2 (B) B2 (C) N2 (D) O2 (E) F2 8. Has the largest bond-dissociation energy 9. Has a bond order of 2 10. Contains 1 sigma (σ) and 2 pi (π) bonds 57. Molecules that have planar configurations include which of the following? I. BCl3 II. CHCl3 III. NC13 (A) I only (B) III only (C) I and II only (D) II and III only (E) I, II, and III 62. The electron-dot structure (Lewis structure) for which of the following molecules would have two unshared pairs of electrons on the central atom? (A) H2S (B) NH3 (C) CH4 (D) HCN (E) CO2 1 68. Which of the following molecules has a dipole moment of zero? (A) C6H6 (benzene) (D) NH3 (B) NO (E) H2S (C) SO2 1999 40. Of the following molecules, which has the largest dipole moment? (A) CO (B) CO2 (C) O2 (D) HF (E) F2 2002 Questions 3-5 refer to the following molecules. (A) CO2 (B) H2O (C) CH4 (D) C2H4 (E) PH3 3. The molecule with only one double bond 4. The molecule with the largest dipole moment 5. The molecule that has trigonal pyramidal geometry 53. According to the VSEPR model, the progressive decrease in the bond angles in the series of molecules CH4, NH3, and H2O is best accounted for by the (A) increasing strength of the bonds (B) decreasing size of the central atom (C) increasing electronegativity of the central atom (D) increasing number of unshared pairs of electrons (E) decreasing repulsion between hydrogen atoms 1997 D Consider the molecules PF3 and PF5. (a) Draw the Lewis electron-dot structures for PF3 and PF5 and predict the molecular geometry of each. (b) Is the PF3 molecule polar, or is it nonpolar? Explain. (c) On the basis of bonding principles, predict whether each of the following compounds exists. In each case, explain your prediction. (i) NF5 (ii) AsF5 2 1999 D Answer the following questions using principles of chemical bonding and molecular structure. (a) Consider the carbon dioxide molecule, CO2, and the carbonate ion, CO32− (i) Draw the complete Lewis electron-dot structure for each species. (ii) Account for the fact at the carbon-oxygen bond length in CO32− is greater than the carbon-oxygen bond length in CO2. (b) Consider the molecules CF4 and SF4. (i) Draw the complete Lewis electron-dot structure for each molecule. (ii) In terms of molecular geometry, account for the fact that the CF4 molecule is nonpolar, whereas the SF4 molecule is polar. 1996 B C2H2(g) + 2 H2(g) → C2H6(g) Information about the substances involved in the reaction represented above is summarized in the following tables. Substance ΔH°f (kJ/mol) Bond Bond Energy (kJ/mol) C2H2(g) 226.7 C-C 347 H2(g) 0 C=C 611 C2H6(g) -84.7 C-H 414 H-H 436 (d) Calculate the value of the C≡C bond energy in C2H2 in kilojoules per mole. 3 2008 part B, form A, question #5 Using principles of atomic and molecular structure and the information in the table below, answer the following questions about atomic fluorine, oxygen, and xenon, as well as some of their compounds. Atom First Ionization Energy (kJ mol-1) F 1,681.0 O 1,313.9 Xe ? (a) Write the equation for the ionization of atomic fluorine that requires 1,681.0 kJ mol-1. (b) Account for the fact that the first ionization energy of atomic fluorine is greater than that of atomic oxygen. (You must discuss both atoms in your response.) (c) Predict whether the first ionization energy of atomic xenon is greater than, less than, or equal to the first ionization energy of atomic fluorine. Justify your prediction. (d) Xenon can react with oxygen and fluorine to form compounds such as XeO3 and XeF4. In the boxes provided, draw the complete Lewis electron-dot diagram for each of the molecules represented below. (e) On the basis of the Lewis electron-dot diagrams you drew for part (d), predict the following: (i) The geometric shape of the XeO3 molecule (ii) The hybridization of the valence orbitals of xenon in XeF4 (f) Predict whether the XeO3 molecule is polar or nonpolar. Justify your prediction. 4