* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Romans
Ancient Roman architecture wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Leges regiae wikipedia , lookup
Centuriate Assembly wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Roman funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Romanization of Hispania wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
Executive magistrates of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
First secessio plebis wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Demography of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Conflict of the Orders wikipedia , lookup
Legislative assemblies of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
History of the Constitution of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
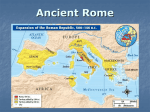
THE ROMANS Founding of Rome ■ Foundation Myth: ■ Romulus & Remus – 753 BCE – Mars – She-wolf Ancient Italy was home to several groups. Both the Etruscans in the north and the Greeks in the south had a major influence on the development of Rome. Roman Republic ■ Tiber River – Latium Plain ■ Etruscans – Etruria (625-509 BCE) – urbanization ■ – – – – – temples augury toga fasces triad of gods (Jupiter, Juno, Minerva) ■ – Forum, Via Apia Adopted from Greeks alphabet ■ Adopted from Greeks ■ Greeks (750-550 BCE) – Magna Graecia ■. The City of Rome Roman Republic ■ Romans’ Foundation Myth of the Republic: – 509 BCE – Rape of Lucretia & Overthrow of Etruscan King ■ Patricians & Plebeians – Patricians were aristocratic landowners who held all political power. ■ They were the minority, but were the only ones who could be elected to political office. – Plebeians were the commoners, the farmers, merchants, artisans who were the majority of the population. ■ They could vote, but could not hold political office. ■ Government – Consuls – 2 men elected each year, commanded the army and ran the government. ■ ■ Could only hold office for 1 year and could not run for office a 2nd year in a row. Possessed imperium “the right to command.” – Senate – 300 men who held office for life, controlled the budget and gave permission for men to run for office. ■ ■ – They were an advisory body, made up of elder statesmen who offered guidance. Their advice, senatus consultum, had the force of law, but was NOT law. Assemblies – Legislative bodies ■ ■ Centuriate Assembly – Made up of all the soldiers, made laws, & voted for consuls and other political offices. Tribal Assembly – Made up of non-soldiers/commoners, made laws Roman Republic ■ Roman government ran on Patronage – the Patron/Client relationship ■ Twelve Tables – first written law code for Rome. ■ Struggle of the Orders (494-287 BCE) – Non-violent – Wealthy plebeians wanted political power/equality. Wanted the ability to marry into the patrician class. ■ They win all of those rights and more. Now, at least 1 consul MUST be a plebeian – Tribunes of the Plebs – New office created to protect plebeians, 12 men elected for 1 year terms – Have the power to veto laws – Plebeian Assembly – New assembly for plebeians to pass laws. Later can pass laws that effect all Roman citizens. Roman Expansion ■ Expansion (493 BCE) – Rome begins conquering throughout Italian peninsula – Roman Confederation (265 BCE) ■ Brilliant system of treaties, explain why Roman Empire so successful ■ 3 levels: – 1)Allied Status – you have Rome’s protection – 2)Municipal Status – you can make legal contracts with Roman citizens, marry a Roman citizen – 3)Full Citizenship – you can vote and hold office in Rome Punic Wars