* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Historical Genetics George Mendel Mendel`s Experiment
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Human leukocyte antigen wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
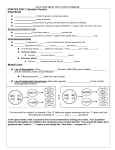
1 Historical Genetics 2 George Mendel 3 Mendel’s Experiment 4 Austrian Monk and Teacher Experimented with pea plants No knowledge of genes or chromosomes Concepts established through math Click on Image to Play Game Genetics Vocabulary Genes: A heredity factors found on chromosomes Alleles: Two genes associated with a specific characteristic. – Each allele is located on a homologous chromosome 5 6 Alleles 7 Mendel’s Law of Segregation 8 Phenotype: The physical appearance of the gene pair Genotype: The genetic combinations or make up of the individual trait. Here’s an Example 10 Alleles of a gene occur in pairs and are separated from each other other during meiosis and then are recombined during fertilization Oh no! More Vocabulary! 9 Dominant Alleles – Only need one gene for the characteristic or trait to be expressed. expressed. – Represented by a capitol letter Recessive Alleles – Must have two genes of the same with the same allele in order for for the trait to show. – Represented by a lower case letter Eye Color The allele for the phenotype of blue eyes is “b” The allele for the phenotype of brown eyes is “B” A Blue eyed in individual can only be “bb” because blue eyes are recessive. An individual with Brown eyes can Have either “BB” or “Bb” because because brown eyes are dominant Are you kidding me, more vocabulary? An individual is homozygous or pure for a trait if they have two of the same allele. – Ex: blue eyes are “bb” An individual is heterozygous for a trait if they have two different alleles for one trait. 1 – Ex: A brown eyed person who is “Bb” 11 Test Cross To determine what genotype an individual is, a test cross can be done. – Depending on what offspring come out will give rise to what genotype genotype the parents could be 12 Pedigree 13 Independent Assortment 14 Heterozygous individuals show a phenotype intermediate between homologous homologous parents “R” = red “r” = white RR = red rr = white Rr= Rr= pink Both alleles are dominant and both phenotypes show at the same time. time. Multiple Alleles 19 Alleles are not completely dominant or recessive. Co-dominance 18 25% would be Homozygous brown 25% would be Homozygous blue 50% would be heterozygous brown Incomplete Dominance 17 To determine what the possible genotypes and phenotypes your kids kids could have you must do a punnet square. Lets cross two heterozygous Brown eyes individuals: Intermediate Inheritance 16 By doing test crosses Mendel found that different traits were inherited inherited independently of one another What color eyes will my kids have? 15 A pedigree chart is a chart which tells one all of the known phenotypes and genotypes genotypes for an organism and its ancestors A genetic history A trait that is based on more than two alleles. Ex: Blood Type Sex Linked Traits Trait’s in which the gene is only found on the X chromosome Examples of SexSex-linked Traits: 2 – – – – RedRed-green colorblindness Male Pattern Baldness Hemophilia Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Many of the traits are more common in men because since they have have only one X chromosome, even if the allele is recessive it will still show. 20 21 Interaction of Heredity and Environment Effect of Light – With out light most plants only produce a yellow pigment – In the presence of light, the plant will start to produce chlorophyll, chlorophyll, turning green and beginning photosynthesis. 22 Effect of Temperature Hair color of the Himalayan Rabbits – – – 23 Typically white with black extremities All white in warm climates Turns black where ice is applied to normally white areas. Identical Twin Studies Twins tend to change phenotypes as they grow older. Believed to happen as being dependant on the environment. 3