* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Roman Republic Full Notes
Roman Senate wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Factorum ac dictorum memorabilium libri IX wikipedia , lookup
Senatus consultum ultimum wikipedia , lookup
Centuriate Assembly wikipedia , lookup
Roman tribe wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Augustus wikipedia , lookup
Leges regiae wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Executive magistrates of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Legislative assemblies of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Conflict of the Orders wikipedia , lookup
History of the Constitution of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
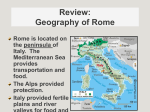
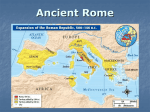
Rome:BirthoftheRepublic GeographyofItaly • CenteroftheMediterraneanbasin • RomanscalleditMareNostrum,“OurSea” • Mountainbarriers • Alpsinthenorth • ApenninerunningdownthelengthoftheItalianpeninsula • Moderatelydivided • TravelwasdifficultbutitofferedanaturalprotectionduringRome’searlydays • Resources • Richagriculturallandinthesouth • Richdepositsofcopper,iron,andtininthenorth • Largepopulationbase TheOriginsoftheRomanState PrehistoricRome • Advantageoussite:sevendefensiblehillsattheTiberford • Mixedburials:Latin,Sabine,andotherearlysettlers • Rich,agriculturalterritoryinthecenterofItaly TheEarlyState • Earlyvillages,onceseparate,joinedtogetherandchosearex,orking • TheheadsoftheoldLatinfamilies,thepatres,constitutedanadvisorybody,thesenatus(bodyof“old men”orelders) TheMythicalOriginsofRome • MythicalfoundingofRomewas753BCEbyRome’sfirstkingRomulus–allegedlythesonofMars, Romangodofwar • AccordingtothismyththerewouldbesevenkingsofRomebeforethebirthoftheRepublic–thelast threekingswereEtruscan RulersofRome • ReignofRomulus –753-716BCE • NumaPompilius –715-674BCE • TulliusHostillius –673-642BCE • AnchusMarcius –642-617BCE • LuciusTarquiniusPriscus(Etruscan) –616-579BCE • ServiusTullius(Etruscan) –578-535BCE • LuciusTarquiniusSuperbus(Etruscan) –535-510BCE • RomanRevolt/EstablishmentoftheRepublic –509BCE 1 TroyandItaly:Virgil’sAeneid • Virgil’sAeneid–writtenbetween29and19BC • AttempttotieRomanlegends–RomulusandEvander-withtheHomericepicsandGreek legends • AeneasandtheTrojans • LegendarysonofVenus(Aphrodite)andtheTrojanAnchises • EscapedthedestructionofTroyandmigratedtoItaly • InItalyalliedhimselfwiththeLatinsandbecametheancestoroftheRomans RapeoftheSabineWomen • Romulus’citywassettledbyallmen • TheSabineswereinvitedtoafestivalandencouragedtobringtheirsistersanddaughters • Atagivensign,theRomans“snatched”(rapio)thewomenfortheirwives • LatertheSabinesdeclaredwartogettheirwomenfolkback • Thewomen,nowmothers,intervened,andthetwogroupsfoundedonestate • ThismayexplainthedualLatin-Sabineoriginsoftheoriginalsettlement Italyin750BCE • Inthemid-8thcenturyBCEtheearlyRomansweresurroundedbymorepowerfulcultures • GreekcoloniesspreadtheircultureandinfluenceinsouthernItaly • TheCarthaginianswerethedominantnavalpower • TheEtruscansruledinthenorthofItaly • ItwouldbetheEtruscansthatwouldcometoruleRome,incorporatingthesmallcityintothegreater kingdomofEtruriafromc.616-509BCE TheEtruscans • 900-500BCE–theEtruscansprosperedinnorthernItaly,alandcalledEtruia • LikelyimmigratedfromtheEasternMediterranean • CalledEtruscansbytheRomans,TyrrhenioibytheGreeks,calledthemselvestheRasenna • LikeGreece,theEtruscansdevelopedindependent,fortifiedcity-states • Smallconfederacieswouldform,intimeleadingtoakingdom • TheEtruscanmilitarywouldcometodominatetheregion • Bythe6thcenturyBCE,theEtruscanmilitaryhadconqueredmuchoftheItalianpeninsula,including RomeandtheislandofCorsica EtruscanReligion • TheEtruscanswerepolytheisticbelievinginmanygods • Believedinpredestination–thatone’sdestinywasalreadydetermined • PriestsknownasAugursreadsignsinnatureandgavepropheciesonthefuture • TheRomanswouldholdmanysimilarbeliefs EtruscaninfluenceonRome • Numerals • Bloodsports(i.e.gladiators) • BeliefinHadesandtheunderworldgods • Augury(foretellingthefuturethroughtheappearanceofnaturalphenomena) • Excessivesuperstition 2 EtruscansexpelledfromRome • AccordingtotheRomanHistorianLivy(c.59BCEtoc.17CE)thelastEtruscankingofRome,Tarquin theProud,wasexpelledbyapopularrebellionin509BCE • RebellionhadbeensparkedbytherapeofthenobleRomanwomanLucretiabytheking’ssonSextus • LuciusJuniusBrutusledtherebellionandwasthefounderoftheRomanRepublic • His(claimed)descendantDecimusJuniusBrutuswouldbethemostfamousofJuliusCaesar’sassassins –anotherkinginthemaking Reality • Itismorelikelythattherewasaslowerbuildupoftensionsbetweenthewealthiestfamiliesandthe kingswhomadeconcessionstothelowerclassesforapowerbase • Thetensionsheightenedbecauseofeconomicdepression,politicaldecay,andEtruscannavallossesto GreeksandCarthaginians • Endofthemonarchymayhavebeenagradualprocessfrom525BCEto474BCE PatriciansandPlebeians • Fromitsbeginning,theRepublichadbeendividedbyclass–thetwomostimportantclasseswerethe PatriciansandthePlebeians • Patricians–elitewealthyfamiliesthatownedmostofthelandandmadeupthearistocracyofRome • Theywouldcontroltherepublicthroughthesenateandwereprincipallyconcernedwithgaining powerandwealth • Plebeians–freebornbutoftenlandlessRomancitizensthatmadeupthemiddleandlowerclassesof Romansociety • Aftervariousreformsingovernmentplebeianscouldbecomeverywealthybutthiswasrare • ThestruggleforpowerbetweenthesetwogroupswoulddefinetheRomanRepublicduringitsfirst centuries BirthoftheRomanRepublic • AtthebirthoftheRepublictheRomanscreatedapoliticalsystemthatwasamixofamonarchical, aristocratic,anddemocraticsystem • TheRomansdidnotwantoneorevenafewmentomakeallthelaws • TheRomansdecidedtobalancethepowerofthegovernmentbetweenthreebranches: • TheExecutiveBranch–ConsulsandMagistrates • TheLegislativeBranch–SenateandLegislativeAssemblies • TheJudicialBranch–CouncilsandCourts • Mostmodernwesterndemocraciesaresetupinthismanner LegislativeBranch AssemblyoftheCenturies(ComitiaCenturiataor"ArmyAssembly”) • ProbablycreatedunderkingServiusformilitarypurposes • Electedconsulsandotherhighermagistrates • Acceptedorrejectedlegislationmadebymagistratesanddeclarationsofwar;ratifiedtreaties AssemblyoftheTribes(ComitiaTributa) • OpentoallRomancitizensandwasthedemocraticassemblyoftheRomanRepublic • Itcouldpasslawsonbehalfofallthepeople PlebeianCouncil(ConciliumPlebis) • Madeupofonlyplebeians • Elected10tribunes • Passedplebiscita(plebiscites)whichhadtheforceoflaw 3 Senate • Undertheking,theSenatehadonlybeenanadvisorycommittee • SlowlygainedmorepowerintheRepublicbecausethey: – Becameapermanentpartofthegovernment – Hadexperience – Hadthedignityoftradition,sinceitexistedfromearliestRomanstate • WereheadsoftheleadingpatricianfamiliesinRomeandappointedfirstbytheconsulsandlaterby thecensors • Controlledthestate’sfinances,exceptinwar • • • • Gaveofficialadvicetomagistrates AnyproposalpassedbytheSenatecouldbevetoedbythePlebeianTribune–thoughhewouldneed tobepresenttodothis ADictatorcouldbeappointedbytheSenateduringanemergency After202BCEtheSenatecouldrespondtoemergenciesbypassingthesenatusconsultumultimum whichsuspendedcivilgovernment ExecutiveBranch • Consul–mostpowerfulpositionintheRepublic,therewerealwaystwo • ElectedforjustoneyearbytheAssemblyoftheCenturies • OnlypatricianscouldstandforconsulinitiallybutthischangedafterPlebeianReforms • Eachconsulhadveto(Latin;“Iforbid”)powerovertheother–noonemanheldtoomuchpowerinthe Republic • ConsulssupervisedtheSenateandorderedtheRomanarmyduringwars • ConsulswhowerepoorgeneralswereoftendisastrousfortheRepublic–thereforeitseemedsmartto electgoodgeneralsasconsuls • Consulshadmanyresponsibilitiesduringpeacetimewhichincludedadministrative,legislative,and judicialroles • Therewerehighlevelsofcorruptionatthistime–anyone,particularlyasenator,whosupportedan individualinbecomingconsulcouldexpectfavors • Mayors,citypolice,taxcollectors–allweremembersoftheexecutivebranchastheywerecharged withexecutingpower JudicialBranch • Sixjudgeswereelectedeverytwoyears • Decidedthepunishmentsthatcriminalswouldreceive • Executivemagistratescouldincludeconsuls,praetors,censors,aediles,quaestors,tribunes,and dictators • Romanlawwasbasedonthetwelvetables,asignificantadvancementinthehistoryoftheRuleofLaw TheTwelveTables • AmajorconstitutionalachievementoftheearlyRomanRepublicwastheestablishmentoftheTwelve Tables–lawswrittendownontwelvetabletsthatwouldapplytoallRomancitizens • Thelawscoveredcivicmatters,crimes,andtherelationsamongcitizensandfamilymembers • Mostimportantlythelawsconfirmedtherightofallfreecitizenstotheprotectionofthelaw 4 TheEarlyRepublic • ThegovernmentoftheearlyRomanRepublicwassetuptokeeppowerinthehandsofthePatricians • OvertimereformswereneededtokeepthePlebeianscontent–theywouldoftenstrikewhenthey werenotcontent,bringingRometoagrindinghaltastheymadeupthelaborforce • Eventuallythiswouldleadto“TheStruggleofOrders”whichlastedfromabout494–287BCE TheStruggleoftheOrders • ThePatricianswerehighlyprivilegedandonecouldonlybebornintothisclasstoreapthebenefits • Plebeianswantedchangeforavarietyofreasons: – Wealthyplebeianswantedsocial,religious,andpoliticalequality – “Middleclass”plebeianswerethebackboneofthearmy – Poorplebeiansneededrelieffromdebt,particularlythepracticeofdebtslavery PlebeianAdvances • 494BCE:FirstSecessionofthePlebs,thePlebeianCouncilwasestablishedalongwiththeelectionof Tribunes • 450BCE:LawoftheTwelveTables • 445BCE:patriciansandplebeianscouldintermarry • 367BCE:plebeianscouldbeelectedConsul • 342BCE:mandatorythatoneConsulwasaplebeian • 339BCE:mandatorythatoneCensorwasaplebeian • 300BCE:halfthepriesthoodmustbeplebeian • 287BCE:LexHortensia–allplebiscitespassedbyPlebeianCouncilhadtheforceoflawthroughout theRomanState 5