* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Rules for Multiplication
Georg Cantor's first set theory article wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Infinitesimal wikipedia , lookup
Elementary arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Hyperreal number wikipedia , lookup
Real number wikipedia , lookup
Division by zero wikipedia , lookup
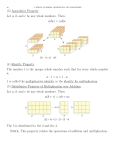
Rules for Multiplication September 12, 2011 Rules for Multiplication Objective To multiply real numbers. Identity Property of Multiplication When you multiply any given real number by 1, the product is equal to the given number. For example: 4 ∙ 1 = 4 and 1 ∙ 4 = 4 The identity element for multiplication is 1. Identity Property of Multiplication There is a unique real number 1 such that for every real number a, 𝒂 ∙ 𝟏 = 𝒂 and 𝟏 ∙ 𝒂 = 𝒂 Multiplicative Property of Zero The equations 4 ∙ 0 = 0 and 0 ∙ 4 = 0 illustrate the multiplicative property of zero: When one (or at least one) of the factors of a product is zero, the product itself is zero. Multiplicative Property of Zero For every real number a: 𝒂 ∙ 𝟎 = 𝟎 and 𝟎 ∙ 𝒂 = 𝟎 Multiplicative Property of 1 What is 4 −1 ? 4 −1 = −1 + −1 + −1 + −1 = −4 Multiplying any real number by 1 produces the opposite of the number. Multiplicative Property of1 For every real number a: 𝒂 −𝟏 = −𝒂 and −𝟏 𝒂 = −𝒂 Multiplicative Property of1 A special case of this property occurs when the value of a is 1. −1 −1 = 1 Using the multiplicative property of 1 with the familiar multiplication facts for positive numbers and properties that you have learned, you can compute the product of any two real numbers. Example 1 Multiply: 4 7 28 4 −7 −28 −4 7 −28 −4 −7 28 Property of Opposites in Products For all real numbers a and b: −𝒂 𝒃 = −𝒂𝒃 𝒂 −𝒃 = −𝒂𝒃 −𝒂 −𝒃 = 𝒂𝒃 Rules for Multiplication Practice in computing products will suggest to you the following rules for multiplication of positive and negative numbers. 1. If two numbers have the same sign, their product is positive. 2. If two numbers have opposite signs, their product is negative. Rules for Multiplication For multiplication with multiple negative numbers, 1. The product of an even number of negative numbers is positive. 2. The product of an odd number of negative numbers is negative. Example 2 Multiply: 4 −6 −7 −5 −840 −2 −8 −7 5 −6 3360 −9 3 0 −5 0 Example 3a Simplify: −3𝑥 −4𝑦 −3𝑥 −4𝑦 = −3 𝑥 −4 𝑦 = −3 −4 𝑥𝑦 = 12𝑥𝑦 Example 3b Simplify: 4𝑝 + −5 4𝑝 + −5 = 4 + −5 𝑝 = −1 𝑝 = −𝑝 Example 4a Simplify: −2 𝑥 − 3𝑦 −2 𝑥 − 3𝑦 = −2𝑥 − −2 3𝑦 = −2𝑥 − −6𝑦 = −2𝑥 + 6𝑦 Example 4b Simplify: 3𝑝 − 4 𝑝 − 2 3𝑝 − 4 𝑝 − 2 = 3𝑝 − 4𝑝 − 4 ∙ 2 = 3𝑝 − 4𝑝 − 8 = 3𝑝 − 4𝑝 + 8 = −𝑝 + 8 Classwork: page 72 Oral Exercises: 1-30 Homework: page 72: 2-34 even, 36-51 3 page 73: Mixed Review