* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download allele. - Petal School District
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified food wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
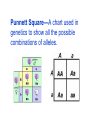
5. Genes are the sections of DNA on chromosomes that control traits. 6. Alleles are different forms of a gene pair. Each one of the pair is an allele. Each organism inherits a combination of two alleles - one from each parent. **Individual alleles control the inheritance of traits. Some are dominant and others are recessive. 7. A dominant allele is one whose trait always shows up in the organism when the allele is present. It blocks another genetic factor. Ex. Dimples 8. A recessive allele is blocked or covered up, whenever the dominant allele is present. Ex. No dimples Dominant and recessive traits are represented by using letters. 9. Dominant traits are represented by capital letters. 10.Recessive traits are represented by lower case letters. Example: B = brown hair b = red hair BB = brown hair / purebred Bb = brown hair / hybrid bb = red hair / purebred 11.Purebred (True-bred)—An organism that always produces offspring with the same form of a trait as the parent. Also known as homozygous. Example: Purebred blonde haired parents will always have blonde haired children. 12. In Mendel’s experiments, P stood for the parent generation, F1 stood for the first generation, and F2 stood for the second generation. 13.Hybrid—An organism that has two different alleles for a trait. ALSO known as heterozygous. 14.Homozygous—an organism that has 2 identical alleles for a trait Example– BB – homozygous for brown hair bb – homozygous for red hair 15.Heterozygous—an organism that has two different alleles for a trait Example – Bb – heterozygous for brown hair 16.Phenotype—physical make-up of an organism ***you can actually see phenotype*** Ex. -- Tall and short. 17.Genotype—genetic make-up of an organism ***you cannot see genotype*** Ex. -- BB, Bb, bb Punnett Square—A chart used in genetics to show all the possible combinations of alleles. Chromosomes are: • located inside the nucleus of cells. • made of DNA which carries genetic information from parent to offspring. Humans have 46 total chromosomes. • 23 in each sex cell. Grasshoppers have 24 chromosomes. • 12 in each sex cell. Dogs have 78 chromosomes. • 39 in each sex cell. House flies have 12 chromosomes. 6 in each sex cell. DNA is the genetic material that carries information about an organism and is passed from parent to offspring. Gene: a segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait. Meiosis: the process by which the number of chromosomes is reduced by half to form sex cells. sperm from the male egg from the female. During meiosis: 1. the chromosome pairs separate, and are distributed to four different cells. The resulting sex cells have only half as many chromosomes as the other cells in the organism. Each gene pair has an allele from mom and an allele from Dad. You have 23 pairs of chromosomes per cell. Each parent contributes one half of the pair. Each chromosome contains thousands of genes. MUTATION • • • Pedigrees • • Selective Breeding Selective breeding is the process of selecting a few organisms with desired traits to serve as parents of the next generation. People use selective breeding to increase the value of plants or animals, such as fruits or vegetables or dairy cows. Examples of selective breeding: Inbreeding – crossing two parents that have identical or similar sets of alleles. Ex: Purebred horses with exceptional speed are crossed to produce offspring to run very fast. Purebred dogs are crossed to maintain hunting skills. 2. Hybridization – the crossing of two genetically different parents for getting the best traits from both parents. Ex: Farmers cross the corn that have the sweetest kernels with a parent that is disease resistant. 3. Cloning - A clone is an organism that is genetically identical to the organism from which it is produced. Example : A cutting from a plant that grows a new plant is genetically identical to the mother plant. Advantages and Disadvantages of Purebreds &include: Hybrids Purebred advantages 1. Working animals perform better 2. Food animals produce better tasting foods 3. Plants may have higher yields 4. Plants may have better tasting foods Purebred disadvantages may include: 1. Inbreeding increased the probability of genetic disorders 2. Purebred species are more expensive 3. Plants may produce unattractive foods 4. Plants may not have disease resistance Hybrid advantages include: 1. Food animals able to produce more food 2. Plants may have higher disease resistances 3. Plants may have more “curb appeal” (attractive appearance, better shipping, etc.) 4. Animals may have larger litters and better survival rates for the young Hybrid disadvantages include: 1. May not always get the desired trait 2. May be more expensive to produce & seeds may not always have high viability 3. May not taste as good as purebred Genetic Engineering is the transfer of genes from one organism into the DNA of another organism. This is also called “gene splicing.” because the DNA molecule is cut open and a gene is “spliced “ into it. Usually involves bacteria. It can produce medicines such as insulin for diabetics. It can improve food crops by making them more tolerant to certain conditions – drought, frost, It may be used one day to replace genes for curing genetic diseases.