* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 1: Psychology*s History and Approaches
Behavioral modernity wikipedia , lookup
Observational methods in psychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Transtheoretical model wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Adherence management coaching wikipedia , lookup
Albert Bandura wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
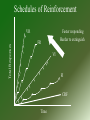
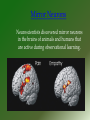
Operant Conditioning Operant Conditioning A type of learning where the frequency of a response depends on its consequence. Edward Thorndike= Law of Effect B. F. Skinner Operant Procedures Appetitive Starts Stimulus Pos Reinforcement (Reward) Neg Punishment Ends Stimulus Aversive Pos Punishment Behavior’s Consequence Stimulus Neg Reinforcement 3 Keys to Operant Conditioning • Positive & negative are mathematical terms, not value judgments. • Reinforcement always increases behavior; punishment always decreases behavior. • The first step is to identify the behavior being learned, and the behavior cannot be the absence of behavior. Big Bang Theory: “Sheldon Shaping Penny” Click picture for video clip Big Bang Theory, Take 2 Click picture for video clip Continuous v. Partial Reinforcement • • • • Continuous Reinforce the behavior EVERYTIME the behavior is exhibited. Usually done when the subject is first learning to make the association. Acquisition comes really fast. But so does extinction. Partial • Reinforce the behavior only SOME of the times it is exhibited. • Acquisition comes more slowly. • But is more resistant to extinction. • FOUR types of Partial Reinforcement schedules. Reinforcement Schedules How often to you give the reinforcer? • Every time or just sometimes you see the behavior. Ratio Schedules Fixed Ratio • Provides a reinforcement after a SET number of responses. Variable Ratio • Provides a reinforcement after a RANDOM number of responses. • Very hard to get acquisition but also very resistant to extinction. Fixed Ration- She gets a manicure for every 5 pounds she loses. Interval Schedules Fixed Interval Variable Interval • Requires a SET amount of time to elapse before giving the reinforcement. • Requires a RANDOM amount of time to elapse before giving the reinforcement. • Very hard to get acquisition but also very resistant to extinction. Fixed Interval: She gets a manicure for every 7 days she stays on her diet. Schedules of Reinforcement Total Responses VR Faster responding Harder to extinguish FR VI FI CRF Time Latent Leaning Edward Toleman Three rat experiment. Latent means hidden. Sometimes learning is not immediately evident. • Rats needed a reason to display what they have learned. • • • • Insight Learning • Wolfgang Kohler and his Chimpanzees. • Some animals learn through the “ah ha” experience. Click pic to see insight learning. Bobo Doll Experiment Learning by Observing • The likelihood of acting on vicarious learning changes when we see the consequences of other people’s behavior • Vicarious reinforcement or vicarious punishment affects the willingness of people to perform behaviors they learned by watching others Observational Learning • Albert Bandura and his BoBo Doll • We learn through modeling behavior from others. • Observational learning + Operant Conditioning = Social Learning Theory Click pic to see some observational learning. Results • Children exposed to the aggressive model were more likely to act in physically aggressive ways than those who were not exposed to the aggressive model. (Boys averaged 38.2 with 12.7 for girls) • Children exposed to the aggressive model were more likely to engage in novel hostile acts. • Children are more influenced by same-sex models. • Results showed that boys exhibited more aggression when exposed to aggressive male models than boys exposed to aggressive female models. When exposed to aggressive male models, the number of aggressive instances exhibited by boys averaged 104 compared to 48.4 aggressive instances exhibited by boys who were exposed to aggressive female models. Live and Virtual Models Virtual Model Live Model Mirror Neurons Neuroscientists discovered mirror neurons in the brains of animals and humans that are active during observational learning.