* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
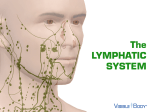
Download The lymphatic vessels in the villi of the small intestine, called , are
Survey
Document related concepts
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Atherosclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Inflammation wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
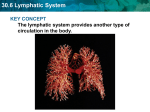
,are involved in the absorption of The lymphatic vessels in the villi of the small intestine, called The smallest vessels in the lymphatic system are called called The walls of lymphatic vessels are most similar to the walls of a, arteries. b. veins. The largest lymph vessel is the a. lumbar trunk. b. thoracic duct. Lymph rejoins the blood and becomes part of the plasma in a. lymph nodes. b. the right and left subclavian veins. Tissue fluid originates from a. the cytoplasm of cells. b. lymph fluid. Lymph formation is most directly dependent on a. increasing osmotic pressure in tissue fluid. b. a blood pressure of at least 100160. . The largest vessels are c. d. capillaries. arterioles. c. d. lymphatic duct. intestinal trunk. c. d. the inferior and superior venae cavae. the right atrium. c. blood plasma. c. a sufficient volume of tissue fluid to create a pressure gradient between tissue and lymph capillaries. diminished peripheral resistance in veins. d. The function(s) of lymph are to a. recapture protein molecules lost in the c. transport foreign particles to lymph nodes. capillary bed. d. recapture electrolytes. b. form tissue fluid. The mechanisms that move lymph through lymph vessels are similar to those that move blood through (arterieslveins). The flow of lymph is greatest during periods of a. physical exercise. c. dream sleep. b. isometric exercise of skeletal muscle. d. REM sleep. Obstruction of lymph circulation will lead to L m p h nodes are shaped like a. almonds. c. kidney beans. b. peas. d. convex disks. Compartments within the node contain dense masses of a. epithelial tissue. c. oocytes. b. cilia. d. lymphocytes. Inflammation of a lymph node is known as Clumps of lymph nodes in mucosa of the ileum are called An infection in the toe would result in enlarged lymph nodes in the a. axilla. c. pelvic cavity. b. inguinal region. d. abdominal cavity. Which of the following types of cells are produced by lymph nodes? a. leukocytes c. eosinophils d. basophils b. lymphocytes The thymus is located in the a. posterior neck. c. upper abdomen. b. mediastinum. d. left pelvis. Which of the following statements about the thymus islare true? a. The thymus tends to increase in size with age, as glandular tissue is replaced by fat and connective tissue. b. The thymus is relatively large during infancy and childhood. The largest of the lymphatic organs is the Which of the following statements about the spleen islare true? a. The spleen is located in the lower left quadrant of the abdomen. b. The spleen functions in the body's defense against infection. c. d. c. d. The thymus produces a substance called thymosin that seems to stimulate the development of lymphatic tissue. The thymus is a firm, multilobed structure. The structure of the spleen is exactly like that of a lymph node. Splenic pulp contains large phagocytes and macrophages on the lining of its venous sinuses. Agents that enter the body and cause disease are called Examples of innate defenses are the a. skin. c. acid environment of the stomach. b. antibodies. d. lymphocytes. The skin is an example of which of the following defense mechanisms? a. immunity c. mechanical barrier b. inflammation d. phagocytosis Innate defensive mechanisms act (more rapidlylmore slowly) than adaptive responses. The enzyme lysozyme, which has antibacterial ability, is present in which of the following body fluids? a. sweat c. tears b. blood d. urine Fever inhibits pathogen growth because a. the increase in temperature inhibits bacterial b. changes in body temperature affect the cell cell division. walls of microrganisms. c. it decreases the amount of iron in the blood. List the four major symptoms of inflammation. The accumulation of white blood cells, bacterial cells, and damaged tissue cells creates a. exudate. c. a scab. b. pus. The most active phagocytes in the blood are and Phagocytes that remain fixed in position within various organs are called a. neutrophils. c. macrophages. b. monocytes. Macrophages are located in the lining of blood vessels in the bone marrow, liver, spleen, and lymph nodes; they form the system. The resistance to specific foreign agents in which certain cells recognize foreign substances and act to destroy them is 35. 36. Some undifferentiated lymphocytes migrate to the and are then called T lymphocytes. Foreign proteins to which lymphocytes respond are called where they undergo changes Lymphocytes seem to be able to recognize specific foreign proteins because c. there are changes in the permeability of the a. of changes in the nucleus of the lymphocyte. cell membrane of the lymphocyte. b. the cytoplasm of the lymphocyte is altered. d. of the presence of receptor molecules on lymphocytes, which fit the molecules of antigens. B lymphocytes respond to foreign protein by a. phagocytosis. c. producing antigens. b. interacting directly with pathogens. d. producing antibodies. immunity. T cells are responsible for fraction of plasma. The antibodies produced by B cells make up the The immunoglobulin that crosses the placenta from the mother to the fetus is immunoglobulin a. b. A. c. M. G. Which of the following are actions of antibodies that protect the body against infection? a. agglutination c. complement b. precipitation d. neutralization The most protective action of antibodies against antigens is activation of An accessory cell is necessary to activate (B cellsIT cells). In which of the following ways are primary and secondary immune responses different? a. Primary responses are more important than c. A primary response is a direct response to an secondary responses. antigen; a secondary response is indirect. b. Primary responses produce more antibodies d. A primary response is the initial response to than secondary responses. an antigen; a secondary response is all subsequent responses to that antigen. A person who receives ready-made antibodies develops artificially acquired immunity. An immune response to a substance harmless to the body is d a n The type of allergic reaction that occurs very quickly and can lead to death is a(n) a. Type I reaction. c. b. Immune complex reaction. d. Which of the following types of grafts are least likely to be rejected? a. Isograft c. antibody-dependent cytotoxic reaction. anaphylactic reaction. Allograft b. Autograft d. Xenograft Age-related decline in the competence of the immune system is due to the loss of The retrovirus that causes Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome is transmitted by a. the airborne route. c. inoculation with infected blood. b. contact with infected articles. d. unknown means. When tolerance to self-substance is lost, and the immune response is directed against the individual's own tissue, the individual is said to have an disease. The rational for giving influenza vaccine to people over 65 is because of c. decreased effectiveness of the immune a. increasing numbers of abnormal "T" cells. b. increasing size of the thymus gland. d. response. slower antibody response to antigens. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 2 1. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. a a b 5,000 to 10,000 b,c yes platelet or thrombocyte l.c,2.a,3.b,4.b,5.c a albumins, globulins, fibrinogen b, c, d b b, d b b fibrinogen, fibrin a,c d positive dissmeinated intravascular coagulation prothrombin time, partial prothrombin time b streptokinase d a hemophilia b a c erythroblastosis fetalis Rhogam a 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32, 33. 34. 35, 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 5 1. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 15 Mastery Test Answers 58. 59. 1. 2. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8, 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 2 1. 22. 23. 24. external defibrillator mediastinum d a d c atria, ventricles stretching a, d c a,b c aotic a cardiac skeleton coronary arteries EKC (electrocardiogram) a d decreases b, c d b b c a endothelium b impermeability dense filtration, osmosis, difision a c a diffusion c b valves b varicose veins b stroke volume heart action, blood volume, resistance to flow, viscosity, peripheral resistance peripheral resistance stroke volume, heart rate c parasympathetic b vasodilator secondary a, b, d a, b d b d left atrium c circle of Willis hepatic portal system cholesterol 16 Mastery Test Answers 1. 2. 3. b myocardial infarction decreases coronary sinus cardiac cycle d b a c 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. a lacteals, fats lymphatic capillaries, collecting ducts b 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 3 1. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41, 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. a edema c d lymphadenitis Peyer's patches b b b b, c spleen b, d pathogens a, c c more rapidly c c redness, swelling, heat, pain b neutrophils, monocytes c mononuclear phagocyte (reticuloendothelial) immunity thymus gland antigens d d cell-mediated gamma globulin b a, b complement T-cells d passive allergic reaction ' a a, b T cells c autoimmune c,d 17 Mastery Test Answers 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. b b 9. c c a, c veins 11. 10. 12. 13. 14. digestion alimentary canal accessory organs b mixing, propelling no b, c a, c, d fienulum c wisdom teeth a c d