* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Body Systems Lymphatic
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Atherosclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
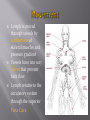
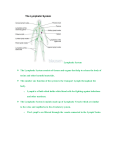
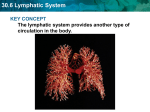
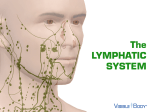
Lymphatic A network of vessels, nodes and organs which collect interstitial fluid lost by the blood and returns it back to circulatory system. (we loose more than 3 liters a day) One Way System Filters bacteria and microorganisms Help maintain movement of nutrients and salts through tissues Absorb fat and fat-soluble vitamins from small intestines Helps to produce and transports white blood cells (Structures dedicated to the production and circulation of lymphocytes, WBC) Spleen- Synthesis antibodies and removes bacteria. Makes and holds RBC and recycles iron. (Can be considered like a large lymph node) Thymus-Produce T cells (for the immune system) Bone Marrow –produces white blood cells Lymph is moved through vessels by contractions of skeletal muscles and pressure gradient Vessels have one way valves that prevent back flow Lymph returns to the circulatory system through the superior Vena Cava Lymphadema- Swelling of the lymph nodes because accumulation of fluid, caused by damage or malformation to the nodes Lymphoma- a cancer that originates in the lymph nodes