* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biomolecules
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
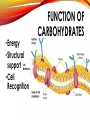
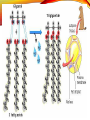
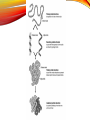
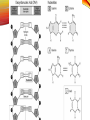
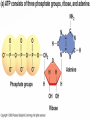
1C BIOMOLECULES BIOMOLECULES • Large complex molecules in cells • Formed from repeating subunits • Most biomolecules are formed from a carbon backbone • Six most common elements in living organisms is • CHONPS BIOMOLECULES • Carbon has FOUR valence electrons • It can bond with up to FOUR other atoms • Example CH4 (Methane) BIOMOLECULES • Monomer – single repeating subunit • Polymer – many monomers bonded together CARBOHYDRATES CARBOHYDRATES • Carbohydrates • Small repeating subunit = sugar • Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen • C:H:O • 1:2:1 CARBOHYDRATES Monosaccharide • Glucose Disaccharide • Lactose, Sucrose CARBOHYDRATES Storage Polysaccharides Starch Glycogen CARBOHYDRATES • Structural Polysaccharides Cellulose Chitin • Energy • Structural support • Cell Recognition FUNCTION OF CARBOHYDRATES LIPIDS • A fat molecule that has similar properties • Examples: • Fats • Oils • Waxes • Phospholipids • Steroids LIPIDS • Repeating subunit = fatty acids • Long chains of carbon bonded to hydrogen with oxygen • Repels water FATS • Saturated fats • Unsaturated fats FUNCTION OF LIPIDS •Energy Storage •Water Barriers PROTEINS • Repeating subunits = amino acids • Only 20 different amino acids • Each amino acid has a different R group or variable group • Long chains of amino acids that twist and fold • Made of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen and sulfur FUNCTION OF PROTEINS •Structure and support •Movement and transportation •Chemical reactions (enzymes) PROTEIN STRUCTURE •Primary Structure •LIST of amino acids present •Secondary Structure •TWIST and FOLD PROTEIN STRUCTURE •Tertiary Structure •TWIST and FOLD AGAIN •Quaternary Structure •TWO or more protein chains NUCLEIC ACID • Repeating subunit – nucleotides • Nucleotide (made of THREE pieces) • SUGAR • BASE • PHOSPHATE NUCLEIC ACIDS ●DNA – DeoxyriboNucleic Acid oSugar = deoxyribose oString of nucleotides made of deoxyribose ●RNA – RiboNucleic Acid oSugar = Ribose oString of nucleotides made of ribose FUNCTION OF NUCLEIC ACIDS •Store and transmit genetic information •“CODE” of DNA depends on sequence of BASES ANOTHER NUCLEOTIDE ●ATP oAdenosine TriPhosphate o3 phosphate groups oBy breaking off the 3rd phosphate group energy is released