* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Genetics
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genome-wide association study wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
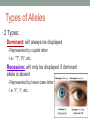
INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS Chapter 10 Genetics • Genetics: the study of heredity • Heredity: the passing of characteristics from parents → offspring • Characteristics = height, eye color, hair texture, etc. • Trait: type of characteristic • i.e.: tall, blue, curly, etc. Genes and Alleles • Gene: a section of DNA that codes for a particular characteristic • i.e.: hair color gene, eye color gene • Alleles: different forms of a gene that codes for a particular trait • i.e.: brown hair allele, blue eye allele Types of Alleles • 2 Types: • Dominant: will always be displayed • Represented by capital letter • i.e.: “T”, “R”, etc. • Recessive: will only be displayed if dominant allele is absent • Represented by lower-case letter • i.e. “t”, “r”, etc. Genotype & Phenotype • Offspring inherit 1 allele from each parent’s homologous chromosome • Genotype: combination of parent’s alleles; genetic makeup • Example: • Mom’s allele → “T” (dominant) • Dad’s allele → “t” (recessive) • Offspring’s genotype = “Tt” • Phenotype: physical appearance; determined by genotype Genotype Combinations • Homozygous: same allele from each parent is inherited (“True-Breed”) • i.e.: “TT”, “tt” • Heterozygous: different allele from each parent is inherited (“Hybrid”) • i.e.: “Tt” • Will usually only show dominant trait Probability • Probability: the likelihood that an event will occur • i.e.: coin flip = ½ or 50% • Determined by: • Probability = # times expected to occur • total # trials • Past outcomes do not affect future ones • Used to predict the outcome of genetic crosses Punnett Squares • Punnett Square: use DAD probability to predict traits of offspring • Based on genotypes of parents • Parents lined up on top & left • Letters inside represent allele combinations of offspring M O M 100% offspring have genotype Tt 100% offspring are tall