* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Integumentary System
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
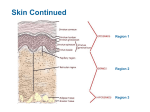
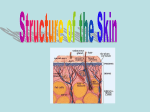
THE DERMIS Pages 116-119 Dermis is made of dense connective tissue Varies in thickness throughout the body Has two layers: ◦ Papillary ◦ Reticular Uneven Contains projections called dermal papillae ◦ contain capillary loops that furnish nutrients to the epidermis ◦ houses pain receptors (free nerve endings) and touch receptors ◦ On hands and feet forms fingerprints: Definite patterns that increase friction and gripping Sweat pores leave identifying “sweat films” Patterns are genetically determined © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Makes up 80% of dermis Collagen and elastic fibers ◦ Strength ◦ Elasticity Blood vessels maintain body temperature Sweat and oil glands Lamellar corpuscles- sensory receptors ◦ Send sensory information about deep pressure (Remember the Merkel cells are responsible for light pressure and are found in the epiderm-derm jx) © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Epidermis Papillary layer Dermis Reticular layer Three pigments contribute to skin color: 1. Melanin Yellow, reddish brown, or black pigments 2. Carotene Orange-yellow pigment from some vegetables 3. Hemoglobin Red coloring from blood cells in dermal capillaries Oxygen content determines the extent of red coloring © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Redness (erythema)—due to embarrassment, inflammation, hypertension, fever, or allergy Pallor (blanching)—due to emotional stress (such as fear), anemia, low blood pressure, impaired blood flow to an area Jaundice (yellowing)—liver disorder Bruises (black and blue marks)—hematomas (blood clots) © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Hair shaft Dermal papillae Epidermis Papillary layer Dermis Pore Appendages of skin • Eccrine sweat gland • Arrector pili muscle • Sebaceous (oil) gland • Hair follicle • Hair root Reticular layer Hypodermis (subcutaneous tissue) Nervous structures • Sensory nerve fiber • Lamellar corpuscle • Hair follicle receptor (root hair plexus) Cutaneous vascular plexus Adipose tissue