* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Matter and Energy
Chemical biology wikipedia , lookup
Chemical warfare wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear transmutation wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Destruction of Syria's chemical weapons wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Determination of equilibrium constants wikipedia , lookup
Fine chemical wikipedia , lookup
Rate equation wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Al-Shifa pharmaceutical factory wikipedia , lookup
California Green Chemistry Initiative wikipedia , lookup
Molecular dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon proliferation wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
Chemical plant wikipedia , lookup
Chemical Corps wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
Chemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
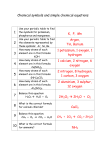
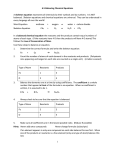
Chemical Formulas, Equations and Reactions Notes Atom • The smallest particle of any pure element. • Only 1 atom • Example: 1 atom of H Element • A substance made up of the SAME type of atom • Example: O2 Compound -a substance made up of atoms of two or more DIFFERENT elements combined in a specific ratio Ex. NaCl or H2O Molecule -Group of 2 or more atoms -Atoms may or may not be of the same element EX. NaCl or O2 • Atom • C, O, H, N • Element • C,C2, O, O2, H, H2, N,N2 • Compound • CH4, H2O, CO2 • Molecule • CH4, H2O, H2, O2, CO2 • 2H2O, 3O2, 2CO2 Chemical Formula -a way of describing the number of atoms that make up one molecule of a compound Ex. C6H1206 H20 Subscript -the number of atoms of that particular element • SUB-Below EX. H20 or CH4 Coefficient -determines the number of molecules (groups) of the formula -This number will be DISTRIBUTED just like in math. It applies to each element and is multiplied by each subscript to find the total number of atoms of each element and a total number of atoms in the molecule. EX. 2H2O 4Al2(SO4)3 CH4 H H C H H 2H20 H H O H H O Identify the Elements, give the number of atoms of each element, and the total number of atoms in the formula 1) 2FeCl3 2) KMnO4 3) 3HgO 4)C6H5COOH 5) 2HCl 6. 4Fe2O3 7. NaClO 8. ZnCl2 9. KClO3 10.24F2 11.3Al2(SO2)3 Chemical Reaction -a change in which one or more chemical substances are rearranged to form different substances. Chemical Equation -a way to show a chemical reaction using chemical formulas. -made up of reactants and products Reactants Products Yield the amount of product obtained as a result of a chemical reaction Components of chemical reaction Reactants Products -are indicated on -are indicated on the right side the left side -new substances -substances that created/PRODUCED react in a in a chemical chemical reaction reaction -inputs -Outputs -Ingredients -Cake Example Reactants Products CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O # of atoms of that element Coefficient (# of molecules) Law of Conservation of Mass -what goes into a chemical reaction will come out of a chemical reaction. -atoms found on the reactants side will also be found on the products side. They will be broken apart and rearranged to create new substances. -creates a “Balanced” equation CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O Photosynthesis 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + O2 Modeling Balanced/Unbalanced Equations Identify whether the chemical reaction is balanced or unbalanced • 4P + 5O2 P4O10 • Mg + O2 MgO • 2Al2O3 4Al + 3O2 • 2HgO 2Hg + O2 • BaCl2 + H2SO4 BaSO4 + HCl Identify Balanced Equations 1) 2Fe + 3Cl2 2FeCl3 2) KMnO4 + HCl KCl + MnCl2 + H2O + Cl2 3) HgO Hg + O2 4) C6H5COOH + O2 CO2 + H2O 5) H2 + Cl2 2 HCl 6) 2Fe + 3O2 Fe2O3 7) 2NaOH + Cl2 NaCl + NaClO + H2O 8) Zn + 2HCl ZnCl2 + H2 9) KClO3 KCl + O2 10)S8 + 24F2 8SF6 SIGNS OF CHEMICAL CHANGES Chemical Property -The ability of a substance to undergo a change that alters its identity. -A characteristic that cannot be observed without altering the substance Chemical Change • Change in which the composition of a substance changes – Changes are not easily reversed Signs of Chemical Changes 1. Change in Color 2. Change in Temperature 3. Change in Odor 4.BubblesGas produced 5. Precipitate (solid) is formed +