* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes. - Net Start Class
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Photopolymer wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Thermal spraying wikipedia , lookup
Stöber process wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Brownian motion wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Abundance of the chemical elements wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Colloidal crystal wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
Nanoparticle wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Particle-size distribution wikipedia , lookup
Sol–gel process wikipedia , lookup
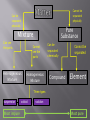
C. Smith Fall 2016 Properties of Matter Matter is any substance that has mass and takes up space (volume). All objects contain matter. Extensive properties are properties that depend on the amount of matter present. Mass Length Volume Intensive properties are used to identify a substance (does not changed based on amount). Density Color Crystalline shape Melting and Boiling point Refractive index Solids Solid particles occupy a regularly fixed position in relation to surrounding particles. Solid particle appears to vibrate around a fixed point. Particles are closely packed and travel a distance equal to only a fraction of their diameter before colliding. Solid particles are arranged in a definite pattern and have definite shape and volume. Liquids Liquid particles do not act independently of each other - motion is limited. Liquid particle slips by each other because the particles have vibratory type of motion. The particles still travel in a straight-line path between collision. Liquids have definitive volume and assume the shape of their container. Gases Gas particles are independent of each other and move in a straight line. Change in direction occurs only with collisions. Gases assume the shape and volume of their container. Plasma Plasma is a high energy electrically charged mixture of ions and electrons. Particles that have been ionized (charged) There exist at extremely high temperatures. Exist at naturally (stars) or man-made (neon signs). While plasma is the most abundant phase of matter in the universe, on earth it only occurs in a few limited places. Bose-Einstein condensate Extremely dense form of matter. Particle motion slowed down by decreasing temperature to cease motion. Consider to be super unexcited and super cold (approaching absolute zero, – 273K) Physical changes are changes in the form of a substance but not in the substance. The substance remains the same after the change but appears different. (Phase change) Physical changes can be reversible (but not always). Examples of phase changes Melting Freezing Boiling/Vaporization Condensation Evaporation Sublimation Chemical changes are changes in which a new substance with different characteristics from the original substance is produced. There are several examples of chemical changes Burning Digestion Fermenting Corrosion Chemical properties describe the reaction of a substance with other material or the reaction within the substance itself. Lack of chemical reactivity is also important. The evidence of a chemical reaction Color Change Formation of a gas Temperatures change. Odor Precipitate (solid) Heterogeneous means more than one type of substance. Heterogeneous matter exists in the form of mixtures. A mixture is matter that consists of two or more different materials. Mixtures can be separated by physical means. (distillation and filtration) Mixtures have phases, which are any region with a uniform set of properties. The boundaries between these phases are called interfaces. Homogeneous means only one type of a substance. Homogeneous matter is matter that is uniformly mixed and cannot be separated easily. Homogeneous matter exist in several forms: Pure Substances- Elements & Compounds Solutions Solutions consist of solute (dissolved material) and solvent (dissolving material). Solute particles are very small and are scattered in the solvent and appear as uniform. Solutions are not always liquid. Filtration • Separates a solid from a liquid • Often used in chemistry labs Distillation • A liquid is boiled into vapor and then condensed into a liquid. • Used to separate water from impurities in the water There are two types of pure substances. Elements Compounds. Substances made of only one kind of atom are called elements. Substances made of more than one kind of substances are called compounds. Elements are the building blocks for all other substances. Cannot be broken down into simpler substances. All atoms of an element have the same number of protons. There are 109 of these currently listed and named on the Periodic Table Metals: found on the left and center of the Table of Elements Non-metals: found on the right side of the Table of Elements Metalloids: found along the stair-step line Synthetic: made in the laboratory and not yet found in nature – many of the Actinide and Lanthanide series and very large # elements. Compounds Compound- Made of molecules- two or more atoms can be separated into simpler substances only by chemical means. Molecules are the smallest particle of a compound that retains its properties and it is composed of 2 or more atoms. When they are broken down, the pieces have completely different properties than the compound. Each element is represented by one- or two- letter chemical symbol. The symbols for most elements consist of the first one or two letters of the element’s name. A chemical formula is a combination of symbols that represents the composition of a compound. A formula shows two things: 1.The elements present in the compound 2. The relative number of atoms of each element in the compound. Example H2O Formulas often contain numerals to indicate the ratio of elements in the compound. The numbers used in the formula are called subscripts. During a chemical reaction, the quantity of matter is unchanged. The mass of products is always equal to the mass of reactants. The same can be said for physical changes. This is known as the Law of Conservation of Mass. The law states that mass can neither be created nor destroyed, it is conserved. Some of the mass can be in the form of energy or a gas. Cannot be separated physically Can be separated physically Pure Substance Mixture Can see the parts Cannot see the parts Heterogeneous Mixture Homogeneous Mixture Can be separated chemically Compound Cannot be separated Element Three types suspension Most impure colloid solution Most pure Nichols, Nancy : Klein Collins Science specialist (Ret.) Textbook: Chemistry , Wilbraham, Staley, Matta, Waterman; Pearson Realize