* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What are the four states of matter?
Stöber process wikipedia , lookup
Photopolymer wikipedia , lookup
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Colloidal crystal wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Freshwater environmental quality parameters wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Thermal spraying wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Water pollution wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
Nanoparticle wikipedia , lookup
Freeze-casting wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Degenerate matter wikipedia , lookup
Particle-size distribution wikipedia , lookup
Sol–gel process wikipedia , lookup
Mineral processing wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
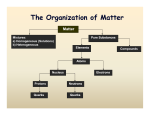
What is matter? Essential Question: What are the differences between the four states of matter? Matter is anything that has volume and mass. The volume of the liquid is measured by graduated cylinders When you measure the volume of liquid remember to look at the meniscus Mass: amount of matter in an object Volume: amount of space an object occupies They have definite shape and volume Particles are pact Particles vibrate in place Liquids take the shape of the container Liquids have definite volume Particles slide past each other Particles are not packed; they are spaced out. Gas changes their shape; indefinite shape Gas changes their volume; indefinite volume Particles are extremely far away from each other; particles move freely Plasma conducts electricity Same properties as gas Physical Properties Chemical properties The ability of the Can be observed or substance to change measured without into a new substance changing the identity of with different the matter. properties. Thermal conductivity Changes of states of matter Ductility: ability to be drawn into Wires. The Density: Mass/volume 3 g/cm The ability of the substance to change into a new substance with different properties. Ex: wood burning and changing into ash and smoke Ability to burn: Flamability Freezing water for ice cubes Sanding a piece of wood Bending a paper clip Mixing oil and vinegar Crushing an aluminum can Cutting your hair Column A Column B ____ sand does not dissolve in water a. State ____ gold can be made into gold foil; thin sheets b. Thermal conductivity ____ ice is the solid form of water. c. Solubility ____ copper can be drawn d. Density out into wire. ____ a foam cup protects your hand from being burned by the hot chocolate the cup contains. e. Ductility ____ ice cubes float in a glass of water. f. malleability Property Red color Melting point Flammability Reacts with acid Odor Reacts with water Density Physical property Chemical property Change Water boiling Iron rusting Baking soda reacting with vinegar Sharpening a pencil Alka-seltzer reacting with water Paper burning Tearing paper Physical change Chemical change It is a pure substance that cannot be separated into simpler substance by physical or chemical means. Each element has it own atomic number (# OF PROTONS) When a new substance is formed Examples : Sour milk, effervescent tablets, and the Statue of Liberty Clues to chemical changes: Color change Fizzing or foaming Heat Production of sound, light, or odor Two or more elements combined chemically together. Compounds can only be separated by chemical means. Two or more elements combined physically together. They can be separated by physical means only. Made out of two or more elements Compounds cannot be separated by physical change while mixtures can. Compounds do not retain the identity of their combined elements, while mixtures do. Compounds must have certain ratio ( H2O) While mixtures can be formed by any ratio ( Pizza, you can add and take out things to it) Heterogeneous mixture Can tell what the mixture is made out of homogeneous mixture Cannot tell what the mixture is made out of