* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 16 Cholinesterase Inhibitors
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of direct thrombin inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of antiandrogens wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of direct Xa inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
5-HT3 antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of beta-blockers wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of neuraminidase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of integrase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotease inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of ACE inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
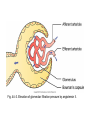
Drugs Acting on the ReninAngiotensin-Aldosterone System Drugs Acting on the ReninAngiotensin-Aldosterone System Physiology of the renin-angiotensinaldosterone system Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors Angiotensin II receptor blockers Aldosterone antagonists Physiology of the ReninAngiotensin-Aldosterone System Type of angiotensin Angiotensin I Angiotensin II Angiotensin III Actions of angiotensin II Vasoconstriction Release of aldosterone Alteration of cardiac and vascular structure Physiology of the ReninAngiotensin-Aldosterone System Actions of aldosterone Regulation of blood volume and blood pressure Pathologic cardiovascular effects Fig. 44–1. Regulation of blood pressure by the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Physiology of the ReninAngiotensin-Aldosterone System Formation of angiotensin II by renin and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) Renin • Catalyzes the formation of angiotensin I from angiotensinogen • Regulation of renin release Angiotensin-converting enzyme (kinase II) • Catalyzes the conversion of angiotensin I (inactive) to angiotensin II (highly active) Physiology of the ReninAngiotensin-Aldosterone System Regulation of blood pressure by the reninangiotensin-aldosterone system Helps regulate blood pressure in the presence of hemorrhage, dehydration, or sodium depletion Acts in two ways • Constricts renal blood vessels • Acts on the kidney to promote retention of sodium and water and excretion of potassium Tissue (local) angiotensin II production Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors Mechanism of action and overview of pharmacologic effects Reducing levels of angiotensin II Increasing levels of bradykinin Pharmacokinetics Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors Therapeutic uses Hypertension Heart failure Myocardial infarction (MI) Diabetic and nondiabetic nephropathy Prevention of MI, stroke, and death in patients at high cardiovascular risk MI = myocardial infarction. Fig. 44–2. Overview of ACE inhibitor actions and pharmacologic effects. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors Adverse effects First-dose hypotension Fetal injury Cough Angioedema Hyperkalemia Dysgeusia and rash Renal failure Neutropenia Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors Drug interactions Diuretics Antihypertensive agents Drugs that raise potassium levels Lithium Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors Preparations, dosage, and administration Except for enalaprilat, all ACE inhibitors are administered orally All available in single-drug formulations Except for captopril and moexipril, all oral formulations may be administered without regard to meals Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers Mechanism of action and overview of pharmacologic effects Block access of angiotensin II Cause dilation of arterioles and veins Prevent angiotensin II from inducing pathologic changes in cardiac structure Reduce excretion of potassium Decrease release of aldosterone Increase renal excretion of sodium and water Do not inhibit kinase II Do not increase levels of bradykinin Fig. 44–3. Elevation of glomerular filtration pressure by angiotensin II. Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers Therapeutic uses Hypertension, heart failure, myocardial infarction Diabetic nephropathy If unable to tolerate ACE inhibitors: protection against MI, stroke, and death from cardiovascular (CV) causes in high-risk patients Migraine headache May prevent development of diabetic retinopathy New data show that ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) are not effective for primary prevention of nephropathy in normotensive diabetic patients Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers Adverse effects Angioedema Fetal harm Renal failure Possibility of promoting cancer Direct Renin Inhibitors Aliskiren (Tekturna) Binds tightly with renin and inhibits the cleavage of angiotensinogen to angiotensin I Side effects • Angioedema, cough, GI effects, hyperkalemia, fetal injury, and death Aldosterone Antagonists Eplerenone (Inspra) Mechanism of action • Selective blockade of aldosterone receptors Therapeutic uses • Hypertension • Heart failure Pharmacokinetics • Absorption is not affected by food Adverse effects • Hyperkalemia Aldosterone Antagonists Eplerenone (Inspra) (cont’d) Drug interactions • Inhibitors of CYP3A4 • Drugs that raise potassium levels • Use with caution when combined with lithium Aldosterone Antagonists Spironolactone (Aldactone) Mechanism of action • Blocks aldosterone receptors • Binds with receptors for other steroid hormones Therapeutic uses • Hypertension • Heart failure Aldosterone Antagonists Spironolactone (Aldactone) (cont’d) Adverse effects • Hyperkalemia • Gynecomastia • Menstrual irregularities • Impotence • Hirsutism • Deepening of the voice