* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 11 test review KEY
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
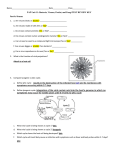
Name____________________________________Date_______________Class_____________ ACA Unit 11: Bacteria, Viruses, Protist, and Fungi TEST REVIEW KEY Part A: Viruses 1. a. Are viruses biotic or abiotic? __________________________ b. Are viruses made of cells (Yes or No)? ___________________ c. Do viruses contain proteins (Yes or No)? _________________ d. Do viruses contain nucleic acids/genetic material (Yes or No)? _________________ e. Can viruses be seen by a compound light microscope (Yes or No)? ___________ f. Are viruses bigger or smaller than bacteria? ______________ g. Can a virus reproduce on its own (Yes or No)? ___________________ 2. What is the function of viral projections? Attach to a host cell 3. Compare lysogenic vs lytic cycle. a. Define lytic cycle: results in the destruction of the infected host cell and its membrane with symptoms occurring within 2-7 days b. Define lysogenic cycle: integration of the viral nucleic acid into the host’s genome in which no symptoms may occur for weeks-years until it reverts to lytic cycle c. What viral cycle is being shown as cycle 1? lytic d. What viral cycle is being shown as cycle 2? lysogenic e. Which cycle shows the host cell being destroyed? lytic f. Which cycle will most likely cause an infection with symptoms such as fever and body aches within 2-7 days? lytic 4. A person infected with HIV may not have symptoms for a period of time (up to years). What type of viral cycle doe HIV display? Lysogenic What type of cell does HIV infect? Helper T cells During this period, the virus is doing what to the body? The virus damages immune cells while using their machinery to produce copies of itself 5. If you were a research immunologist and wanted to develop an antiviral drug to work against a specific virus, what should you study about the virus? The mechanism used by the virus to infect cells 6. A. What is the function of the glycoprotein show on the HIV virus? Used for attachment B. What is the function of cilia? Used to move fluids surrounding the cell 6. Some viruses, such as the influenza virus, can be transmitted through the air. In which scenario would all the individuals be exposed and get sick? Put a yes or no. A. working in the same building ______no_______ D. working for the same company _____no______ B. riding in the same car _____yes________ E. riding to work on the same train _____no_______ C. living in the same country _____no________ F. living in the same city _____no________ 7. Virus are very specific in what cells they can attach to. This can be referred to as a lock and key model. The following cell is shown below. Draw a virus with projections that would allow it to attach itself to the host. Part B: Bacteria 8. Do bacteria contain membrane bound organelles such as a nucleus? ______no_______ If you looked under a microscope at a cyanobacteria, would you be able to see the presence of a nuclear membrane? ___no_____ 9. What type of cell would you classify bacteria (prokaryote OR eukaryote)? ____________________________ 10. Define antibiotics: medicine used to kill bacteria 11. a. Do viruses react/respond to antibiotics? ___no______Explain_____________nonliving_________________ 12. You have bacteria living in your large intestine that helps you digest a wider variety of goods and produce vitamin K. What type of symbiotic relationship do you have with the bacteria in your gut? __mutualism__ Antibiotics can cause patients to exhibit digestive side effects. Explain why this may happen. Mutualistic bacteria being killed in digestive tract 13. Examine the image to the right. The grey area represents the amount of bacterial growth. a. After day 4, which disinfectant worked the best? __1__ How did you know? Largest white area with no growth around disc b. After day 4, which disinfectant worked the least? __2___How did you know? All shaded which represents bacterial growth around disc 14. Draw a prokaryote and label the genetic material (DNA), pili, flagellum, cell wall 15. What are the two functions of the pili? a. help the cell attach to surfaces b. attach to other bacteria cell to exchange of genetic material c. What is the function of the flagellum? movement 16. The bacterium is reproducing. What is the name of the process being shown to the right? Binary fission 17. A lichen is composed of a fungus and cyanobacterium living in symbiosis. The fungus provides shelter and nutrients to the cyanobacterium. The cyanobacterium provides food to the fungus. What type of relationship is this considered to be? Mutualism 18. Name the bacterial shapes A. __bacilli______ B. ____spirillum_________ C. _____cocci_______ 19. a. What type of organism will live next to the nodules of plant roots and fix nitrogen in the soil for the plants to uptake? bacteria b. What type of symbiotic relationship is this an example of mutualism Part C: Protist and Fungi 20. Which student would correctly identify the protist shown? 2 21. A paramecium was placed into a hypertonic solution. a. Which way will water move (IN or OUT) of the cell? Out b. Will the paramecium swell or shrivel? shrivel 22. Since fungi will secrete substances that are toxic to bacteria by breaking down their cell walls. If the fungi can be used to kill bacteria then what type of medicine can we produce from them? antibiotics 23. Fill in the chart by placing a yes or no for each characteristics pertaining to a fungus. 24. What is missing from the food web shown to the right? Fungal decomposers to recycle and return nutrients to the environment Define decomposer: break down dead or decaying organisms to return organic compounds to soil 25. Place the levels of taxonomy in order from biggest to smallest: Use the taxonomic chart you filled in: In which level would arthropods be most closely related? species 26. How many kingdoms are there? 6 Would there be more families or genera? genera Would there more genera or more species? species