* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 1 exam Review
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
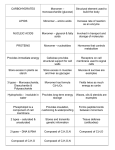
Biochemistry & Scientific Method Review 1. What element is found in all living (organic) things? It is considered the most important element for life. CARBON 2. What are the four basic biomolecules? LIPIDS, NUCLEIC ACIDS, PROTEINS and CARBOHDRATES 3. Which elements are found in ALL biomolecules? C (carbon), H (hydrogen) and O (oxygen) 4. Which elements are found in each of the following biomolecules? a. Carbohydates: C, H, O b. Lipids: C, H, O (but very little oxygen) c. Proteins: C, H, O, N, P, S d. Nucleic Acids: C, H, O, N, P 5. When monomers combine, POLYMERS are formed. 6. Explain Dehydration Synthesis. Monomer + monomer polymer + H2O An OH group from the end of one monomer bonds with a H from the end of another monomer A water molecule is lost from the reactants and is formed as a product (condenses out) A bond is formed between the 2 open atoms on each end of the monomers to form a polymer 7. Explain Hydrolysis. H2O + polymer monomer + monomer A water molecule is added to break the bond The OH group from the water molecule bonds with the end of one monomer and the H bonds with the end of the other monomer This breaks the bond between the two monomers 8. Label each of the following two graphics as hydrolysis or dehydration synthesis 9. For each of the following biomolecules, list the required information a. Proteins i. AMINO ACIDS (what monomers?) can combine through dehydration synthesis to form various types of proteins. ii. Proteins form through peptide bonds. iii. List the functions of proteins. 1. 2. 3. 4. Change the rate of chemical rxn’s (enzymes) Regulate cell processes Give bodies structure Transports materials into and out of the cell ex. Oxygen (hemoglobin) iv. Name and draw the monomer of a protein. Monomer= Amino Acid v. What is most important about the monomer of proteins? “BUILDING BLOCKS” for all life on earth. vi. Enzymes are a type of protein. What is the function of an enzyme? Hint: use the term “activation energy”. Enzymes are made of proteins, and act as catalysts, making chemical reactions easier. They do this by lowering the activation energy level to speed up the process. vii. What is enzyme “denaturing”, what can cause it to denature, and what is the result of denaturing? Denaturing changes the shape of the active site so the enzyme can not bind to the substrate. pH and heat can cause denaturing. viii. Label the parts of this enzymatic reaction (XYZ), and explain each of the steps (I, II, III). X= SUBSTRATE, Y = ENZYME, Z= PRODUCT b. Lipids i. Fatty acid (what monomer) combine through dehydration synthesis to form Lipids. ii. List the possible functions of lipids: 1. Insulation: store body heat 2. Protection: cell membranes 3. Long-term energy storage iii. Illustrations – Draw a Triglyceride – Is this a monomer or polymer? POLYMER c. Carbohydrates i. Monosaccharide and/or disaccharide can combine through dehydration synthesis to form the polymers, called POLYSACCHARIDE. ii. List a molecule example, and give an example of foods in which you can find each: 1. Monosaccharide – Glucose: honey, fruit sugar 2. Disaccharide – lactose: milk 3. Polysaccharide- starch: potoatoes iii. List the possible functions of carbohydrates: 1. Short term energy storage 2. Quick release energy iv. Illustration – Draw and label a monosaccharide, disaccharide, and polysaccharide. Monosaccharide: Disaccharide: Polysaccharide: d. Nucleic Acids i. NUCLEOTIDES (what monomers?) can combine through dehydration synthesis to form DNA or RNA, two types of nucleic acids. ii. List the possible functions of this biomolecule: Store and transmit genetic information. iii. Monomer with illustration, and Polymer with illustration Monomer: Nucleotide Polymer: DNA RNA 10. Explain the importance of having a control, or control group, in an experiment. It’s the constant (unchanged) in an experiment and is used to compare the experimental groups against. For example: In the apple enzyme lab: The slice of apple that your group did nothing to (was not boiled, put into lemon juice or sugar solution) was the control group. 11. When analyzing the data from an experiment, what is the difference between an observation and an inference? (think about how we knew which biomolecules were in which foods or how we knew the enzyme speed was slowed down) Observation – using one or more of the 5 senses to perceive objects or events Inference – a conclusion made on the based on observations, evidence, and reasoning 12. What is the difference between a theory and a hypothesis? Theory: Explanation of a natural phenomenon (situation or occurrence) based on many observations and investigations over time; generally accepted as fact Ex: Cell Theory, Gene Theory Hypothesis: A testable idea or explanation to a question. This can be written as an “If _________, then _________.” statement. Ex: If an apple is cut, then it will turn brown. 13. List and describe the 8 characteristics of living organisms. 1. ALL living things are made up of CELLS: Cell- basic unit of structure and function in all living things. Unicellular-Single celled organisms. Ex. All bacteria, many protists, and some fungi Multicellular- More than one- usually lots more. Ex Adult humans 60-90 trillions of cells 2. Displays ORGANIZATION: Molecular organization –Molecules are organized into cells and organelles that carry out all processes an organism needs to live. Atom-molecule-organelle-cell-tissue-organorgan system-organism… 3. Requires ENERGY: Organisms must continually take in energy in order to grow, reproduce, and maintain homeostasis. Autotrophs and Heterotrophs. 4. GROWTH & DEVELOPMENT: Cell growth- One cell increases in size. Cell division- All life starts as a single cell, Cells divide and make copies of themselves. More cells = more mass. 5. REPRODUCTION: Without adequate amounts of reproduction each generation, species go extinct. Two types of reproduction: Asexual and Sexual. 6. MAINTAINS HOMEOSTASIS: The process of keeping a stable internal environment necessary for cellular processes even when external conditions are unfavorable. Ex. Blood sugar level, Temperature, Water level, pH level and Oxygen level. 7. RESPONDS TO STIMULI: Organisms must respond to stimuli appropriately in order to stay alive Stimulus = anything in an organism’s external or internal environment that causes a reaction or response Response = a reaction to a stimulus Ex) if a shark smells blood in the water, it will respond by moving towards it 8. EVOLVE: Evolution - Genetic changes in a population ( group of organisms of the same species in the same area) over generations. Failure of a population to adapt to a changing environment may result in the loss of that population.