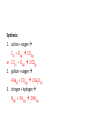* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Rate equation wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic reforming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Eutrophication wikipedia , lookup
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
Artificial photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Solid nitrogen wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Freshwater environmental quality parameters wikipedia , lookup
Acid–base reaction wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Water splitting wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Nitrogen dioxide poisoning wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Write and balance the following reactions: • Aqueous solutions of silver nitrate and potassium iodide are mixed. Silver iodide and potassium nitrate are produced. Use your solubility chart to figure out which one is the precipitate. silver nitrate(aq) + potassium iodide(aq) silver iodide + potassium nitrate AgNO3(aq) + KI(aq) AgI(s) + KNO3(aq) Write and balance the following reactions: 2. When nitrogen dioxide is bubbled through water it produces nitric acid and nitrogen monoxide. What are the states of matter of nitrogen dioxide, nitric acid and nitrogen monoxide? Nitrogen dioxide + water(l) nitric acid + nitrogen monoxide Nitrogen dioxide(g) + water(l) nitric acid(aq) + nitrogen monoxide(g) NO2(g) + H2O(l) HNO3(aq) + NO(g) 3 NO2(g) + H2O(l) 2 HNO3(aq) + NO(g) • Write balanced chemical equations for the following synthesis and decomposition chemical reactions. • Figure out what the states of matter should be at room temperature. • Predict products according to the type of reaction. Synthesis: 1. carbon + oxygen 2. gallium + oxygen 3. nitrogen + hydrogen Synthesis: 1. carbon + oxygen C(s) + O2(g) CO2(g) or 2 C(s) + O2(g) 2 CO(g) 2. gallium + oxygen 4 Ga(s) + 3 O2(g) 2 Ga2O3(s) 3. nitrogen + hydrogen N2(g) + 3 H2(g) 2 NH3(g) Decomposition: 1. sodium oxide 2. aluminum chloride 3. calcium carbonate 4. potassium chlorate Decomposition: 1. sodium oxide D 2 Na2O(s) 4 Na(s) + O2(g) 2. aluminum chloride D 2 AlCl3(s) 2 Al(s) + 3 Cl2(g) Decomposition: 3. calcium carbonate D CaCO3(s) CaO(s) + CO2(g) 4. potassium chlorate D 2 KClO3(s) 2 KCl(s) + 3 O2(g) The Activity Series For each of the following reactants, use the activity series to determine whether the reaction would take place or not. If no reaction takes. If a reaction does take placeplace, write NR in the blank, write the formulas for the products of the reaction. (Hint: If an active metal replaces the hydrogen in water, the hydroxide of the active metal forms. H-OH) a. Li(s) + Fe(NO3)3(aq) _________ b. Au(s) + HCl(aq) __________ c. Cl2(g) + KBr(aq) ___________ d. Cu(s) + Al(NO3)3(aq) ________ e. Ag(s) + HBr(aq) _________ f. Ni(s) + SnCl2(aq) ___________ The Activity Series 2. For each of the following reactants, use the activity series to determine whether the reaction would take place or not. If no reaction takes place, write NR in the blank. If a reaction does take place, write the formulas for the products of the reaction. (Hint: If an active metal replaces the hydrogen in water, the hydroxide of the active metal forms.) a. 3 Li(s) + Fe(NO3)3(aq) 3 LiNO3(aq) + Fe(s) b. Au(s) + HCl(aq) NR c. Cl2(g) + 2 KBr(aq) 2 KCl(aq) + Br2(l) d. Cu(s) + Al(NO3)3(aq) NR e. Ag(s) + HBr(aq) NR f. Ni(s) + SnCl2(aq) Sn(s) + NiCl2(aq) Use the activity series or solubility table to predict the product of the following reactions: Na(s) + SrBr2(aq) CrI3(aq) + KCl(aq) Zn(s) + H2SO3(aq) K2CO3(aq) + HI(aq) Use the activity series or solubility table to predict the product of the following reactions: 2 Na(s) + SrBr2(aq) NR CrI3(aq) + 3 KCl(aq) CrCl3(s) + 3 KI(aq) (DR – ppt) Zn(s) + H2SO3(aq) ZnSO3(aq) + H2(g) (SR – metal + acid) K2CO3(aq) + 2 HI(aq) 2 KI(aq) + H2CO3(aq) (DR – gas) H2O(l) + CO2(g) Use the activity series or solubility table to predict the product of the following reactions: Na(s) + H2O(l) HC2H3O2(aq) + (NH4)2S(aq) Fe(s) + CuCl2(aq) HBr(aq) + Ba(OH)2(aq) Use the activity series or solubility table to predict the product of the following reactions: 2 Na(s) + 2 H2O(l) 2 NaOH(aq) + H2(g) (SR – metal + H2O) 2 HC2H3O2(aq) +(NH4)2S(aq) H2S(g)+2 NH4C2H3O2(aq)(DR – gas) Fe(s) + CuCl2(aq) Cu(s) + FeCl2(aq) (SR – metal/metal) 2 HBr(aq) + Ba(OH)2(aq) BaBr2(aq) + 2 H2O(l) (DR – acid-base neutralization) 1. Is # of H in hydrocarbon divisible by 4? a) If yes, hydrocarbon coefficient = 1 b) if no, hydrocarbon coefficient = 2 2. Balance hydrogen 3. Balance carbon 4. Balance oxygen LAST Balance the following complete combustion reactions: ___C3H8(g) + ___O2(g) ___CO2(g) + ___H2O(g) ___C5H12(g) + ___O2(g) ___CO2(g) + ___H2O(g) Balance Combustion Reactions Now balance the chemical reactions for the complete combustion of hexane(C6H14) and decane (C10H22): ___C6H14(g) + ___O2(g) ___CO2(g) + ___H2O(g) ___C10H22(g) + ___O2(g) ___CO2(g) + ___H2O(g) Write balanced chemical equations for the complete combustion of • propane (C3H8) C3H8(g) + O2(g) CO2(g) + H2O(g) + heat C3H8(g) + O2(g) C3H8(g) + O2(g) 3 CO2(g) + 4 H2O(g) + heat CO2(g) + 4 H2O(g) + heat C3H8(g) + 5 O2(g) 3 CO2(g) + 4 H2O(g) + heat Write balanced chemical equations for the complete combustion of decane (C10H22) C10H22(g) + O2(g) CO2(g) + H2O(g) + heat 2 C10H22(g) + 2 C10H22(g) + O2(g) CO2(g) + 22 H2O(g) + heat O2(g) 20 CO2(g) + 22 H2O(g) + heat 2 C10H22(g) + 31 O2(g) 20 CO2(g) + 22 H2O(g) + heat