* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 6: Biochemistry
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
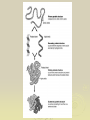
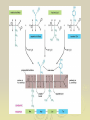
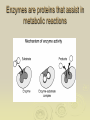
Chapter 2: Biochemistry Part 2: Organic Molecules 1. Organic molecules A. contain many carbon atoms B. they are polymers (long chains of small molecules) C. condensation reactions make monomers into polymers Monomer (small) Polymer (long chain of monomers) monosaccharide (simple sugar) polysaccharide (complex carbohydrate) glycerol, fatty acid fat (a lipid) amino acid protein nucleotide nucleic acid 2. Carbohydrates a. sugars and starches b. used for energy (short term and long term) c. ex. glucose, fructose, sucrose, starch, cellulose Monomers Monosaccharides combine in condensation reactions to form Disaccharides Starches are polysaccharides used to store energy in plants. Amylose starch Mammals store food in the liver in the form of glycogen Cellulose provides strength for plant cells 3. Proteins a. used for structure, enzymes, cell identification. b. long chains of amino acids c. ex. hemoglobin (blood), collagen (skin), amylase (digestion), keratin (hair), myosin (muscles) Amino acids are the monomers of proteins Glycine R= H Alanine R= CH3 Serine Cysteine R= H2COH R= SH-CH2 Amino acids join to form protiens Enzymes are proteins that assist in metabolic reactions 4. Lipids a. fats and oils b. used for energy storage, lubrication, insulation, building cell membranes c. ex. butter, oils, lard Unsaturated fats are more likely to react and break apart. HHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH H-C-C-C-C-C-C-C-C-C-C-C-C-C-C-C-C HHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH Saturated fats are less likely to react, staying stay large; therefore, they are less healthy. 5. Nucleic Acids a. store information for the cell b. made of chains of nucleotides c. ex. DNA, RNA Homework Copy the following pictures into your notes: Figure 2-13 Figure 2-14 Figure 2-15 Figure 2-16 No, I don’t know what pages they are on; however, I DO know they are in chapter 2. Homework Read pages 161-167 Copy the 4 molecules into your notes (lipid, carbohydrate, protein, nucleic acid) Read p. 166 about how enzymes work Do question 5 on p. 167 If blue = amino acids, it’s___________ If purple = nucleotides, it’s___________ If pink = sugars, it’s________________ If brown = glycerol, it’s_____________ And white must be ______